Abstract
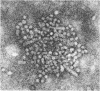
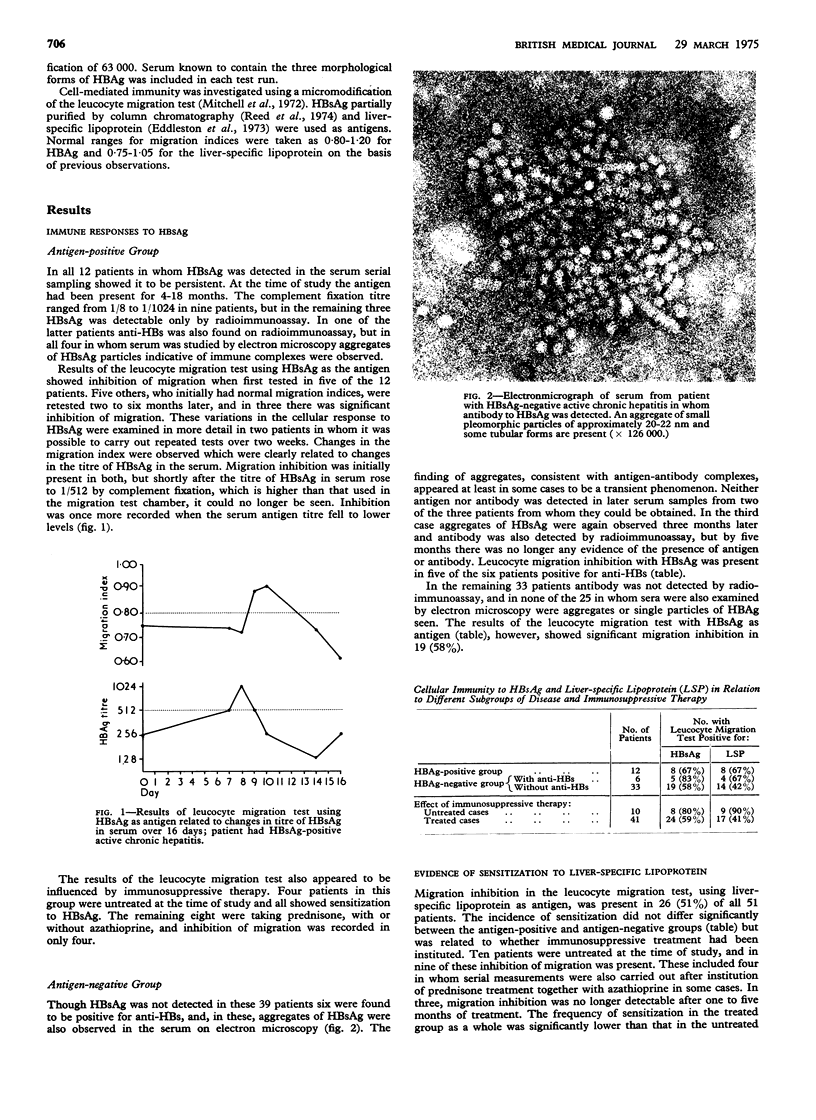
The hepatitis-B surface antigen (HBsAG) may be persistently present in the serum in a few cases of active chronic hepatitis but the cause of the disease in most patients is unknown. In a study of 39 HBsAg-negative cases cell-mediated immunity to HBsAg was observed in 24 (62%), suggesting a high frequency of previous infection with the hepatitis-B virus. Hepatitis-B surface antibody was detectable by radioimmunoassay in six patients, in all of whom complexes of HBsAg were present in the serum on electron microscopy. Out of 12 patients with HBsAg-positive active chronic hepatitis who were also studied eight, including all those untreated at the time, showed a cellular response to the antigen. Evidence of sensitization to a liver-specific cell surface lipoprotein was found with similar frequency in the two groups. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that hepatitis-B virus infection is important in initiating the disease in many cases of active chronic hepatitis and that sensitization to the liver cell membrane antigen is the autoimmune process responsible for the perpetuation of the liver injury.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Fox R. A., Sherlock S. Cellular immunity and hepatitis-associated, Australia antigen liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Apr 1;1(7753):723–726. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Inadequate antibody response to hBAg or suppressor T-cell defect in development of active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Smith M. G., Mitchell C. G., Reed W. D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Cell-mediated immunity to a human liver-specific antigen in patients with active chronic hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1972 Aug 12;2(7772):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92904-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. G., Smith M. G., Golding P. L., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Evaluation of the leucocyte migration test as a measure of delayed hypersensitivty in man. Suppression of migration inhibition by puromycin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Aug;11(4):535–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. D., Mitchell C. G., Eddleston A. L., Lee W. M., Williams R., Zuckerman A. J. Exposure and immunity to hepatitis-B virus in a liver unit. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):581–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92646-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. D., Stern R. B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R., Zuckerman A. J., Bowes A., Earl P. M. Detection of hepatitis-B antigen by radioimmunoassay in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in Great Britain. Lancet. 1973 Sep 29;2(7831):690–694. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]