Abstract
1 Activation of pre-junctional α-adrenoceptors at the skeletal neuromuscular junction enhances acetylcholine release whereas activation of such receptors at autonomic nerve endings inhibits transmitter output. In the present study the characteristics of pre-junctional α-adrenoceptors at motor nerve terminals have been compared with post-junctional (vascular) α-adrenoceptors in the cat hind limb.
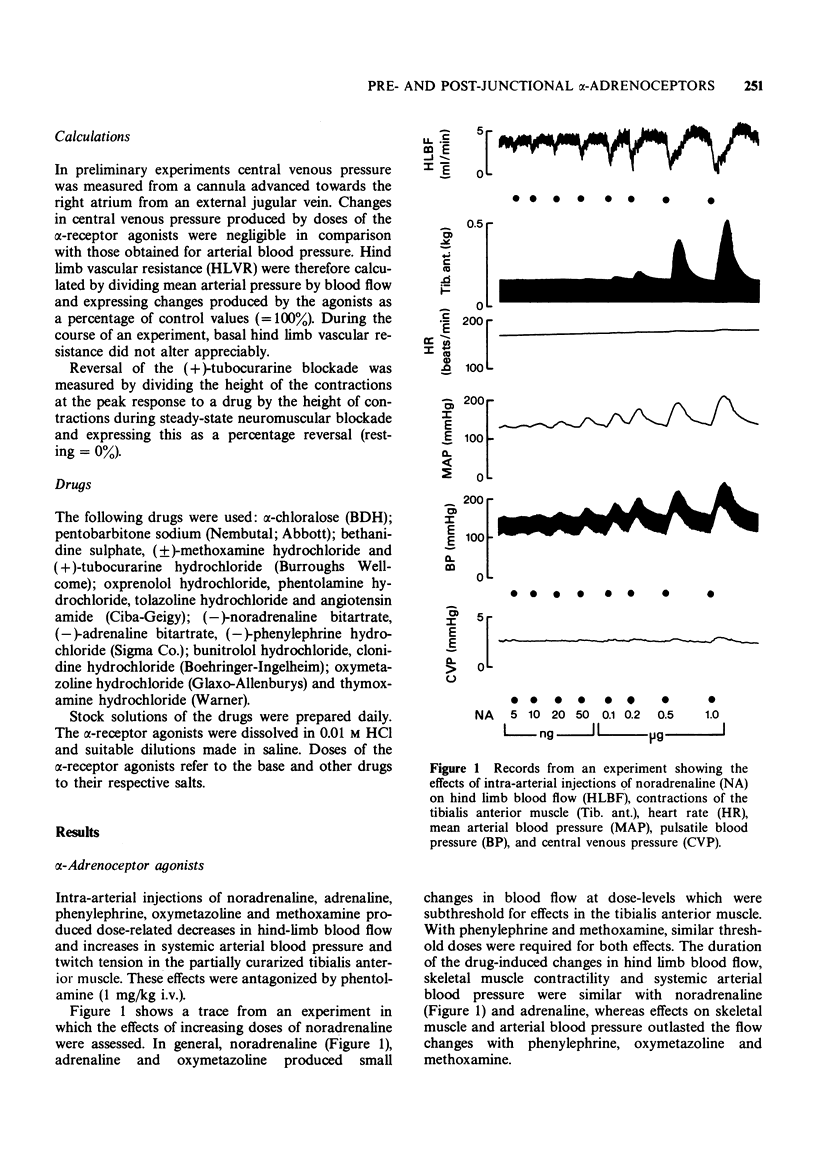
2 Reversal of partial (+)-tubocurarine blockade of contractions of the tibialis anterior muscle was used to monitor pre-junctional activity and increases in hindlimb vascular resistance to assess post-junctional actions at α-adrenoceptors.
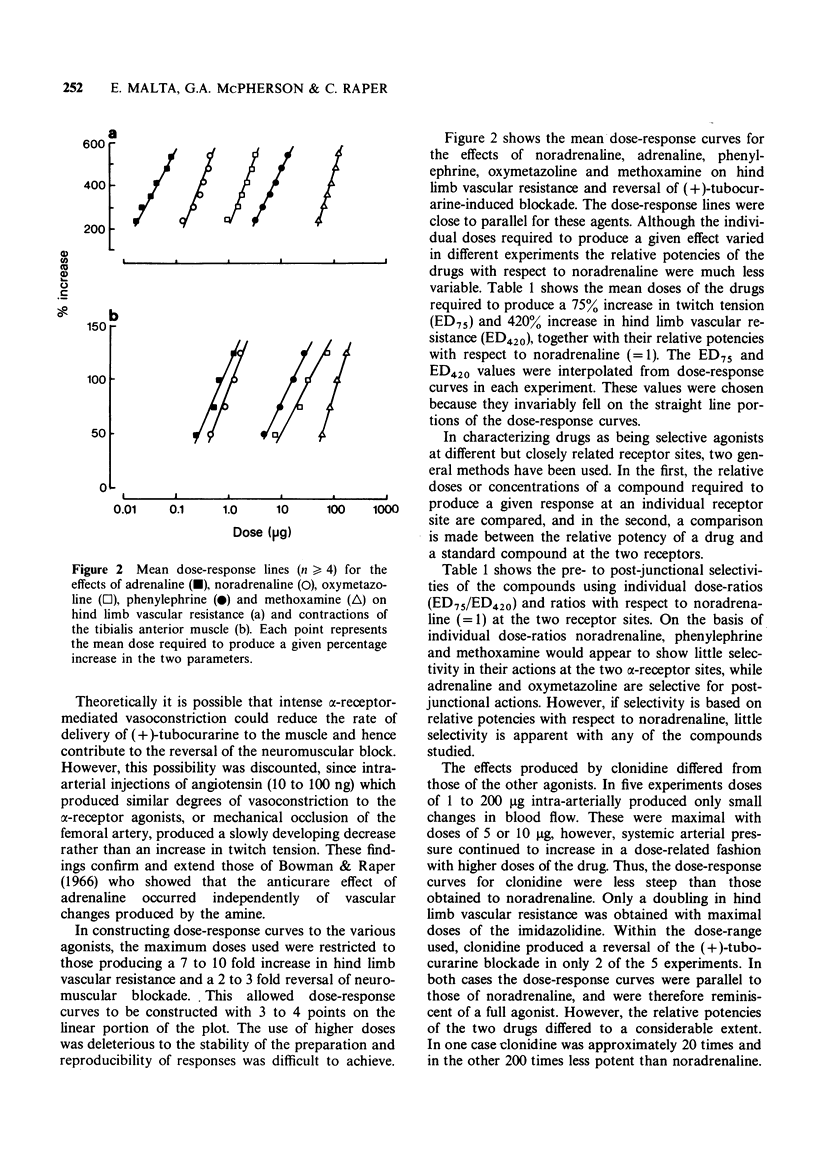
3 Responses to intra-arterial injections of noradrenaline, adrenaline, phenylephrine, oxymetazoline, methoxamine and clonidine were monitored. Dose-response lines for all the compounds except clonidine were parallel. The latter agent produced only weak and inconsistent effects.
4 Ratios of the doses of the agents required to produce pre- and post-junctional effects indicated that oxymetazoline and adrenaline possessed some preferential activity at post-junctional sites, whereas the remaining agents were non-selective in their actions. If dose-ratios with respect to noradrenaline were compared at the two sites none of the compounds possessed a marked degree of selectivity.
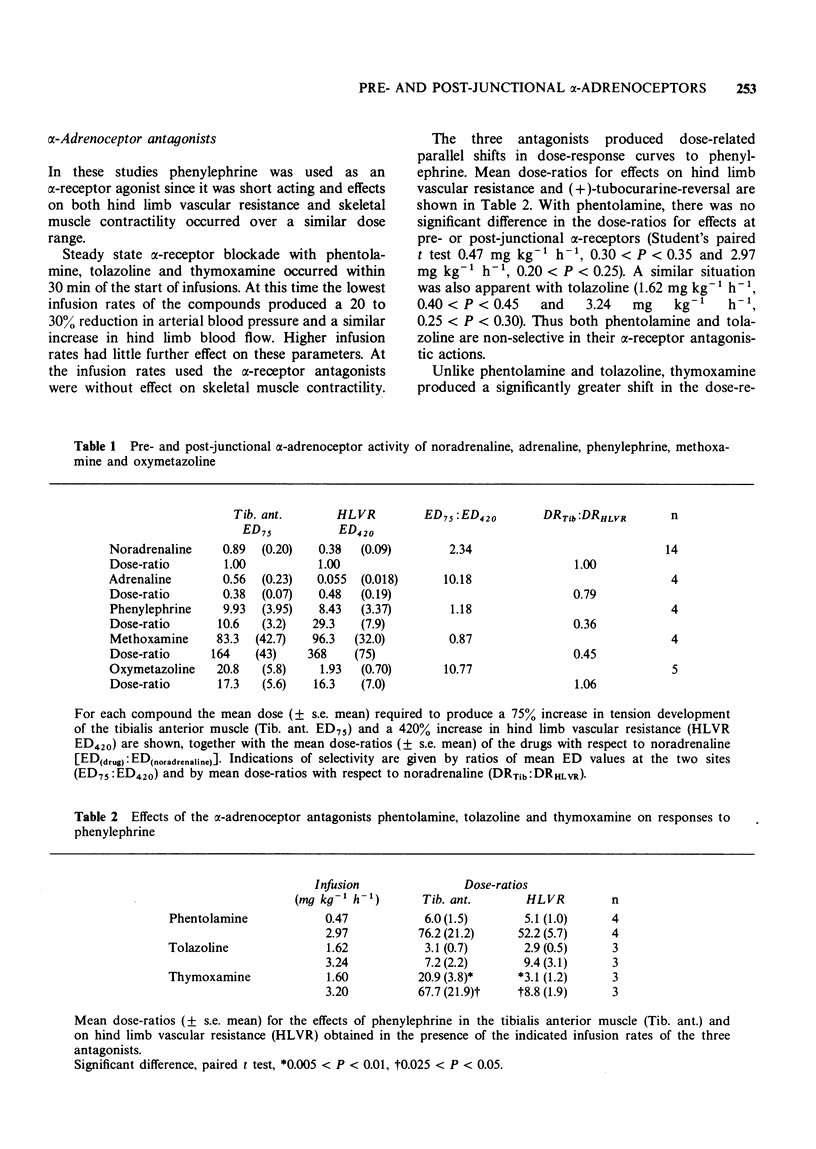
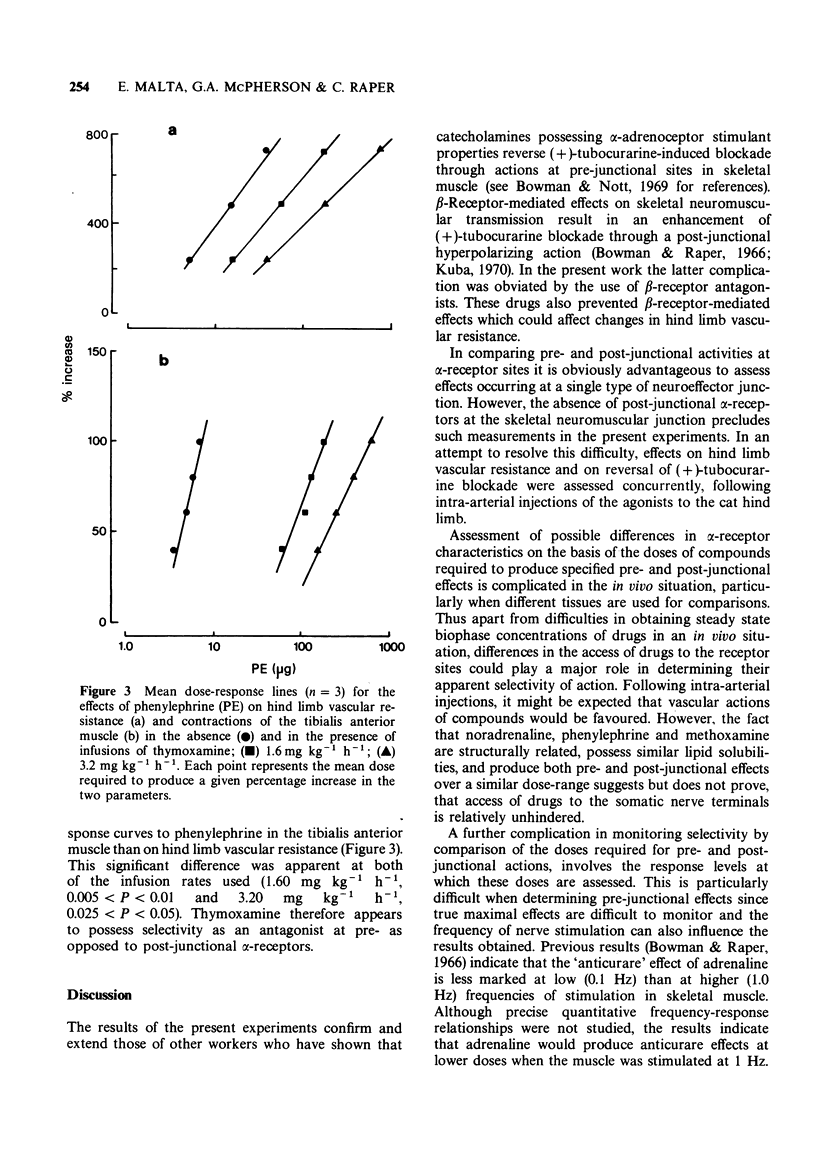
5 In the presence of phentolamine or tolazoline, dose-response curves to the pre- and post-junctional effects of phenylephrine were shifted to a similar extent. Thymoxamine showed preferential activity as a pre-junctional α-receptor antagonist.
6 In comparing the results of this study with those of other authors, it is apparent that there are marked differences in the characteristics of pre-junctional α-receptors at the skeletal neuromuscular junction and at autonomic nerve endings. The pre- and post-junctional α-receptors in skeletal muscle show less divergence.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Grabowska M., Strömbom U. Different alpha-adrenoreceptors in the central nervous system mediating biochemical and functional effects of clonidine and receptor blocking agents. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976;292(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00506488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Crema A. The effect of catecholamines and sympathetic stimulation on the release of acetylcholine from the guinea-pig colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 May;36(1):1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Giacomelli A., Tamberi F. Noradrenaline inhibition of acetylcholine release from guinea-pig brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;48(2):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. C., Nott M. W. Actions of sympathomimetic amines and their antagonists on skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1969 Mar;21(1):27–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. C., Raper C. Effects of sympathomimetic amines on neuromuscular transmission. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Aug;27(2):313–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubeddu L., Barnes E. M., Langer S. Z., Weiner N. Release of norepinephrine and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase by nerve stimulation. I. Role of neuronal and extraneuronal uptake and of alpha presynaptic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Sep;190(3):431–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Everitt J. Inhibitory effects of clonidine on responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):559–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on pre- and postsynaptically located alpha-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;36(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterisation of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 21;42(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors which regulate-cholinergic activity in the guinea-pig ileum [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):513P–513P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N., Karczmar A. G. The presynaptic site of action of norepinephrine in the superior cervical ganglion of guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Feb;200(2):328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeusler G. Studies on the possible contribution of a peripheral presynaptic action of clonidine and dopamine to their vascular effects under in vivo conditions. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;295(3):191–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00505086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepburn E. R., Reynoldson J. A., Li D. M., Bentley G. A. Effects of clonidine on vascular responses in kidney and hindlimbs of cats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1976 Nov-Dec;3(6):609–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1976.tb00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J., Vizi E. S. Presynaptic inhibition of acetylcholine release by endogenous and exogenous noradrenaline at high rate of stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):554P–555P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J., Watt A. J. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K. Effects of catecholamines on the neuromuscular junction in the rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):551–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on acetylcholine output by guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle strip. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):10–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on release of acetylcholine from guinea-pig ileum longitudinal strips. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;259(2):199–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00537789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


