Abstract
1 The effects of endogenous noradrenaline released by tyramine and the influence of depletion of the tissue noradrenaline with reserpine and/or α-methyl-p-tyrosine on the twitch responses of the field-stimulated mouse vas deferens have been studied.
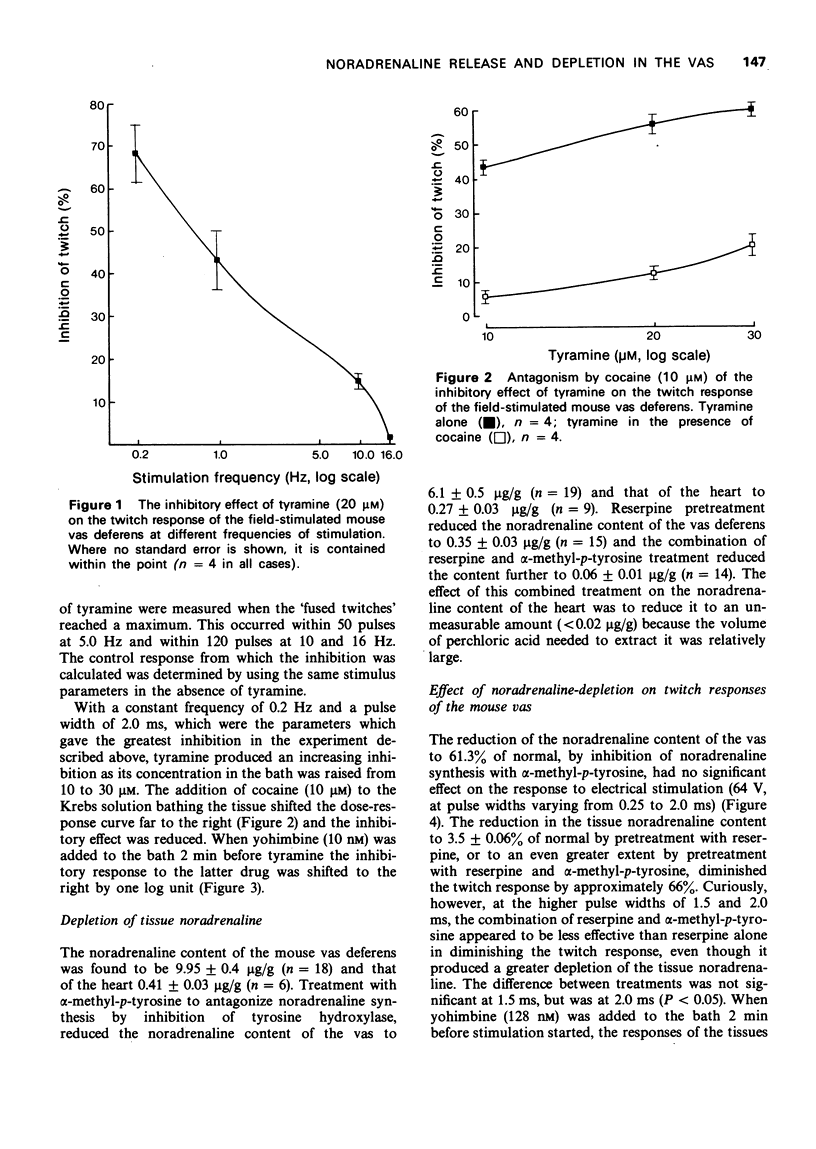
2 Tyramine (10-40 μM) inhibited the twitch responses to field stimulation and failed to produce a contraction. The inhibition decreased as the rate of stimulation increased.
3 The inhibition produced by tyramine was antagonized by cocaine (10 μM) and by yohimbine (10 nM), which indicated that it was produced by released noradrenaline acting on presynaptic α-adrenoceptors.
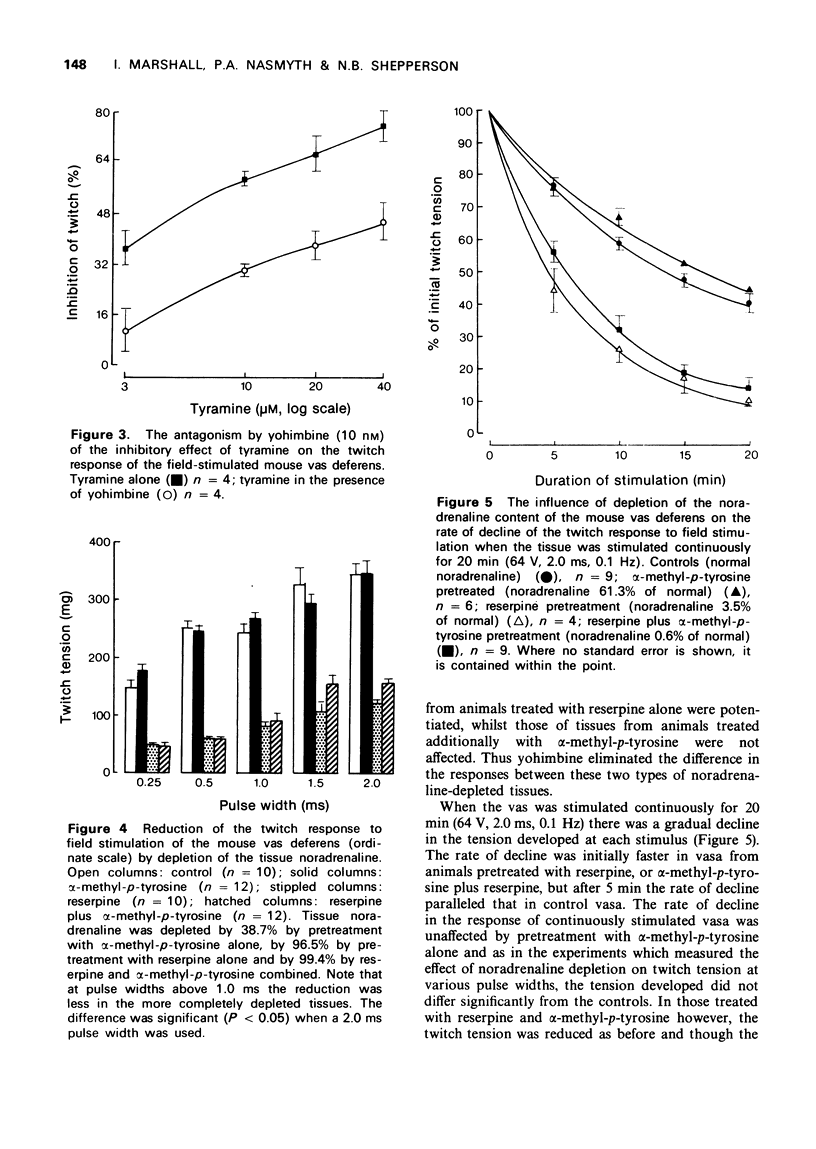
4 Depletion of the tissue noradrenaline by 39% by blockade of the synthesis of noradrenaline with α-methyl-p-tyrosine, was without effect on the twitch response but it reduced the inhibitory effect of tyramine.
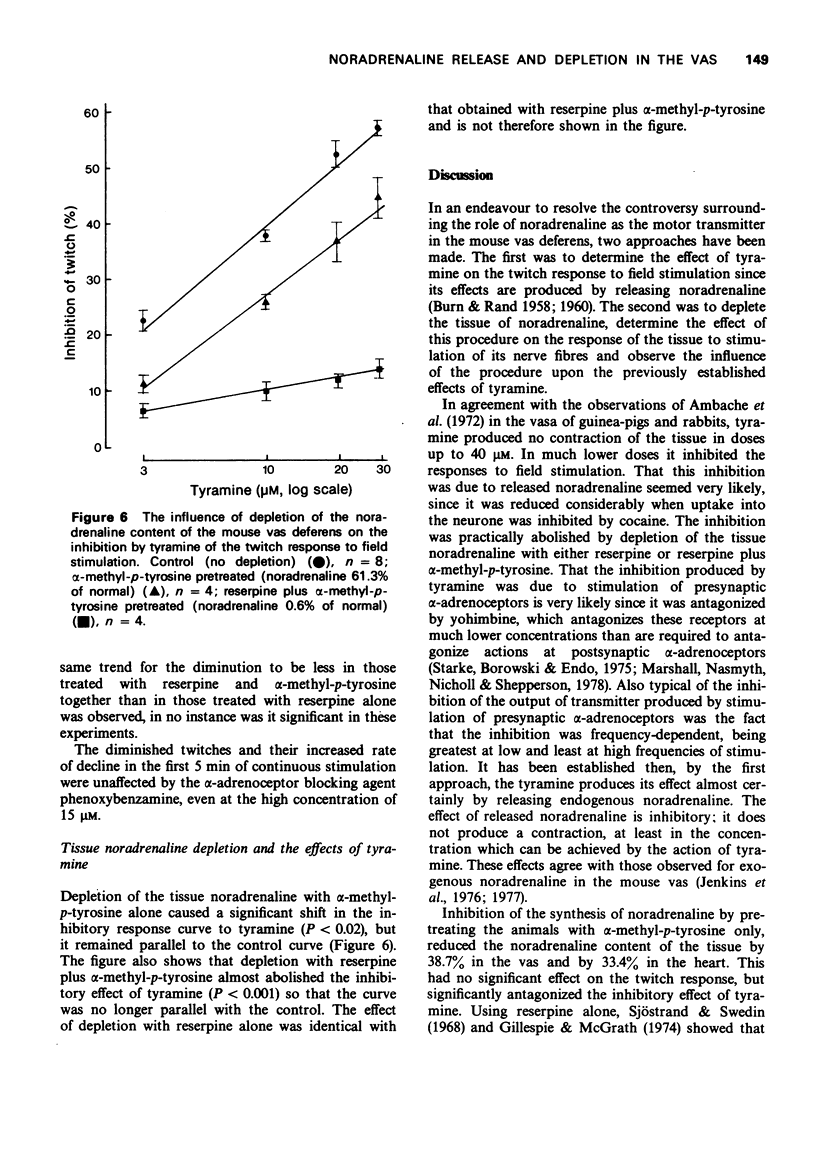
5 Depletion of the tissue noradrenaline by 96.5% with reserpine alone and by 99.4%, with a combination of reserpine and α-methyl-p-tyrosine, reduced the twitch responses by approximately 66% and virtually abolished the inhibition produced by tyramine. It also increased the rate of decline of the responses when the tissue was continuously stimulated. The remaining twitch was not antagonized by phenoxybenzamine (15 μM).
6 Residual twitches were bigger in tissues depleted by 99.4% than in those depleted by only 96.5%. This difference was eliminated in the presence of yohimbine (128 nM).
7 It is concluded that inhibition of the twitch responses by tyramine is produced by stimulation of presynaptic α-adrenoceptors and that the twitch response is associated with stimulation of the sympathetic neurone, but that it is not mediated by postsynaptic α-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD J. Purification and properties of phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1657–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Dunk L. P., Verney J., Zar M. A. Inhibition of post-ganglionic motor transmission in vas deferens by indirectly acting sympathomimetic drugs. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):433–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. Evidence against adrenergic motor transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):359–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRMINGHAM A. T., WILSON A. B. PREGANGLIONIC AND POSTGANGLIONIC STIMULATION OF THE GUINEA-PIG ISOLATED VAS DEFERENS PREPARATION. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:569–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. The action of sympathomimetic amines in animals treated with reserpine. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):314–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. The effect of precursors of noradrenalin on the response to tyramine and sympathetic stimulation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Mar;15:47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb01209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The effect of pithing and of nerve stimulation on the depletion of noradrenaline by reserpine in the rat anococcygeus muscle and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(4):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D. P., Starman B. J., Johnson D. G., Williams R. H. A sensitive radioenzymatic assay for norepinephrine in tissues and plasma. Life Sci. 1975 Feb 1;16(3):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M. Effect of morphine on adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Assessment of agonist and antogonist potencies of narcotic analgesics. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;53(3):371–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. A., Marshall I., Nasmyth P. A. An inhibitory role for noradrenaline in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):649–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. E., Spriggs T. L. Noradrenaline and motor transmission in the vas deferens of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;53(3):323–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITT M., SPECTOR S., SJOERDSMA A., UDENFRIEND S. ELUCIDATION OF THE RATE-LIMITING STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN THE PERFUSED GUINEA-PIG HEART. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Apr;148:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. L. The relation between norepinephrine content and response to sympathetic nerve stimulation of various organs of cats pretreated with reserpine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Apr;156(1):137–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall I., Nasmyth P. A., Nicholl C. G., Shepperson N. B. alpha-Adrenoceptors in the mouse vas deferens and their effects on its response to electrical stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):147–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07018.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand N. O., Swedin G. Effect of reserpine on the noradrenaline content of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle compared with the submaxillary gland and the heart of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Mar;72(3):370–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb03859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Borowski E., Endo T. Preferential blockade of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors by yohimbine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;34(2):385–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Krusz J. Effect of reserpine, phenoxybenzamine and cocaine on neuromuscular transmission in the vas deferens of the guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 May;181(2):310–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler U. S., Hedqvist P. Evidence for an alpha- and beta2-receptor mediated inhibition of the twitch response in the guinea pig vas deferens by noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Apr;93(4):572–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


