Abstract
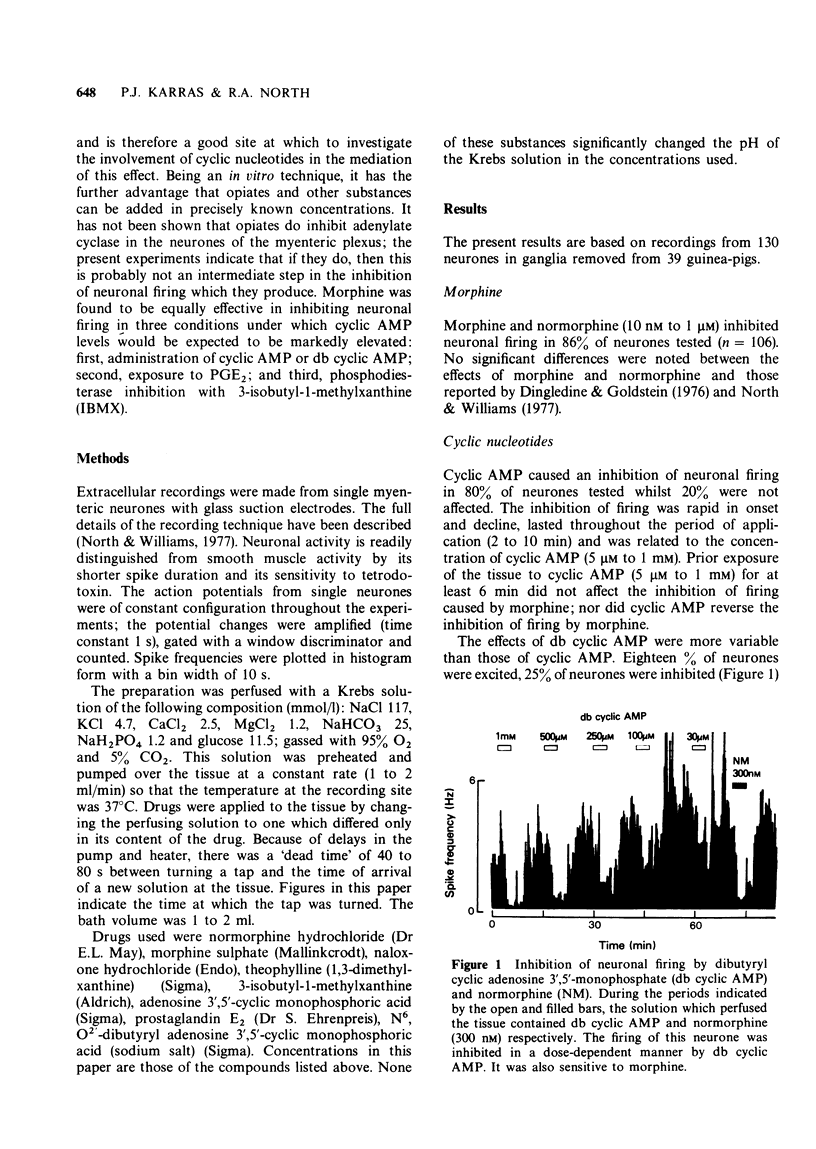
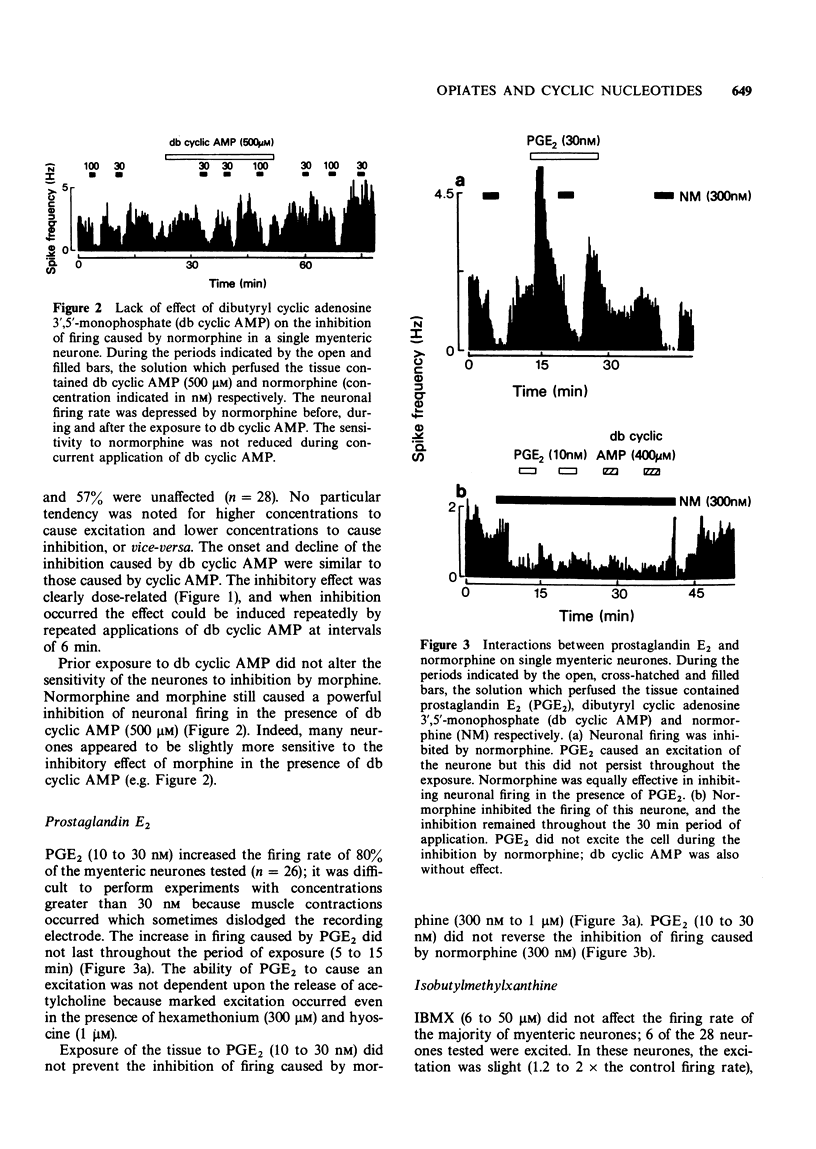
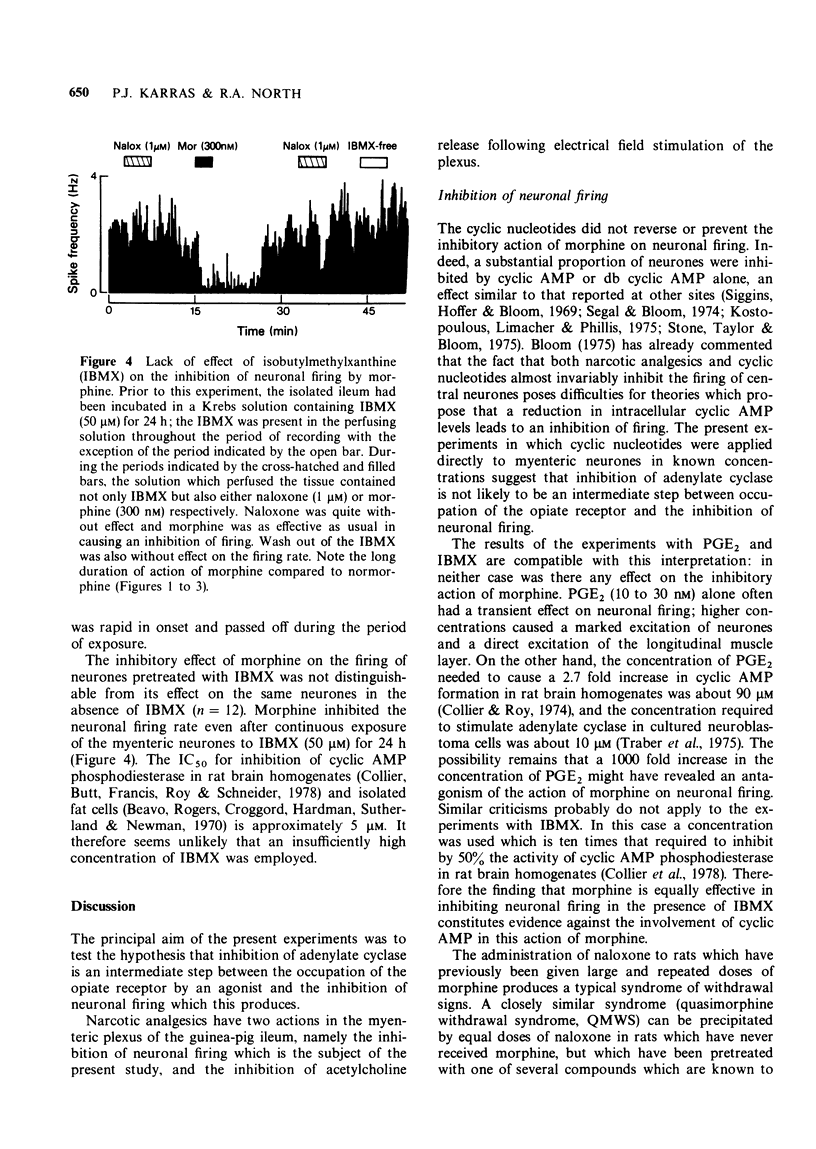
1. Extracellular recordings were made in vitro from single neurones of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. 2. Neuronal firing was inhibited by morphine and normorphine (10 nM to 1 micrometer). Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cyclic AMP) (100 micrometer to 1 mM) also inhibited the firing of the majority of the neurones. Prostaglandin E2 usually caused a short-lasting excitation of myenteric neurones and the phosphodiesterase inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine was usually without effect on firing rate. 3. The inhibition of neuronal firing by normorphine was unaffected by prior and/or concurrent administration of cyclic AMP, dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, prostaglandin E2 or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine. As these four treatments might be expected to elevate intracellular levels of cyclic AMP, the results lend no support to the notion that a reduction in intracellular cyclic AMP is essential to the inhibition of firing produced by morphine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Rogers N. L., Crofford O. B., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Newman E. V. Effects of xanthine derivatives on lipolysis and on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;6(6):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Francis D. L., McDonald-Gibson W. J., Roy A. C., Saeed S. A. Prostaglandins, cyclic AMP and the mechanism of opiate dependence. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 1;17(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90242-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Francis D. L., Roy A. C. Opiates, cyclic nucleotides, and xanthines. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1976;15:337–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Roy A. C. Morphine-like drugs inhibit the stimulation of E prostaglandins of cyclic AMP formation by rat brain homogenate. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):24–27. doi: 10.1038/248024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Snyder S. H. Receptor binding and pharmacological activity of opiates in the guinea-pig intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Jul;194(1):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Goldstein A. Effect of synaptic transmission blockade on morphine action in the guinea-pig myenteric plexus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jan;196(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Goldstein A., Kendig J. Effects of narcotic opiates and serotonin on the electrical behavior of neurons in the guinea pig myenteric plexus. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 1;14(11):2299–2309. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Goldstein A. Single neuron studies of opiate action in the guinea pig myenteric plexus. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 1;17(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenpreis S., Greenberg J., Belman S. Prostaglandins reverse inhibition of electrically-induced contractions of guinea pig ileum by morphine, indomethacin and acetylsalicylic acid. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 31;245(148):280–282. doi: 10.1038/newbio245280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenpreis S., Sato T., Takayanagi I., Comaty J. E., Takagi K. Mechanism of morphine block of electrical activity in ganglia of Auerbach's plexus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;40(2):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri S., Santagostino A., Braga P. C., Galatulas I. Decreased antinociceptive effect of morphine in rats treated intraventricularly with prostaglandin E1. Psychopharmacologia. 1974;39(3):231–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00421030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. L., Roy A. C., Collier H. O. Morphone abstinence and quasi-abstinence effects after phosphodiesterase inhibitors and naloxone. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1901–1906. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R., Musacchio J. M. Interactions of morphine, adenosine, adenosine triphosphate and phosphodiesterase inhibitors on the field-stimulated guinea-pig ileum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Sep;194(3):575–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi E., Mori M., Yamada S., Kumitomo M. Effects of purine compounds on cholinergic nerves. Specificity of adenosine and related compounds on acetylcholine release in electircally stimulated guinea pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Apr 1;48(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. K., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate antagonism of morphine analgesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 May;185(2):336–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Waterfield A. A. In vitro models in the study of structure-activity relationships of narcotic analgesics. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:29–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Kinetic parameters of narcotic agonists and antagonists, with particular reference to N-allylnoroxymorphone (naloxone). Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):266–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostopoulos G. K., Limacher J. J., Phillis J. W. Action of various adenine derivatives on cerebellar Purkinje cells. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 25;88(1):162–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90966-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Karras P. J. Opiate tolerance and dependence induced in vitro in single myenteric neurones. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):73–75. doi: 10.1038/272073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tonini M. The mechanism of action of narcotic analgesics in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T. Extracellular recording from the guinea-pig myenteric plexus and the action of morphine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep 1;45(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Zieglgänsberger W. Opiate withdrawal signs in single myenteric neurones. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 7;144(1):208–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Takayanagi I., Takagi K. Effects of acetylcholine releasing drugs on electrical activities obtained from Auerbach's plexus in the guinea pig ileum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;24(3):447–451. doi: 10.1254/jjp.24.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Takayanagi I., Takagi K. Pharmacological properties of electrical activities obtained from neurons in Auerbach's plexus. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1973 Oct;23(5):665–671. doi: 10.1254/jjp.23.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Jhamandas K. H. Inhibition of acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerves by adenosine, adenine nucleotides and morphine: antagonism by theophylline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 May;197(2):379–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Cartwright C. Sensitization of the smooth muscle by prostaglandin E1 contributes to reversal of drug-induced inhibition of the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;294(3):257–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00508393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Bloom F. E. The action of norepinephrine in the rat hippocampus. I. Iontophoretic studies. Brain Res. 1974 May 31;72(1):79–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90652-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. Dual regulation of adenylate cyclase accounts for narcotic dependence and tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. Opiate-dependent modulation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggins G. R., Hoffer B. J., Bloom F. E. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate: possible mediator for norepinephrine effects on cerebellar Purkinje cells. Science. 1969 Sep 5;165(3897):1018–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3897.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Taylor D. A., Bloom F. E. Cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP may mediate opposite neuronal responses in the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):845–847. doi: 10.1126/science.163488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi K., Takayanagi I. Effect of N 6 , 2'-O-dibutyryl 3'5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate, 3', 5',-cyclic adenosine monophosphate and adenosine triphosphate on acetylcholine output from cholinergic nerves in guinea pig ileum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;22(1):33–36. doi: 10.1254/jjp.22.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber J., Fischer K., Latzin S., Hamprecht B. Morphine antagonises action of prostaglandin in neuroblastoma and neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cells. Nature. 1975 Jan 10;253(5487):120–122. doi: 10.1038/253120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkening D., Mishra R. K., Makman M. H. Effects of morphine on dopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase and on cyclic GMP formation in primate brain amygdaloid nucleus. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1129–1137. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


