Abstract
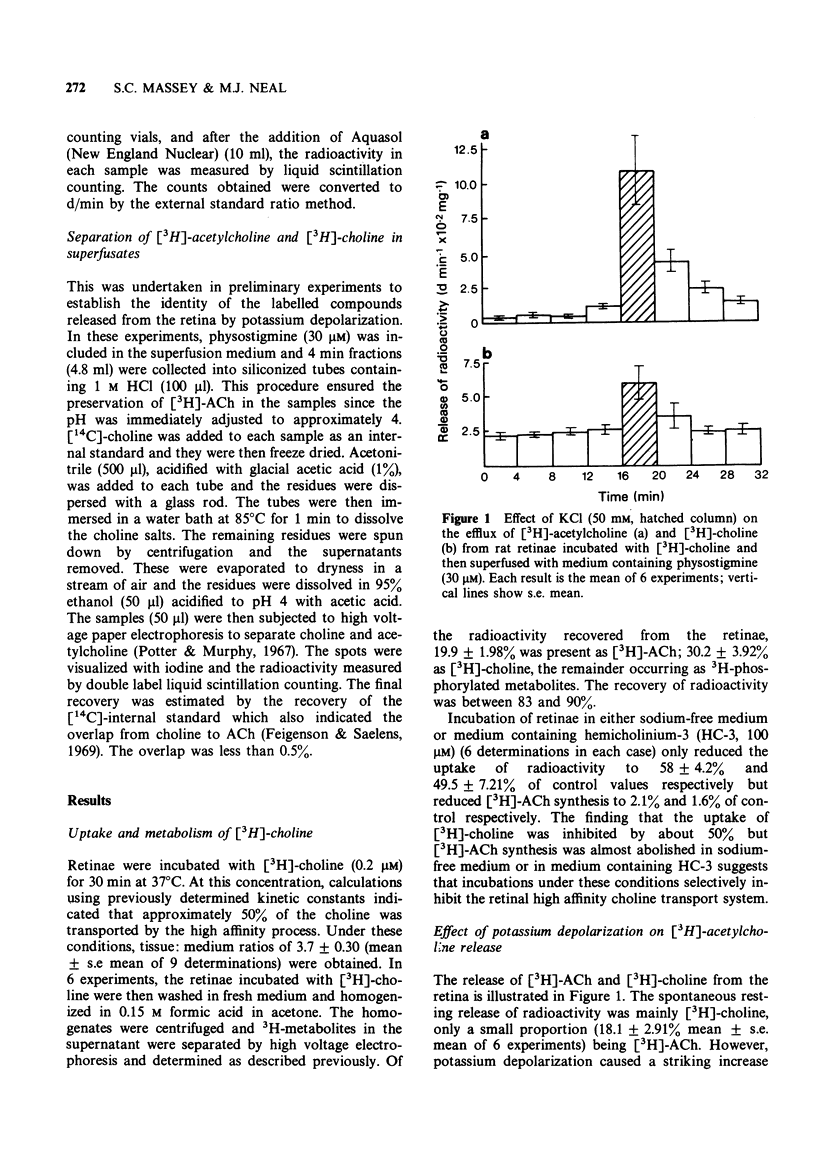
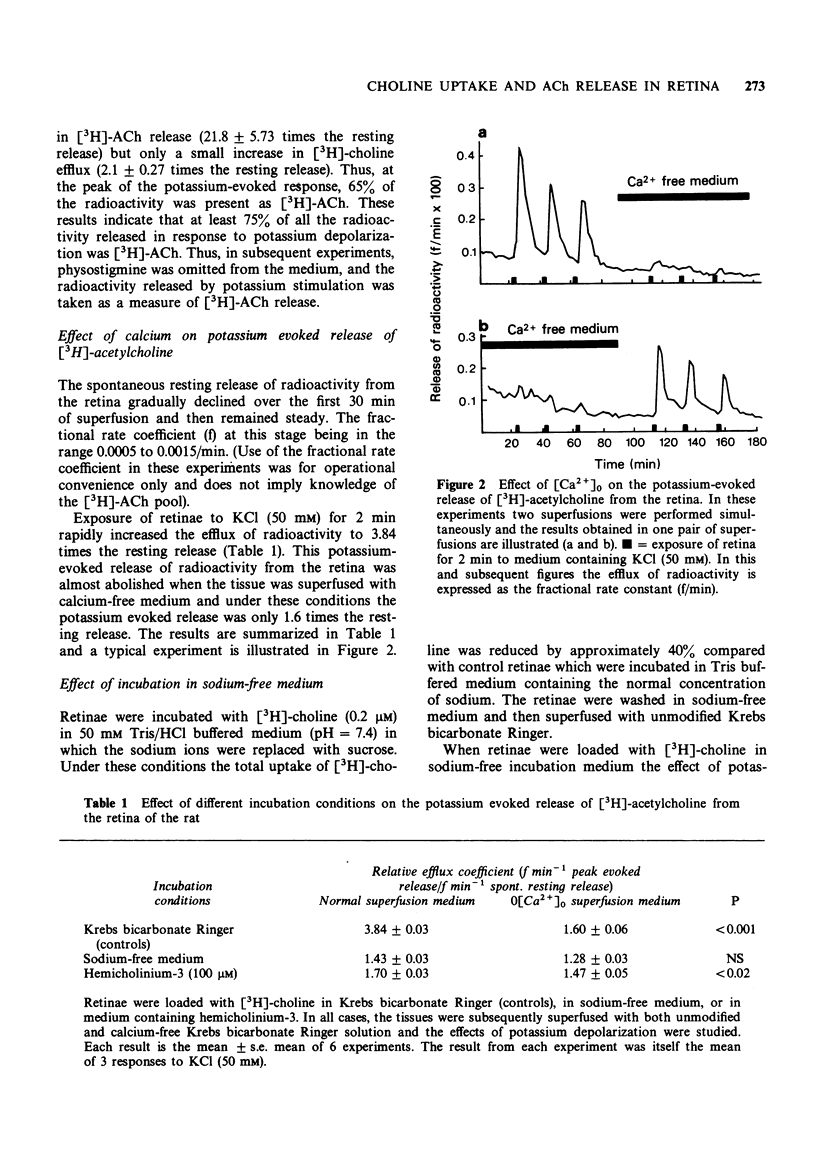
1. The effect of potassium depolarization on the release of [3H]-acetylcholine ([3H]-ACh) from the isolated retina of the rat was studied. 2. Exposure of retinae to medium containing KCl (50 mM) evoked a large increase in the efflux of [3H]-ACh with only a small concurrent increase in the efflux of [3H]-choline. The KCl-evoked release of [3H]-ACh was almost abolished in calcium-free medium. 3. Incubation of retinae with [3H]-choline in sodium-free medium, or medium containing hemicholinum-3 (HC-3), procedures that are believed to inhibit selectively the high affinity choline transport system, reduced the retinal uptake of [3H]-choline by approximately 50% and the synthesis of [3H]-ACh by about 97%. 4. The potassium-evoked release of [3H]-ACh was almost abolished in retinae that had been loaded with [3H]-choline in sodium-free medium or medium containing HC-3, and subsequently superfused in normal medium. 5. It is suggested that as in other areas of the nervous system, a sodium-dependent, high affinity uptake system for choline is important in retinal cholinergic nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF
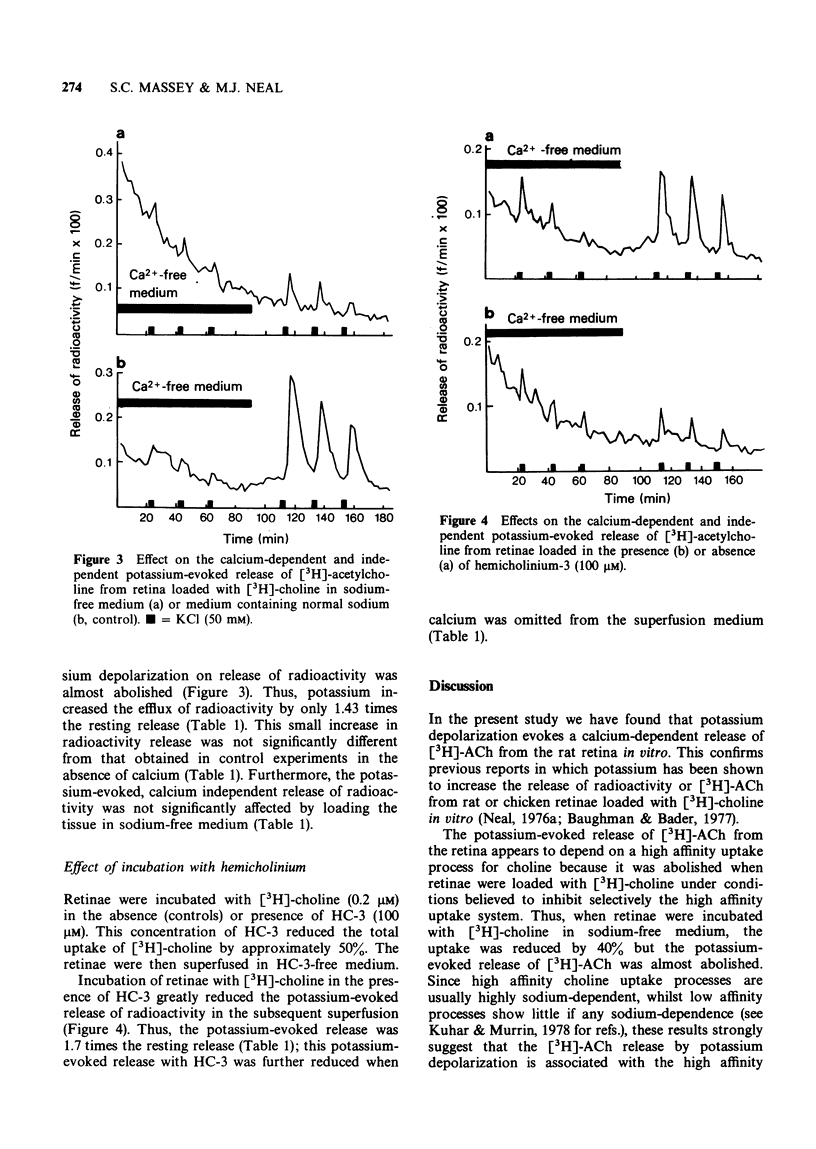


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughman R. W., Bader C. R. Biochemical characterization and cellular localization of the cholinergic system in the chicken retina. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 23;138(3):469–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90684-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Neal M. J. Differential effect of veratridine and potassium depolarization on [3H]GABA release from neurones and glia [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:58P–59P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenson M. E., Saelens J. K. An enzyme assay for acetylcholine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;18(6):1479–1486. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90262-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins A. J., Neal M. J. Activation of high affinity choline uptake in sympathetic ganglia by potassium depolarization [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):112P–113P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins A. J., Neal M. J. The effects of potassium depolarization on the metabolism of [3H]choline by rat sympathetic ganglia [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:67P–68P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., DeHaven R. N., Yamamura H. I., Rommel-Spacher H., Simon J. R. Further evidence for cholinergic habenulo-interpeduncular neurons: pharmacologic and functional characteristics. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 31;97(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Murrin L. C. Sodium-dependent, high affinity choline uptake. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Sethy V. H., Roth R. H., Aghajanian G. K. Choline: selective accumulation by central cholinergic neurons. J Neurochem. 1973 Feb;20(2):581–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masland R. H., Ames A., 3rd Responses to acetylcholine of ganglion cells in an isolated mammalian retina. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1220–1235. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masland R. H., Livingstone C. J. Effect of stimulation with light on synthesis and release of acetylcholine by an isolated mammalian retina. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1210–1219. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey S. C., Neal M. J. Light evoked release of acetylcholine from the rabbit retina in vivo [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:51P–52P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder A. H., Yamamura H. I., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Release of acetylcholine from hippocampal slices by potassium depolarization: dependence on high affinity choline uptake. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 19;70(2):372–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J. Amino acid transmitter substances in the vertebrate retina. Gen Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;7(5):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(76)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J., Gilroy J. High-affinity choline transport in the isolated retina. Brain Res. 1975 Aug 15;93(3):548–551. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols C. W., Koelle G. B. Comparison of the localization of acetylcholinesterase and non-specific cholinesterase activities in mammalian and avian retinas. J Comp Neurol. 1968 May;133(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/cne.901330102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T., Murphy W. Electrophoresis of acetylcholine, choline and related compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jul 7;16(7):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. D., McDougal D. B., Jr The distribution of choline acetyltransferase activity in vertebrate retina. J Neurochem. 1976 Mar;26(3):521–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., Pilar G. Selective localization of a high affinity choline uptake system and its role in ACh formation in cholinergic nerve terminals. J Neurochem. 1976 Jun;26(6):1133–1138. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Maloney G. J., Ling A., Daniels M. P. Identification of synaptic acetylcholine receptor sites in retina with peroxidase-labeled alpha-bungarotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3268–3272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. High affinity transport of choline into synaptosomes of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Dec;21(6):1355–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


