Abstract
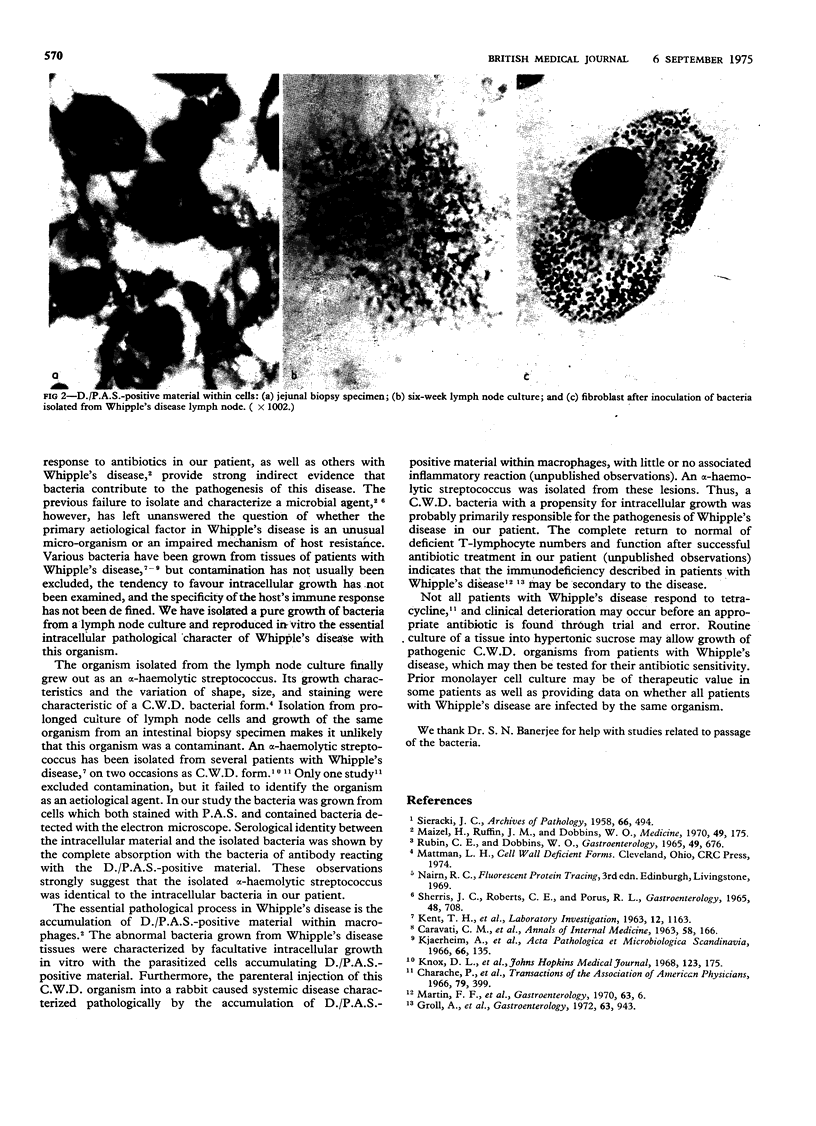
A cell wall deficient form of an alpha-haemolytic streptococcus was grown from a prolonged monolayer cell culture of a lymph node taken from a patient with Whipple's disease. Serological cross reactivity was shown between the organism and the material within Whipple's disease macrophages positive for diastase-resistant periodic acid-Schiff (D./P.A.S.). In vitro studies characterized the organism as a facultative intracellular parasite which caused the accumulation within cells of D./P.A.S.-positive material. These results suggest that a pathogenic bacterium is the essential aetiological agent and that the culture of Whipple's disease tissues in hypertonic media may have practical value.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARAVATI C. M., LITCH M., WEISIGER B. B., RAGLAND S., BERLINER H. Diagnosis of Whipple's disease by rectal biopsy with a report of three additional cases. Ann Intern Med. 1963 Jan;58:166–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-58-1-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charache P., Bayless T. M., Shelley W. M., Hendrix T. R. Atypical bacteria in Whipple's disease. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1966;79:399–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groll A., Valberg L. S., Simon J. B., Eidinger D., Wilson B., Forsdyke D. R. Immunological defect in Whipple's disease. Gastroenterology. 1972 Dec;63(6):943–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT T. H., LAYTON J. M., CLIFTON J. A., SCHEDL H. P. WHIPPLE'S DISEASE: LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES COMBINED WITH CLINICAL STUDIES SUGGESTING AN INFECTIVE NATURE. Lab Invest. 1963 Dec;12:1163–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaerheim A., Midtvedt T., Skrede S., Gjone E. Bacteria in Whipple's disease. Isolation of a Haemophilus strain from the jejunal propria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(1):135–142. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox D. I., Bayless T. M., Yardley J. H., Charache P. Whipple's disease presenting with ocular inflammation and minimal intestinal symptoms. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1968 Oct;123(4):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel H., Ruffin J. M., Dobbins W. O., 3rd Whipple's disease: a review of 19 patients from one hospital and a review of the literature since 1950. Medicine (Baltimore) 1970 May;49(3):175–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. F., Vilseck J., Dobbins W. O., 3rd, Buckley C. E., 3rd, Tyor M. P. Immunological alterations in patients with treated Whipple's disease. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jul;63(1):6–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. E., Dobbins W. O., 3rd Peroral biopsy of the small intestine. A review of its diagnostic usefulness. Gastroenterology. 1965 Dec;49(6):676–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRIS J. C., ROBERTS C. E., PORUS R. L. MICROBIOLOGICAL STUDIES OF INTESTINAL BIOPSIES TAKEN DURING ACTIVE WHIPPLE'S DISEASE. Gastroenterology. 1965 Jun;48:708–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]