Abstract
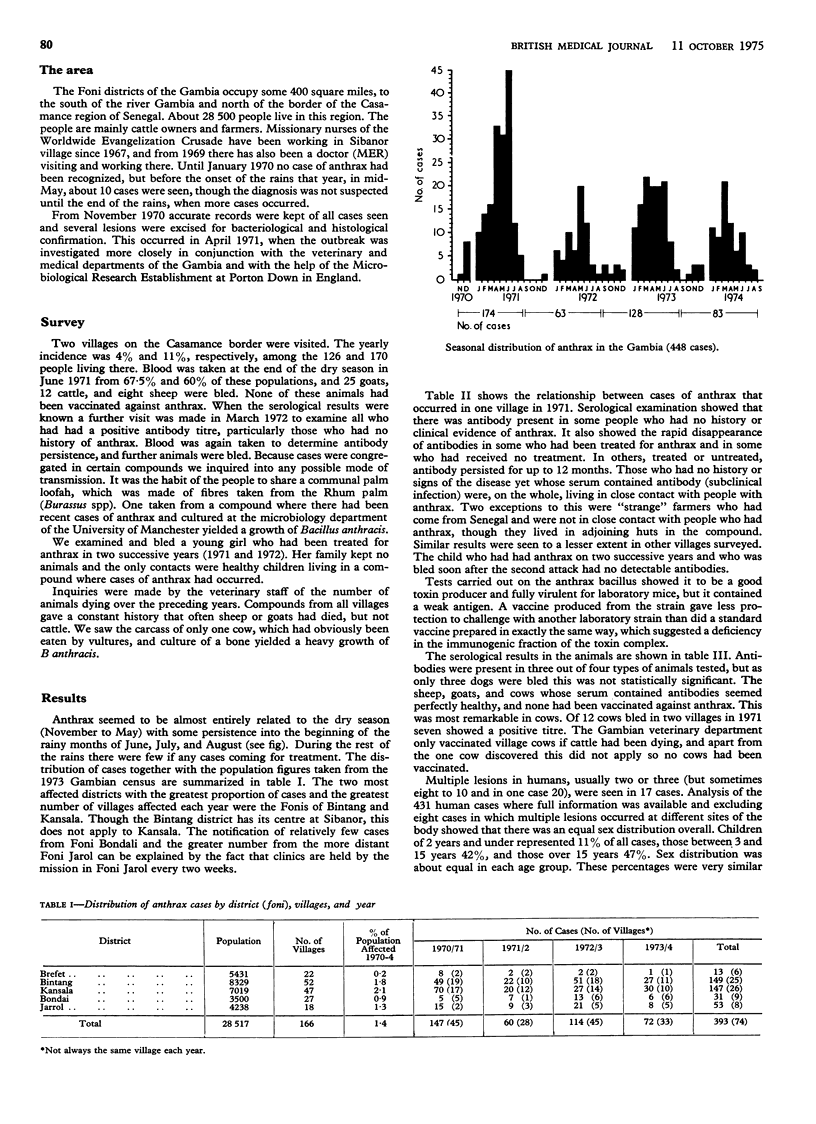
Epidemiological data on 448 cases of human cutaneous anthrax from the Gambia showed that this particular strain of anthrax bacillus causes widespread morbidity and some mortality with, at the same time, subclinical infection. Analysis also showed that anthrax is not an occupationally related disease in the Gambia.
The possibility of human-to-human spread, affecting all age groups and both sexes, by means of a communal toilet article was also shown. The fact that the strain is a good toxin producer but contains a weak antigen may have accounted for the repeated clinical infection and the fact that antibody titres were generally transient. Subclinical infection in animals was also found, particularly in sheep and goats, and also, with an unusually low mortality, in cows. Insect vectors were not excluded, but were unlikely. Vultures may spread the disease from village to village. Some possible public health and immunization procedures are discussed, with a view to containing this difficult problem in this part of west Africa.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELTON F. C., DARLOW H. M., HENDERSON D. W. The use of anthrax antigen to immunise man and monkey. Lancet. 1956 Sep 8;271(6941):476–479. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91968-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENDALL N. R., GROUNDS J. G. THE INCIDENCE AND EPIDEMIOLOGY OF DISEASE IN KENYA. I. SOME DISEASES OF SOCIAL SIGNIFICANCE. J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 Apr;68:77–CONTD. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHOUT E., SEHAT A., ASHRAF M. ANTHRAX: A CONTINOUS PROBLEM IN SOUTHWEST IRAN. Am J Med Sci. 1964 May;247:565–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor I. A., Rahman A. K., Thomson A. M., Billewicz W. Z., Thompson B. The health of young children in a West African (Gambian) village. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1970;64(1):48–77. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(70)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN P. S., RAY J. G., Jr, BRACHMAN P. S., PLOTKIN S. A., PAGANO J. S. Serologic testing for anthrax antibodies in workers in a goat hair processing mill. Am J Hyg. 1960 Jul;72:32–37. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


