Abstract
Leguminous plants produce 5-deoxyflavonoids and 5-deoxyisoflavonoids that play essential roles in legume-microbe interactions. Together with chalcone polyketide reductase and cytochrome P450 2-hydroxyisoflavanone synthase, the chalcone isomerase (CHI) of leguminous plants is fundamental in the construction of these ecophysiologically active flavonoids. Although CHIs of nonleguminous plants isomerize only 6′-hydroxychalcone to 5-hydroxyflavanone (CHIs with this function are referred to as type I), leguminous CHIs convert both 6′-deoxychalcone and 6′-hydroxychalcone to 5-deoxyflavanone and 5-hydroxyflavanone, respectively (referred to as type II). In this study, we isolated multiple CHI cDNAs (cCHI1–cCHI3) from a model legume, Lotus japonicus. In contrast to previous observations, the amino acid sequence of CHI2 was highly homologous to nonleguminous CHIs, whereas CHI1 and CHI3 were the conventional leguminous type. Furthermore, genome sequence analysis revealed that four CHI genes (CHI1–3 and a putative gene, CHI4) form a tandem cluster within 15 kb. Biochemical analysis with recombinant CHIs expressed in Escherichia coli confirmed that CHI1 and CHI3 are type II CHIs and that CHI2 is a type I CHI. The occurrence of both types of CHIs is probably common in leguminous plants, and it was suggested that type II CHIs evolved from an ancestral CHI by gene duplication and began to produce 5-deoxy(iso)flavonoids along with the establishment of the Fabaceae.
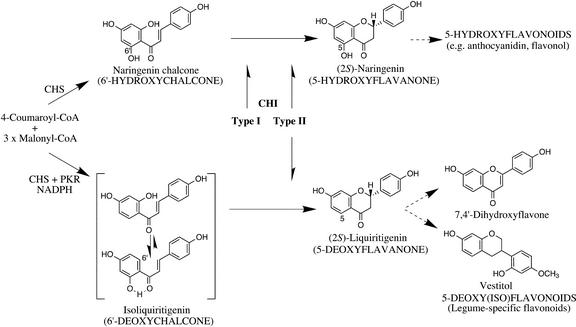
Leguminous plants contain flavonoids that are essential to their interactions with other organisms and ultimately beneficial for the successful habituation of the producer legumes in the environment. For example, these flavonoids act as inducers of rhizobial nod genes in host-specific symbiotic nitrogen fixation and also as inducible antimicrobial phytoalexins (Dewick, 1986; Peters et al., 1986; Redmond et al., 1986; Harborne, 1994; Stafford, 1997; Aoki et al., 2000). They often possess one or both of the following characteristic structures: an isoflavonoid with a 1,2-diarylpropane skeleton and/or a 5-deoxyflavonoid with a hydrogen atom directly attached at C-5, in contrast to general flavonoids, which have the 1,3-diarylpropane skeleton and oxygen functions attached at C-5 (Fig. 1). About 95% of isoflavonoids are found in legumes, and 60% of leguminous flavonoids are 5-deoxyflavonoids (Hegnauer and Gpayer-Barkmeijer, 1993). The isoflavonoid skeleton is constructed by a cytochrome P450 2-hydroxyisoflavanone synthase (Akashi et al., 1999; Jung et al., 2000; Steele et al., 1999; Shimada et al., 2000), and the biosynthesis of 5-deoxyflavonoid structures requires two sequential enzyme reactions. First, polyketide reductase coacting with chalcone synthase removes the oxygen atom originating from the carbonyl of one of the precursor acetyl-CoAs to produce 2′,4,4′-trihydroxychalcone (isoliquiritigenin; abbreviated as 6′-deoxychalcone for simplicity; Tropf et al., 1995; Akashi et al., 1996), and then chalcone isomerase (CHI) isomerizes 6′-deoxychalcone into 7,4′-dihydroxyflavanone (liquiritigenin; abbreviated as 5-deoxyflavanone), from which 5-deoxyflavonoid subclasses, mainly isoflavone and flavone derivatives, are produced. Although 6′-deoxychalcones are distributed in a few nonleguminous plant families (Rieseberg et al., 1987), the subsequent 5-deoxyflavonoid pathway, starting with the isomerization of 6′-deoxychalcone, is highly limited to leguminous plants (Giannasi, 1988). Therefore, CHIs of leguminous plants should be important in the production of family-specific ecophysiologically active flavonoids.
Figure 1.
The flavonoid pathway in leguminous plants. Type I CHIs isomerize only 6′-hydroxychalcone as the substrate, whereas type II CHIs accept both 6′-deoxychalcone and 6′-hydroxychalcone. CHI activity toward 6′-deoxychalcone is essential to produce the biologically active 5-deoxyflavonoids that are predominantly distributed in leguminous plants. 6′-Deoxychalcone is stable because of the intramolecular hydrogen bond between 2′-hydroxyl and carbonyl group.
CHI (EC 5.5.1.6) catalyzes the stereospecific isomerization of chalcones into their corresponding (2S)-flavanones. Although chalcones are nonenzymatically isomerized into (2RS)-flavanones easily, only (2S)-flavanones are intermediates of the subsequent flavonoid metabolism. In contrast to a rapid isomerization of 2′,4,4′,6′-tetrahydroxychalcone (naringenin chalcone; abbreviated as 6′-hydroxychalcone) into 5,7,4′-trihydroxyflavanone (naringenin; abbreviated as 5-hydroxyflavanone), the isomerization of 6′-deoxychalcone to 5-deoxyflavanone is rather slow because of the intramolecular hydrogen bond in the substrate molecule (see Fig. 1): No substantial isomerization in neutral solution is observed without the enzyme or chemical catalyst. Although one-half of the nonenzymatic products, i.e. (2S)-flavanones, can be the intermediates of subsequent flavonoid metabolism, the general distribution of CHI in higher plants suggests the significance of this enzyme in the flavonoid pathway. In Arabidopsis, the only functional CHI gene (TT5) is essential for the biosynthesis of anthocyanin and other flavonoids (Winkel-Shirley et al., 1995).
CHIs are classified into two types, and their distributions are highly family specific. CHIs generally found in nonlegumes isomerize only 6′-hydroxychalcone to 5-hydroxyflavanone. CHIs with this catalytic function are referred to as type I CHIs in this article. On the other hand, most, if not all, of the CHIs of leguminous plants so far found have activities toward both 6′-deoxychalcone and 6′-hydroxychalcone, yielding 5-deoxyflavanone and 5-hydroxyflavanone, respectively (referred to as type II CHI). The antigenic cross-reactivity of the proteins and cDNA cross hybridization (Dixon et al., 1988) suggested that the different substrate specificities of CHIs between leguminous and nonleguminous plants result from the different structures of CHI proteins. Also, cDNAs and genes that encode both types of CHIs have been cloned from various plant species (Mehdy and Lamb, 1987; van Tunen et al., 1988; Blyden et al., 1991; Grotewold and Peterson, 1994; Sparvoli et al., 1994; Wood and Davies, 1994; Terai et al., 1996), and the deduced amino acid sequences of the same type of CHI showed high identity (>70%), whereas the identity between type I and II CHIs is only about 50%.
Recently, x-ray crystallography of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) CHI (type II CHI) showed the stereostructure of the protein and revealed the dynamic reaction course of the catalysis (Jez et al., 2000; Jez and Noel, 2002): The substrate bound to the active site cleft is shaped into a constrained conformation and converted into the product very efficiently by a general acid base catalysis mechanism. Some amino acid residues possibly affecting the acceptability of 6′-hydroxy- and 6′-deoxychalcones at the active site were suggested, but the exact structural basis of broad and narrow substrate specificity of CHI is still unclear without the x-ray analysis of type I CHI. Also, although the fold found in CHI protein structure is unique to higher plants and its evolutionary aspects are of special interest, the reason for the appearance of type II CHI in legumes is another intriguing question that is not answered at present. Further, considering the possible biotechnological applications of CHIs, e.g. the utilization of CHI in the increased production of flavonoids in transgenic plants (Muir et al., 2001) and the use of the narrow specificity of type I CHI for the accumulation of the yellow pigment 6′-deoxychalcone in flower petals (Davies et al., 1998), detailed studies on CHI genes and proteins should be significant.
Recently, biochemical evidence suggested for the first time that a leguminous plant licorice (Glycyrrhiza echinata) contains both type I and type II CHI isozymes (Kimura et al., 2001). A difference in responsiveness in their expression to elicitor treatment was also shown. Given that the two types of CHIs have different protein structures, the CHI isozymes of licorice are likely to be encoded by different genes, and such a case may be common in leguminous plants. We undertook a molecular and biochemical analysis of CHIs of Lotus japonicus. This diploid perennial legume has been used as a model plant for the study of classical and molecular genetics of the Fabaceae (Handberg and Stougaard, 1992; Schauser et al., 1999). More than 26,000 expressed sequenced tag sequences have been reported (Asamizu et al., 2000; Endo et al., 2000), and a whole-genome sequencing project is in progress (Sato et al., 2001). Although information on the flavonoid metabolism of this plant has been limited, our recent work identified cDNAs encoding the enzymes of isoflavonoid biosynthesis (Shimada et al., 2000) and characterized mutants deficient in the biosynthesis of anthocyanin and condensed tannin (Aoki et al., 2000).
In this study, we identified CHI genes of L. japonicus that encode both types of isozymes. Examination of the genome structure revealed for the first time, to our knowledge, the cluster of CHI genes, and phylogenetic analysis suggested the origin of the legume-specific type II CHI.
RESULTS
Cloning of Two Sequence Types of CHI cDNAs from L. japonicus
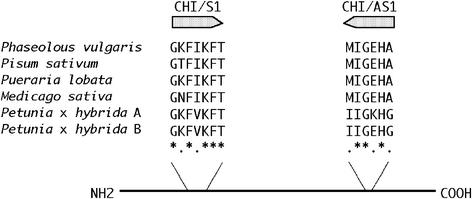
To isolate the CHI cDNAs of L. japonicus, degenerate oligonucleotide primers were designed from highly conserved regions found in both type I and type II CHIs (Fig. 2). PCR with the degenerate primers CHI/S1 and CHI/AS1 using the cDNA synthesized from mRNA of whole-plant organs of L. japonicus accession B-129 Gifu, including flowers and nitrogen-fixing nodules, as the template gave primer-specific products (about 500 bp).
Figure 2.
Primer set for the cloning of CHI cDNAs from L. japonicus. Degenerate primers were designed from conserved amino acid sequences found in both known type I (Petunia hybrida) and type II CHIs (Medicago sativa, Phaseolus vulgaris, Pisum sativum, and Pueraria lobata).
Nucleotide sequence analysis of eight cloned cDNA fragments identified three partial CHI cDNAs. The nucleotide sequences of two partial cDNAs (represented by five clones) were about 80% identical to the type II CHI of a leguminous plant, alfalfa. The other (represented by three clones) had 74% identity to the type I CHI of a nonleguminous plant Elaeagnus umbellata, but had much lower homology (about 50%) to the alfalfa CHI. Three sets of specific primers were designed based on the sequence of each partial cDNA, and 3′- and 5′-RACE were performed. After RACE, three further sets of specific primers were designed, and three full-length CHIs, cCHI1, cCHI2, and cCHI3, were obtained.
cCHI1 (GenBank accession no. AB054801), cCHI2 (GenBank accession no. AB054802), and cCHI3 (GenBank accession no. AB073787) were deduced to contain open reading frames consisting of 681, 666, and 678 bp encoding polypeptides of 226 (24.4 kD), 221 (23.9 kD), and 225 amino acids (24.2 kD), respectively. The amino acid sequences of both CHI1 and CHI3 had the highest identities to the known CHI of the legume P. vulgaris (77.3% and 77.2%, respectively) and CHI2 to that of the nonlegume Vitis vinifera (74.2%). The amino acid identity between CHI1 and CHI3 is 90% and that between CHI1 and CHI2 is 53% (Table I).
Table I.
Sequence homology of CHIs
| CHI | Legume-Specific
Group
|
Nonlegume Group
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
L.
japonicus
|
Alfalfa | P. lobata | P. vulgaris |
L. japonicus
|
Citrus sinensis | E. umbellata | Ipomoea purpurea | V. vinifera | ||
| CHI3 | CHI4 | CHI2 | ||||||||
| % | ||||||||||
| Legume-specific group | ||||||||||
| L. japonicus | ||||||||||
| CHI1 | 90 /91 | 93 /93 | 76 /79 | 74 /78 | 77 /79 | 53 /63 | 56 /64 | 57 /62 | 56 /63 | 55 /64 |
| CHI3 | 89 /89 | 75 /79 | 75 /78 | 77 /77 | 52 /62 | 55 /67 | 55 /62 | 54 /63 | 53 /65 | |
| CHI4 | 73 /79 | 73 /78 | 75 /76 | 51 /62 | 55 /64 | 56 /60 | 45 /61 | 54 /62 | ||
| M. sativa | 81 /79 | 82 /79 | 52 /64 | 56 /64 | 58 /62 | 45 /62 | 55 /63 | |||
| P. lobata | 86 /83 | 56 /67 | 57 /67 | 55 /64 | 55 /64 | 55 /65 | ||||
| P. vulgaris | 55 /65 | 56 /65 | 57 /63 | 56 /64 | 55 /63 | |||||
| Nonlegume group | ||||||||||
| L. japonicus CHI2 | 72 /74 | 73 /71 | 69 /71 | 74 /72 | ||||||
| C. sinensis | 75 /72 | 65 /63 | 76 /76 | |||||||
| E. umbellata | 70 /67 | 75 /75 | ||||||||
| I. purpurea | 70 /72 | |||||||||
Identity (%) of amino acid sequence/identity (%) of nucleotide sequence.
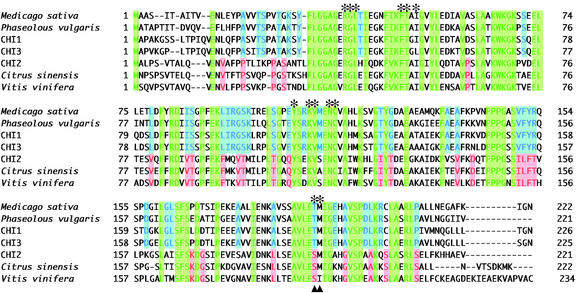
The amino acid sequences deduced from the three full-length cDNAs of L. japonicus are aligned with known typical type I and type II CHIs in Figure 3, in which amino acid residues common to both types of CHIs and those characteristic to each type are shown in different colors. CHI1 and CHI3 share many common residues with known type II CHIs, and CHI2 with type I CHIs. The residues forming the active site (Jez et al., 2000) are conserved in all CHIs compared (e.g. Arg-40, Gly-41, Leu-42, Phe-51, Thr-52, Tyr-110, Lys-113, Val-114, Asn-117, and Cys-118 in CHI1). The residues that have been postulated to determine the substrate preference in type II CHI (Jez et al., 2000) are conserved in both CHI1 (Thr-194 and Met-195) and CHI3 (Thr-193 and Met-194), and the Thr is replaced by Ser in CHI2 as in other type I CHIs.
Figure 3.
Amino acid sequence alignment of CHIs. Conserved residues in type I CHIs (red), type II CHIs (blue), and both types of CHIs (green) are highlighted. The residues that compose the active site are indicated with asterisks. Arrows indicate the residues proposed to affect substrate preference between 6′-deoxychalcone and 6′-hydroxychalcone (Jez et al., 2000).
Comparison of Amino Acid and Nucleotide Sequences of CHIs
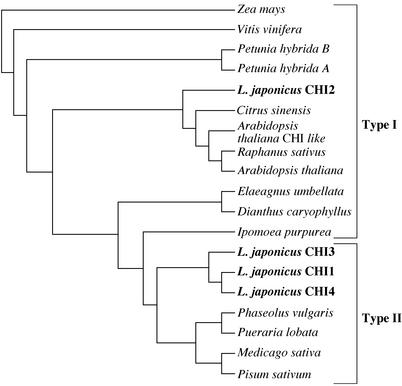
A phylogenetic tree generated by the neighbor-joining method based on the amino acid sequences of CHIs shows that all the leguminous CHIs so far reported and the three L. japonicus CHIs (CHI1, CHI3, and CHI4; see the next section), constitute a monophyletic group (Fig. 4). On the other hand, L. japonicus CHI2 is included in a polyphyletic group with other CHIs from various nonleguminous plants.
Figure 4.
A phylogenetic tree based on deduced amino acid sequences of various CHIs. Amino acid sequences were analyzed using the CLUSTALW program. Known type II CHIs form a subgroup, and CHI1, CHI3, and CHI4 belong to this subgroup. CHI2 is classified into the type I CHI group. For accession numbers of the CHI sequences, see “Materials and Methods.”
Identities of the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of six legume-specific CHIs (including L. japonicus CHIs 1, 3, and 4) and four nonleguminous CHIs plus L. japonicus CHI2 were calculated in every combination (Table I). Based on this comparison, Table II summarizes the identities in both amino acid and nucleotide sequences within the legume-specific CHIs (L-L), within the nonleguminous CHIs (N-N), and between the two groups (L-N). The high identity in both sequences (about 80%) within the legume-specific CHIs (L-L comparison) shows a close orthologous relationship of these CHIs. Although nonleguminous CHIs are distributed to diverse plant families and form a polyphyletic group, the N-N comparison displays a moderate identity (about 70%). In contrast, the nucleotide identity between the two groups (L-N comparison) is significantly lower (about 64%) than that in the N-N comparison, and amino acid identity revealed a still lower value (about 55%). The ratio of the amino acid identity to the nucleotide identity among the related genes affords the criterion for the frequencies of synonymous and non-synonymous base substitutions between them. The value 0.86 in the L-N comparison shown in Table II probably reflect frequent non-synonymous substitutions between the two groups, in contrast to the case of the L-L and N-N comparisons, where the ratio is around 1. The actual non-synonymous substitution ratio was also analyzed in three representative examples. Between CHI1 and CHI2 (L-N comparison), non-synonymous substitutions are found in 204 sites of 248 base-substituted sites, and the non-synonymous substitution rate is 0.82. The non-synonymous substitution rates between CHI1 and CHI3 (L-L comparison) and between CHI2 and the C. sinensis CHI (N-N comparison) were 0.43 (25/58) and 0.59 (106/179), respectively. These results are consistent with the interpretation on the data in Table II that non-synonymous substitution is predominant between legume-specific and nonleguminous CHIs.
Table II.
Comparison of nucleotide and amino acid sequences of legume-specific and nonleguminous CHIs
| Comparison | Identity
|
Amino Acid Identity/Nucleotide Identity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid | Nucleotide | ||
| % | |||
| L-L (15) | 79.7 ± 6.7 | 81.0 ± 5.5 | 0.98 ± 0.04 |
| N-N (10) | 70.2 ± 6.3 | 70.3 ± 3.9 | 1.02 ± 0.04 |
| L-N (30) | 54.7a ± 1.7 | 63.6b ± 1.8 | 0.86a ± 0.03 |
The mean value and sd of the identities among CHIs in Table I were calculated in three categories: within the legume-specific group (L-L), within the nonleguminous group (N-N), and between the legume-specific and the nonleguminous groups (L-N). The nos. of the combinations are indicated in parentheses. The significance of the difference in mean values was estimated by the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Significantly different from L-L and N-N (P < 0.0001).
Significantly different from L-L and N-N (P < 0.05).
Structure of L. japonicus CHI Gene Family
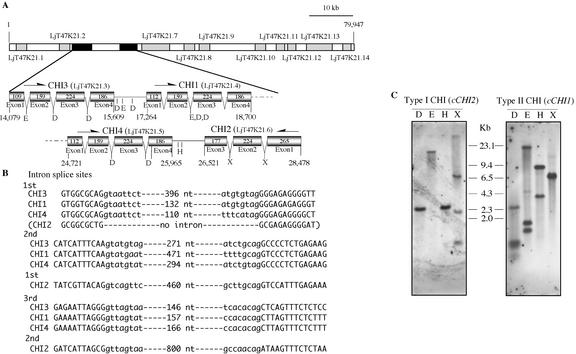
A TAC library of L. japonicus accession MG-20 Miyakojima generated for the structural analysis of its genome (Sato et al., 2001) was used as the template for screening of CHI genes. A primer set for cCHI1 amplified two clones, LjT05E21 and LjT47K21, and another primer set for cCHI2 did LjT16P04 and, again, LjT47K21. The sequence of LjT47K21 (79,947 bp; GenBank accession no. AP004250) showed that CHI3, CHI1, and CHI2 genes are present within about 15 kb (Fig. 5A). Detailed inspection of the LjT47K21 sequence revealed another CHI sequence between CHI1 and CHI2, and it was designated CHI4. The deduced cCHI4 contained an open reading frame (681 bp) encoding a polypeptide of 226 amino acids (24.5 kD) that showed about 90% identity to L. japonicus CHI1 and CHI3. The three genes, CHI1, CHI3, and CHI4, orthologous to type II CHIs, have the same orientation, and commonly comprise four exons. The sizes of the respective exons among these three genes are strictly conserved, i.e. 159 bp for exon 2, 224 bp for exon 3, and 186 bp for exon 4, except for exon 1, which is 109 bp in CHI1 and 112 bp in CHI3 and CHI4. The type I ortholog CHI2 has the opposite orientation and comprises three exons. The size of exon 1 (265 bp) of CHI2 is about the sum of exons 1 and 2 of type II ortholog CHIs, and exons 2 (224 bp) and 3 (177 bp) of CHI2 have the same or similar sizes to exons 3 and 4 of type II ortholog CHIs, respectively. The sequences of the exons around the intron splice sites are highly conserved (Fig. 5B). In contrast, the sizes and sequences of introns are variable throughout the CHI genes.
Figure 5.
Genomic organization of CHI genes in L. japonicus. A, Physical and restriction map of L. japonicus CHI genes on the LjT47K21 clone. The two black parts represent the regions of the CHI genes. One region contains the CHI3 and CHI1 genes, and the other contains CHI4 and CHI2 genes. The gray boxes indicate the exons of the CHI genes, and the arrows show the orientation of each gene. Numbers indicate the base pairs of each exon. A restriction map of the CHI gene by DraI (D), EcoRI (E), HindIII (H), and XbaI (X) is also presented. The dotted parts indicate the expected gene regions that are annotated as follows: LjT47K21.1 (partial gene fragment), LjT47K21.2 (pseudogene of unknown protein), LjT47K21.7 (partial gene of cationic peroxidase), LjT47K21.8 (cationic peroxidase), LjT47K21.9 (hypothetical protein), LjT47K21.10 (putative ABC transporter protein), LjT47K21.11 (pseudogene of putative retroelement), LjT47K21.12 (unknown protein), LjT47K21.13 (unknown protein), and LjT47K21.14 (hypothetical protein). B, DNA sequences at exon/intron junctions. Exons are in capital letters and introns in small letters. Note that high sequence similarities are found in the exon regions adjacent to introns. C, Southern-blot analysis of the L. japonicus genome. Genomic DNA was digested with DraI (D), EcoRI (E), HindIII (H), or XbaI (X), hybridized at 42°C, and washed twice at 55°C in 0.5× SSC solution containing 0.1% (w/v) SDS. cCHI1 and cCHI2 probes have no restriction site for any restriction endonuclease used.
End sequences of the other clones, LjT05E21 and LjT16P04, were found in LjT47K21 (data not shown). Gel-blot analysis of the genomic DNA confirmed the number of CHI genes in L. japonicus (Fig. 5C). When DraI-, EcoRI-, HindIII-, and XbaI-digested DNA samples were probed with cCHI1 and cCHI2, the numbers and sizes of the hybridization signals matched well with the predicted fragments from the restriction map of LjT47K21, except in the case of probing DraI- or EcoRI-digested DNA with cCHI1. However, the latter results were also understandable because type II CHI DNA fragments of similar length would be raised from DraI or EcoRI digestion of the genome. Thus, no other CHI genes exist in L. japonicus, and CHI genes are located in a single locus. LjT47K21 was mapped on the short arm terminal of chromosome V (data not shown).
Catalytic Functions of CHI Proteins
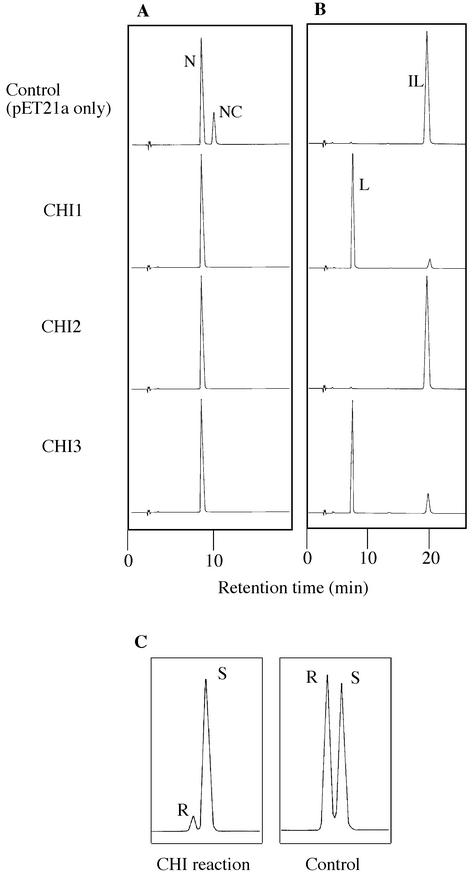
CHI activities were examined using the extracts of the recombinant Escherichia coli expressing CHI cDNAs. HPLC elution profiles of ethyl acetate-extracted reaction products showed that CHI1 and CHI3 yielded 5-hydroxyflavanone (naringenin) and 5-deoxyflavanone (liquiritigenin) from the incubation with 6′-hydroxychalcone (naringenin chalcone) and 6′-deoxychalcone (isoliquiritigenin) as substrates, respectively (Fig. 6, A and B). On the other hand, CHI2 produced 5-hydroxyflavanone from 6′-hydroxychalcone but did not produce 5-deoxy-flavanone from 6′-deoxychalcone (Fig. 6B). Thus, it was shown that CHI1 and CHI3 are type II CHIs, which accept both 6′-deoxychalcone and 6′-hydroxychalcone as substrates, whereas CHI2 is a type I CHI, which only cyclizes 6′-hydroxychalcone.
Figure 6.
HPLC profiles of the products of CHI1, CHI2, and CHI3 reactions. A, The reaction with 6′-hydroxychalcone (naringenin chalcone) as the substrate. All CHI proteins (CHI1–3) isomerized naringenin chalcone to 5,7,4′-trihydroxyflavanone (naringenin). Naringenin was also found in the control reaction, which used crude enzyme extract from E. coli harboring vector only, because of a spontaneous cyclization of the substrate. B, The reaction with 6′-deoxychalcone (isoliquiritigenin) as the substrate. CHI1 and CHI3 proteins were active to isoliquiritigenin, and the peak of the product 7,4′-dihydroxyflavanone (liquiritigenin) was observed. No product was observed in the control and CHI2 reactions. C, Separation of (2R)- and (2S)-naringenin by a chiral separation column. The CHI2 (type I) reaction with naringenin chalcone dominantly gave (2S)-naringenin, and the same result was observed with CHI1 (type II) reaction (data not shown). On the other hand, (2RS)-naringenin was found in the control reaction. IL, Isoliquiritigenin; NC, naringenin chalcone; N, naringenin; L, liquiritigenin.
The control reaction with 6′-hydroxychalcone using a preparation of E. coli without the cCHI insert gave a peak of naringenin (see Fig. 6A, top), which should be ascribed to the nonenzymatical conversion to (2RS)-naringenin. To confirm the enzymatic cyclization by CHI proteins, the stereochemistry of naringenin at C-2 position was estimated by HPLC on a chiral column. As shown in Figure 6C, (2S)-naringenin was dominantly produced compared with (2R)-naringenin in the presence of CHI1 or CHI2 protein, whereas only a racemic mixture of naringenin was found in the control reaction.
Properties of CHI Proteins
His-fused CHI proteins were isolated from the crude extract of the recombinant E. coli by affinity column chromatography. The SDS-PAGE of the isolated CHI proteins showed bands around the predicted molecular masses, 25,482 D (CHI1 + 6× His), 24,998 D (CHI2 + 6× His), and 25,338 D (CHI3 + 6× His), respectively (data not shown). Table III shows the kinetic properties of CHI isozymes. The Km and Vmax of CHI1 and CHI3 for 6′-hydroxychalcone and 6′-deoxychalcone were similar. Only the Vmax value of CHI1 toward 6′-hydroxychalcone was higher than that of 6′-deoxychalcone. On the other hand, the Vmax of CHI2 toward 6′-hydroxychalcone was about three times that of CHI1. No reaction for 6′-deoxychalcone was observed even when the CHI2 protein in the reaction mixture was concentrated up to 102 fold (data not shown). The optimal pH for each CHI reaction with 6′-hydroxychalcone was 7.5 to 8.5.
Table III.
Properties of CHI isozymes from L. japonicus
| CHI Isozyme |
Km
|
Vmax
|
pH Optimal | Molecular Mass | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCa | ILb | NCa | ILb | |||
| μm | nmol s−1 mg−1 | D | ||||
| CHI1 | 3 | 4 | 2,500 | 1,030 | 7.5–8.0 | 24,400 |
| CHI2 | 3 | NDc | 6,900 | NDc | 7.5–8.5 | 23,900 |
| CHI3 | 5 | 8 | 1,400 | 1,500 | 8.0–8.5 | 24,200 |
NC, Naringenin chalcone.
IL, Isoliquiritigenin.
ND, Not detected.
Elicitor Response Expression of CHI Isozymes in L. japonicus
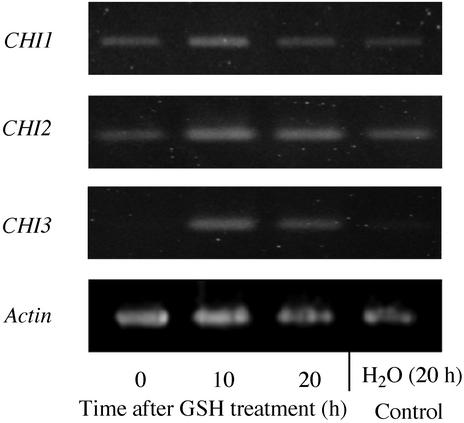
Treatment of L. japonicus with reduced glutathione (GSH) induces the accumulation of a 5-deoxyisoflavan vestitol and the expression of its biosynthetic genes (Shimada et al., 2000). To examine the expression of CHI genes in GSH-treated seedlings, mRNA was isolated at different times after elicitation and subjected to reverse transcription (RT)-PCR analysis using specific primers that discriminate the sequences of CHI isoforms. Because the sequences of cCHI1 and cCHI3 are highly conserved in the coding region, gene-specific primers were designed based on the 3′-untranslated regions. Different amplification cycles were tested for each primer sets to estimate the relative levels of transcripts and also to detect the low level of expression.
The transcript accumulation of all the three CHIs increased at 10 h after elicitation and then decreased (Fig. 7). Although the transcripts of CHI1 and CHI2 were observed in untreated (0 h) and the control (water-treated) seedlings (Fig. 7), the CHI3 transcript was not detected in these tissues by 30 cycles of PCR amplification. However, the signal of CHI3 transcript emerged after 35-cycle amplification in nonelicited seedlings (data not shown), suggesting that CHI1 through CHI3 are, to some extent, expressed without elicitation. On the other hand, the CHI4 transcript was not observed in any seedlings analyzed (data not shown).
Figure 7.
Expression of CHI mRNA in L. japonicus seedlings on GSH treatment. mRNA was isolated from seedlings after the GSH or water treatment. The PCR primers for CHI1 and CHI3 amplify the 3′-untranslated regions of cCHI1 and cCHI3, and, thus, distinguish these mRNAs. The primers for CHI2 amplification were the same as that used in cCHI2 cloning. Amplification of the actin gene (Shimada et al., 2000) served as a control to adjust the amount of PCR template DNA. The PCR was performed with 30 cycles for CHI1 and CHI3 and 25 cycles for CHI2.
DISCUSSION
We identified three CHI cDNAs (cCHI1–3) and the corresponding genes as well as a putative CHI gene (CHI4) from a model legume L. japonicus. In contrast to previous observations that only type II CHI is present in leguminous plants, CHI2 displays the nonleguminous type amino acid sequence and type I substrate specificity. CHI1 and CHI3, with legume-specific sequences, are type II CHIs. These results clearly demonstrated that the two groups of CHIs, classified on the basis of amino acid sequence, correspond to the functional types based on the catalytic activity. Transcripts of three CHI genes were constitutively detected in L. japonicus seedlings, and the accumulation of the CHI1 and CHI3 transcripts was increased by GSH treatment, which induces an isoflavan phytoalexin, vestitol (Shimada et al., 2000). These expression patterns together with their kinetic parameters indicate that these three CHIs of L. japonicus correspond to the CHI isozymes of another legume, licorice, in which two type II CHIs and one type I CHI were biochemically characterized (Kimura et al., 2001). Furthermore, expressed sequence tag data of soybean (Glycine max; GenBank accession nos.: type I, AW733840; and type II, BI974353) and Medicago truncatula (GenBank accession nos.: type I, BI310352; and type II, BF520356) suggest the occurrence of both types of CHIs, indicating that leguminous plants generally have multiple CHI isozymes.
The expression patterns of CHI1 and CHI3 are consistent with those of other biosynthetic genes of isoflavan phytoalexin(s) such as 2-hydroxyiso-flavanone synthase, isoflavone 2′-hydroxylase, and isoflavone reductase, which are coordinately and transiently induced on GSH treatment (Shimada et al., 2000). L. japonicus accumulates 5-hydroxyflavonoids, i.e. anthocyanins, condensed tannins, and flavonols (Aoki et al., 2000). These are most naturally supposed to be synthesized via the action of CHI2, the type I CHI of L. japonicus, but it is possible that CHI1 and CHI3 are involved in their biosynthesis, because type II CHIs can isomerize both 6′-hydroxy- and 6′-deoxychalcones. No expression of CHI4 was observed in L. japonicus seedlings under the same experimental conditions for the detection of the expression of other isozymes. Thus, the cDNA was unavailable and the catalytic activity could not be determined, but the amino acid sequence homology and its genome organization strongly suggested that CHI4 is a type II CHI. The 5′-flanking regions of the four CHI genes revealed several candidates of the cis-acting elements (data not shown). The mechanism of the regulation of the expression of CHI isozymes, including CHI4, needs further detailed investigation. Also, the transgenic L. japonicus suppressed in the expression of either type I or type II CHI gene would be useful to elucidate the physiological functions of both types of CHIs in leguminous plants.
To our best knowledge, type II CHI is distributed only to leguminous plants (Heller and Forkmann, 1993). Heterologous expression of chalcone polyketide reductase in petunia resulted in the accumulation of yellow pigments (Davies et al., 1998). It is suggested that 6′-deoxychalcone synthesized in the transgenic petunia is not incorporated into the further flavonoid pathway because petunia lacks endogenous type II CHI activity and that 6′-deoxychalcone is converted to the yellow derivatives. On the other hand, maize (Zea mays) BMS cells expressing cDNAs encoding 2-hydroxyisoflavanone synthase and chalcone polyketide reductase produced a small amount of 5-deoxyisoflavone, daidzein (Yu et al., 2000). The phylogenetic tree (Fig. 4) shows that maize CHI is included in the nonleguminous (type I) group. Nonenzymatic isomerization of 6′-deoxychalcone may occur in maize cells, or maize may have another unidentified class of CHI that has a weak 6′-deoxychalcone isomerase activity.
In Arabidopsis, several enzymes in the 5-hydroxyflavonoid pathway are thought to interact with each other and form a macromolecular complex on endomembranes (Burbulis and Winkel-Shirley, 1999; Saslowsky and Winkel-Shirley, 2001; Winkel-Shirley, 2001). Maize CHI cDNA fully complemented Arabidopsis tt5 mutant (Dong et al., 2001), and either the endogenous CHI or heterologously expressed maize CHI was implicated in the posttranslational modification at a Cys residue in Arabidopsis cells to perform a role in the complex formation. On the other hand, enzymes of the specific 5-deoxy(iso)flavonoid pathway such as chalcone synthase, polyketide reductase, and CHI have been suggested to be parts of the putative enzyme complex in leguminous plant cells (Dixon et al., 1996). Therefore, it is envisaged that, in leguminous plants producing both 5-hydroxy- and 5-deoxyflavonoids, type I and type II CHIs participate in distinct enzyme complexes devoted to producing, for example, anthocyanin pigments and phytoalexins in different organs and/or in different subcellular locations. The localization and interaction of both types of L. japonicus CHIs with other enzymes should be examined, although the Cys modification is not the case in L. japonicus CHI2 because it lacks the corresponding Cys residues conserved in Arabidopsis and maize CHIs.
The four CHI genes are present tandemly in L. japonicus chromosome V. Only a few gene clusters of plant enzymes involved in secondary metabolism are known: e.g. in soybean, four chalcone synthase genes are present within 10 kb (Akada and Dube, 1995), and three tandem copies of the dihydroflavonol 4-reductase genes are characterized in the Japanese and common morning glories (Ipomoea nil and Ipomoea purpurea, respectively; Inagaki et al., 1999). However, the characteristic difference in the substrate specificity among the products of the multigene family of L. japonicus CHI is unique. The occurrence of a cluster of both genes encoding general (type I) and legume-specific (type II) CHIs suggests that the origin of type II CHIs is attributed to a local gene duplication of an ancestral CHI. The numbers and sizes of exons and the conserved sequences surrounding each exon-intron junction indicate that exons 1 and 2 of the type II CHI gene arose from the insertion of an intron in exon 1 of type I CHI gene after gene duplication. It appears that intron-junctional sliding has not occurred in the evolution of CHI genes of L. japonicus (Higashimoto and Liddle, 1993; Stoltzfus et al., 1994; Schäfer et al., 1999).
L. japonicus CHI1, 3, 4, and other legume-specific type II CHIs comprise a monophyletic group. L. japonicus CHI2 is categorized into the polyphyletic nonleguminous group composed of type I CHIs. These phylogenetic relationships suggest that the gene duplication event that generated the legume-specific type II CHIs occurred at an evolutionary stage before the divergence of the Fabaceae. Also, comparison of amino acid and nucleotide sequences of the two types of plant CHIs (Table II) revealed two characteristic features. The first is the lower nucleotide identity in the “interphyletic” comparison between the legume-specific (type II) and nonleguminous groups (type I) than that within the nonleguminous group, which is polyphyletic itself. This indicates a high evolutionary rate of type II CHIs after the gene duplication. The second is poorly conserved amino acid residues compared with the nucleotides in the comparison between the two groups, which probably result from predominant non-synonymous substitution. These two features together imply a low functional constraint, i.e. the low significance of the gene (Kimura, 1968; Kimura and Ohta, 1974). Therefore, the evolution of the legume-specific CHIs can be best explained by the hypothesis that one of the duplicated genes lost its functional significance or became a pseudogene and accumulated mutations. Along with the establishment of the Fabaceae, the ancestral type II CHI, together with other biosynthetic enzymes such as polyketide reductase and cytochrome P450s, exerted a new function in the legume-specific 5-deoxy(iso)flavonoid biosynthesis producing phytoalexins and symbiotic signals, which has been essential for the ecological fitness of leguminous plants.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Material
Intact plants of Lotus japonicus accession B-129 Gifu, which were flowering and forming nitrogen-fixing nodules under the greenhouse condition, were harvested, frozen with liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C until use for mRNA preparation.
Cloning of CHI cDNAs
mRNA was isolated from whole plants of L. japonicus (1 g fresh weight) using Straight A's mRNA isolation system (Novagen, Madison, WI). One microgram of mRNA was used to synthesize first strand cDNA using Superscript II RNase H− Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen, Groningen, The Netherlands). Degenerate oligonucleotide primers were designed from highly conserved amino acid regions of known CHI sequences and named CHI/S1 (5′-GNACNTTYATHAARTTYAC-3′) and CHI/AS1 (5′- GCRTGYTCNCCDATCAT-3′). Second strand cDNA synthesis and ligation of adaptor sequences were performed with a Marathon cDNA Amplification Kit (CLONTECH, Palo Alto, CA). To obtain the full-length sequences of three CHI clones, the resulting cDNA was subjected to 3′- and 5′-RACE with ExTaq DNA polymerase (Takara, Tokyo) using the following gene-specific primers: LCHIs1 (5′-ACCAAGTGGAAGGGTAAGAGCTCAC-3′), LCHIas1 (5′-GGGAGTCCTGCAACTCTTGTGAGCT-3′), CHI/R/S1 (5′-GACGATG-ATCTTGCCATTGACG-3′), CHI/RAS2 (5′-CGCTAATGATCCTTTAGGC-AACACTGT-3′), and LCHIs3 (5′-CTTCTACAGAGACATCATTTCAAGC-3′) and LCHIas3 (5′-CCACAGCTTCTTTTTCTGGTAAA-3′). Three sets of specific primers containing NdeI or SalI sites (shown in bold type) were designed to amplify full-length cDNAs: LCHI/Nde (5′-TGAGGGCATAT-GGCACCAGCAAAAGGAT-3′) and LCHI/Sal2 (5′-CTTTTCAATCT-GTCGACGTTTCCAGTGAGG-3′) for cCHI1, NCHI/Nde (5′-AATATCAT-ATGGCACTACCGTCGGTCA-3′) and NCHI/Sal (5′-GTGCTCCGTCGACA-ACTTCCGCATGGT-3′) for cCHI2, and CHI3Nde (5′-GTGTTATTTGTGT-GAGTGAAACATATGGCG-3′) and CHI3Sal (5′-TCAACCTTCCGATGT-CGACGTTTCCAC-3′) for cCHI3. In these primers, the stop codon was modified to GAC (underlined) to produce a His-tagged fusion protein. PCR was carried out using KOD DNA polymerase (Toyobo, Tokyo) with 30 cycles of denaturation for 15 s at 94°C, annealing for 10 s at 60°C, and extension for 1 min at 72°C, followed by a final extension for 5 min, using a PTC-200 DNA Engine (MJ Research, Waltham, MA). PCR products were digested with NdeI and SalI, and then ligated to pT7Blue vectors (Novagen) digested with NdeI and SalI. Three independent clones were sequenced using an LIC-4000 DNA sequencer (LI-COR, Lincoln, NE).
Phylogenetic Analysis
Predicted amino acid sequences of CHIs were used for phylogenetic analysis. A neighbor-joining tree was produced from the results of 1,000 bootstrap replicates using the CLUSTALW program (Thompson et al., 1994) of the DNA Data Bank of Japan (Shizuoka, Japan). The phylogenetic tree was displayed by TreeView software (R.D.M. Page, University of Glasgow, UK).
Genome Structure of the CHI Locus and Genetic Mapping
Generation of a genome library with a TAC vector (Liu et al., 1999) from genomic DNA of L. japonicus accession MG-20 Miyakojima, sequencing strategy, and gene assignment were carried out as described elsewhere (Sato et al., 2001). The library was screened for the CHI genes by the PCR method using primer sets based on the sequences of cCHI1 (L00878, 5′-TGA-AAAATTTGCAGAAGCCTTCAGG-3′; and L00879, 5′-TTTGATCACTTTA-TTGATAGGAAGG-3′) and cCHI2 (L00880, 5′-TAGATAATAAACTGCTTTCAGAGGC-3′; and L00881, 5′-ACTTGGTTAGGGTACTATTGAATCC-3′). The nucleotide sequence of a clone, LjT47K21, thus isolated revealed that it includes genes encoding CHI1–3 and an additional CHI (CHI4). Genetic mapping was carried out with a single sequence repeat marker found in LjT47K21 as described by Sato et al. (2001).
Southern-Blot Analysis
Genome DNAs of L. japonicus B-129 Gifu were isolated using a DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). Ten micrograms of genome DNA was digested with DraI, EcoRI, HindIII, or XbaI. Electrophoresis, blotting, and hybridization were performed according to DIG hybridization protocol (Roche, Basel). The washing was done at 55°C for 15 min in 0.5× SSC and 0.1% (w/v) SDS solution. This step was repeated twice.
Expression of CHI Recombinant Proteins in Escherichia coli
Each plasmid vector with cCHI cDNA inserted was digested with NdeI and SalI, and resulting fragments were subcloned into the E. coli expression vector pET21a (Novagen). The constructs were subjected to sequence analysis and introduced into the E. coli strain BL21(DE3). Expression of the recombinant protein was induced by the addition of 1 mm isopropyl-thio-β-d-galactoside. E. coli cells were then harvested by centrifugation at 3,000g for 5 min and washed with 0.1 m potassium-phosphate (pH 7.5) containing 10% (w/v) Suc and 14 mm 2-mercaptoethanol. After washing, cells were collected by centrifugation at 3,000g for 5 min, frozen with liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C.
To disrupt cells, the cell pellet was suspended in 10 mL of start buffer (supplied in the HisTrap Kit; Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ), vortexed in the presence of glass beads (0.35–0.60-mm diameter), and then centrifuged at 6,000g for 10 min at 4°C. The supernatant was used as the crude enzyme solution. The protein content was calculated by the Bradford method (Bradford, 1976). The recombinant enzyme was isolated from the crude extract using the HisTrap kit according to the manufacturer's protocol. The eluted enzyme was ultrafiltered by an ultrafilter unit USY-1 (Advantec, Tokyo); dissolved in 1 mL of 50 mm potassium-phosphate buffer containing 50 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, and 1 mm dithiothreitol (pH 7.5); and then stored at 4°C.
CHI Assay
6′-Hydroxychalcone or 6′-deoxychalcone (10 μg each in 10 μL of ethanol) was incubated at 30°C for 5 min with 0.49 mL of 50 mm potassium-phosphate (pH 7.5) containing 10 μL of crude enzyme (total 0.5 mL). The reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate, and the products were analyzed by HPLC. HPLC was performed using a Shim-pack CLC-ODS column (6.0 × 150 mm; Shimadzu, Kyoto) with 40% (v/v) methanol and 3% (v/v) acetic acid in water at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1 at 40°C, and the eluate was monitored at 304 nm. To analyze the stereochemistry of CHI reaction products, 6′-hydroxychalcone and the crude extract of E. coli expressing CHI isozymes were incubated at 30°C for 3 h. An extract of E. coli transformed by the vector without insert was used for the control under the same condition. The reaction product was developed on a silica-gel thin-layer chromatography plate (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) with the solvent toluene:ethyl acetate:methanol:light petroleum (6:4:1:3 [v/v]), and the naringenin spot (RF = 0.44) was recovered. The sample was then analyzed by HPLC on a Chiracel OD-RH column (4.6 × 150 mm; Daicel, Tokyo) with 35% (v/v) aqueous acetonitrile at a flow rate of 0.5 mL min−1 at 30°C, and the eluate was monitored at 290 nm.
Kinetic Properties
Enzyme activity was assayed in 50 mm potassium-phosphate buffer (1.5 mL, pH 7.5) containing His-fused proteins (CHI1, 27 ng; CHI2, 10 ng; and CHI3, 60 ng). The decrease of substrate A395 was monitored using a DU640 spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, CA). Determinations of the Km and the Vmax for both 6′-hydroxychalcone and 6′-deoxychalcone were performed with varied substrate concentration ranges between 0.8 and 23 μm. Km and Vmax values were calculated using a Lineweaver-Burk plot. The optimal pH was determined in 50 mm potassium phosphate at pH range 6.0 to 8.0 and 50 mm Tricine-HCl at pH range 7.5 to 8.5 using 6′-hydroxychalcone as a substrate.
RT-PCR Analysis
mRNA isolation and RT were performed as described previously (Shimada et al., 2000). The quantity of each template was adjusted to give roughly equal amplification of actin cDNA. For analysis of CHI1 and CHI3 expression, gene-specific primers were redesigned based on the coding regions and 3′-untranslated regions of these cDNAs as follows: CHI1rts1 (5′-CCTCACTGGAAACTGACAAGATTGAAAAGT-3′), CHI1rtas1 (5′-GATAGGAAGGTAAAAGATACACAAACAAAT-3′), CHI3rts1 (5′-CTGTTTCCCCTGATTTGAAGCGTTGTTTGG-3′), and CHI3rtas1 (5′-TTATCTTTTGTAGCAGCAGCCAGCACTTTC-3′). The same primers as described above were used for amplification of the CHI2 transcript. RT-PCR was carried out with 0.5 pmol each of specific primers using ExTaq DNA polymerase (Takara) in a final volume of 20 μL according to the manufacturer's protocol. The reaction was performed at 95°C for 1 min followed by 30 cycles of 95°C for 15 s, 60°C for 10 s, and 72°C for 1 min, and a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. The products (5 μL) were subjected to electrophoresis on 1.2% (w/v) agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide.
Accession Numbers for CHIs
GenBank accession numbers for the amino acid sequences of CHIs are: Arabidopsis (P41088), Citrus sinensis (BAA36552), Dianthus caryophyllus (Q43754), Elaeagnus umbellata (O65333), I. purpurea (O22604), alfalfa (Medicago sativa; P28012), Pueraria lobata (Q43056), Phaseolus vulgaris (P14298), petunia (Petunia hybrida) CHIA (AAF60296), petunia CHIB (P11651), Raphanus sativus (O22651), Vitis vinifera (P51117), and maize (Zea mays; Q08704). The GenBank accession numbers for nucleotide sequences are: C. sinensis (AB011794), E. umbellata (AF061808), I. purpurea (AF028238), alfalfa (M91079), P. lobata (D63577), P. vulgaris (S54703), and V. vinifera (X75963).
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Sports, Science and Culture of Japan (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Area [A] no. 12045261).
Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/doi/10.1104/pp.004820.
LITERATURE CITED
- Akada S, Dube SK. Organization of soybean chalcone synthase gene clusters and characterization of a new member of the family. Plant Mol Biol. 1995;29:189–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00043645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi T, Aoki T, Ayabe S. Cloning and functional expression of a cytochrome P450 cDNA encoding 2-hydroxyisoflavanone synthase involved in biosynthesis of the isoflavonoid skeleton in licorice. Plant Physiol. 1999;121:821–828. doi: 10.1104/pp.121.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi T, Furuno T, Futami K, Honda M, Takahashi T, Welle R, Ayabe S. A cDNA for polyketide reductase (accession no. D83718) that catalyzes the formation of 6′-deoxychalcone from cultured Glycyrrhiza echinataL. cells (PGR 96023) Plant Physiol. 1996;111:347. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki T, Akashi T, Ayabe S. Flavonoids of leguminous plants: structure, biological activity, and biosynthesis. J Plant Res. 2000;113:475–488. [Google Scholar]
- Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Sato S, Tabata S. Generation of 7137 non-redundant expressed sequence tags from a legume, Lotus japonicus. DNA Res. 2000;7:127–130. doi: 10.1093/dnares/7.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyden ER, Doerner PW, Lamb CJ, Dixon RA. Sequence analysis of a chalcone isomerase cDNA of Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Mol Biol. 1991;16:167–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00017927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbulis IE, Winkel-Shirley B. Interactions among enzymes of the Arabidopsisflavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:12929–12934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies KM, Bloor SJ, Spiller GB, Deroles SC. Production of yellow colour in flowers: redirection of flavonoid biosynthesis in Petunia. Plant J. 1998;13:259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Dewick PM. Isoflavonoids. In: Harborne JB, editor. The Flavonoids. Advances in Research Since 1980. London: Chapman and Hall; 1986. pp. 125–209. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon RA, Blyden ER, Robbins MP, van Tunen AJ, Mol JN. Comparative biochemistry of chalcone isomerase. Phytochemistry. 1988;27:2801–2808. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon RA, Lamb CJ, Masoud S, Sewalt VJ, Paiva NL. Metabolic engineering: prospects for crop improvement through the genetic manipulation of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and defense responses—a review. Gene. 1996;179:61–71. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X, Braun EL, Grotewold E. Functional conservation of plant secondary metabolic enzymes revealed by complementation of Arabidopsis flavonoid mutants with maize genes. Plant Physiol. 2001;127:46–57. doi: 10.1104/pp.127.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M, Kokubun T, Takahata Y, Higashitani A, Tabata S, Watanabe M. Analysis of expressed sequence tags of flower buds in Lotus japonicus. DNA Res. 2000;7:213–216. doi: 10.1093/dnares/7.3.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannasi DE. Flavonoids and evolution in the dicotyledons. In: Harborne JB, editor. The Flavonoids: Advances in Research Since 1980. London: Chapman and Hall; 1988. pp. 479–504. [Google Scholar]
- Grotewold E, Peterson T. Isolation and characterization of a maize gene encoding chalcone flavanone isomerase. Mol Gen Genet. 1994;242:1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00277341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handberg K, Stougaard J. Lotus japonicus, an autogamous, diploid legume species for classical and molecular genetics. Plant J. 1992;2:487–496. [Google Scholar]
- Harborne JB. Phytochemistry of the Leguminosae. In: Bisby FA, Buckingham J, Harborne JB, editors. Phytochemical Dictionary of the Leguminosae. London: Chapman and Hall; 1994. , pp xx–xxii. [Google Scholar]
- Hegnauer R, Gpayer-Barkmeijer RJ. Relevance of seed polysaccharides and flavonoids for the classification of the Leguminosae: a chemotaxonomic approach. Phytochemistry. 1993;34:3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Heller W, Forkmann G. Biosynthesis of Flavonoid. In: Harbone JB, editor. The Flavonoids: Advances in Research Since 1986. London: Chapman and Hall; 1993. pp. 499–536. [Google Scholar]
- Higashimoto Y, Liddle RA. Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding rat glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;193:182–190. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki Y, Johzuka-Hisatomi Y, Mori T, Takahashi S, Hayakawa Y, Peyachoknagul S, Ozeki Y, Iida S. Genomic organization of the genes encoding dihydroflavonol 4-reductase for flower pigmentation in the Japanese and common morning glories. Gene. 1999;226:181–188. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00571-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jez JM, Bowman ME, Dixon RA, Noel JP. Structure and mechanism of the evolutionarily unique plant enzyme chalcone isomerase. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:786–791. doi: 10.1038/79025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jez JM, Noel JP. Reaction mechanism of chalcone isomerase. pH dependence, diffusion control, and product binding differences. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:1361–1369. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109224200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung W, Yu O, Lau SMC, O'Keefe DP, Odell J, Fader G, McGonigle B. Identification and expression of isoflavone synthase, the key enzyme for biosynthesis of isoflavones in legumes. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:208–212. doi: 10.1038/72671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Evolutionary rate at the molecular level. Nature. 1968;217:624–626. doi: 10.1038/217624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M, Ohta T. On some principles governing molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1974;71:2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y, Aoki T, Ayabe S. Chalcone isomerase isozymes with different substrate specificities toward 6′-hydroxy and 6′-deoxychalcones in cultured cells of Glycyrrhiza echinata, a leguminous plant producing 5-deoxyflavonoids. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001;42:1169–1173. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pce130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Shirano Y, Fukaki H, Yanai Y, Tasaka M, Tabata S, Shibata D. Complementation of plant mutants with large genomic DNA fragments by a transformation-competent artificial chromosome vector accelerates positional cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:6535–6540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdy MC, Lamb CJ. Chalcone isomerase cDNA cloning and mRNA induction by fungal elicitor, wounding and infection. EMBO J. 1987;6:1527–1533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir SR, Collins GJ, Robinson S, Hughes S, Bovy A, De Vos CHR, van Tunen AJ, Verhoeyen ME. Overexpression of petunia chalcone isomerase in tomato results in fruit containing increased levels of flavonols. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19:470–474. doi: 10.1038/88150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters NK, Frost JW, Long SR. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium melilotinodulation genes. Science. 1986;233:977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond JW, Batley M, Djordjeic MA, Innes RW, Kuempel PL, Rolfe BG. Flavones induce expression of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Nature. 1986;323:632–635. [Google Scholar]
- Rieseberg LH, Soltis DE, Arnold D. Variation and localization of flavonoid aglycones in Helianthus annuus (Compositae) Am J Bot. 1987;74:224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Saslowsky D, Winkel-Shirley B. Localization of flavonoid enzymes in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J. 2001;27:37–48. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S, Kaneko T, Nakamura Y, Asamizu E, Kato T, Tabata S. Structural analysis of Lotus japonicusgenome. I. Sequence features and mapping of fifty-six TAC clones which cover the 5.4 Mb regions of the genome. DNA Res. 2001;8:311–318. doi: 10.1093/dnares/8.6.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer UA, Reed DW, Hunter DG, Yao K, Weninger AM, Tsang EWT, Reaney MJT, MacKenzie SL, Covello PS. An example of intron junctional sliding in the gene families encoding squalene monooxygenase homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus. Plant Mol Biol. 1999;39:721–728. doi: 10.1023/a:1006172120929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauser L, Roussis A, Stiller J, Stougaard J. A plant regulator controlling development of symbiotic root nodules. Nature. 1999;402:191–195. doi: 10.1038/46058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada N, Akashi T, Aoki T, Ayabe S. Induction of isoflavonoid pathway in the model legume Lotus japonicus: molecular characterization of enzymes involved in phytoalexin biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2000;160:37–47. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9452(00)00355-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparvoli F, Martin C, Scienza A, Gavazzi G, Tonelli C. Cloning and molecular analysis of structural genes involved in flavonoid and stilbene biosynthesis in grape (Vitis viniferaL.) Plant Mol Biol. 1994;24:743–755. doi: 10.1007/BF00029856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford HA. Role of flavonoids in symbiotic and defense functions in legume roots. Bot Rev. 1997;63:27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Steele CL, Gijzen M, Qutob D, Dixon RA. Molecular characterization of the enzyme catalyzing the aryl migration reaction of isoflavonoid biosynthesis in soybean. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999;367:146–150. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus A, Spencer DF, Zuker M, Logsdon JMN, Doolittle F. Testing the exon theory of genes: the evidence from protein structure. Science. 1994;265:202–207. doi: 10.1126/science.8023140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terai Y, Fujii I, Byun SH, Nakajima O, Hakamatsuka T, Ebizuka Y, Sankawa U. Cloning of chalcone-flavanone isomerase cDNA from Pueraria lobata and its overexpression in Escherichia coli. Prot Expr Purif. 1996;8:183–190. doi: 10.1006/prep.1996.0091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropf S, Karcher B, Schröder G, Schröder J. Reaction mechanisms of homodimeric plant polyketide synthase (stilbenes and chalcone synthase): A single active site for the condensing reaction is sufficient for synthesis of stilbenes, chalcones, and 6′-deoxychalcones. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7922–7928. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.7922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tunen AJ, Koes RE, Spelt CE, van der Krol AR, Stuitje AR, Mol JNM. Cloning of the two chalcone flavanone isomerase genes from Petunia hybrida: coordinate, light-regulated and differential expression of flavonoid genes. EMBO J. 1988;7:1257–1263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02939.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkel-Shirley B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 2001;126:485–493. doi: 10.1104/pp.126.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkel-Shirley B, Kubasek WL, Storz G, Bruggemann E, Koornneef M, Ausubel FM, Goodman HM. Analysis of Arabidopsis mutants deficient in flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant J. 1995;8:659–671. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.08050659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood AJ, Davies E. A cDNA encoding chalcone isomerase from aged pea epicotyls. Plant Physiol. 1994;104:1465–1466. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu O, Jung W, Shi J, Croes RA, Fader GM, McGonigle B, Odell JT. Production of the isoflavones genistein and daidzein in non-legume dicot and monocot tissues. Plant Physiol. 2000;124:781–793. doi: 10.1104/pp.124.2.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]