Abstract
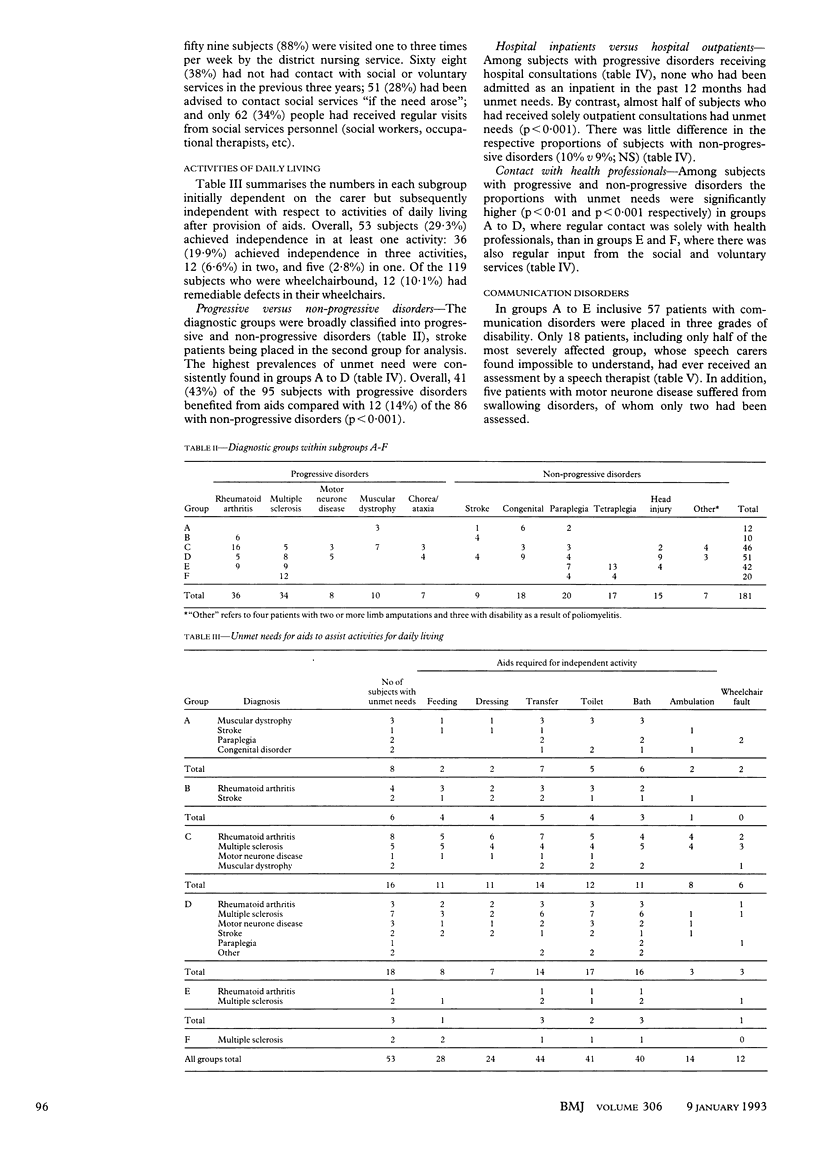
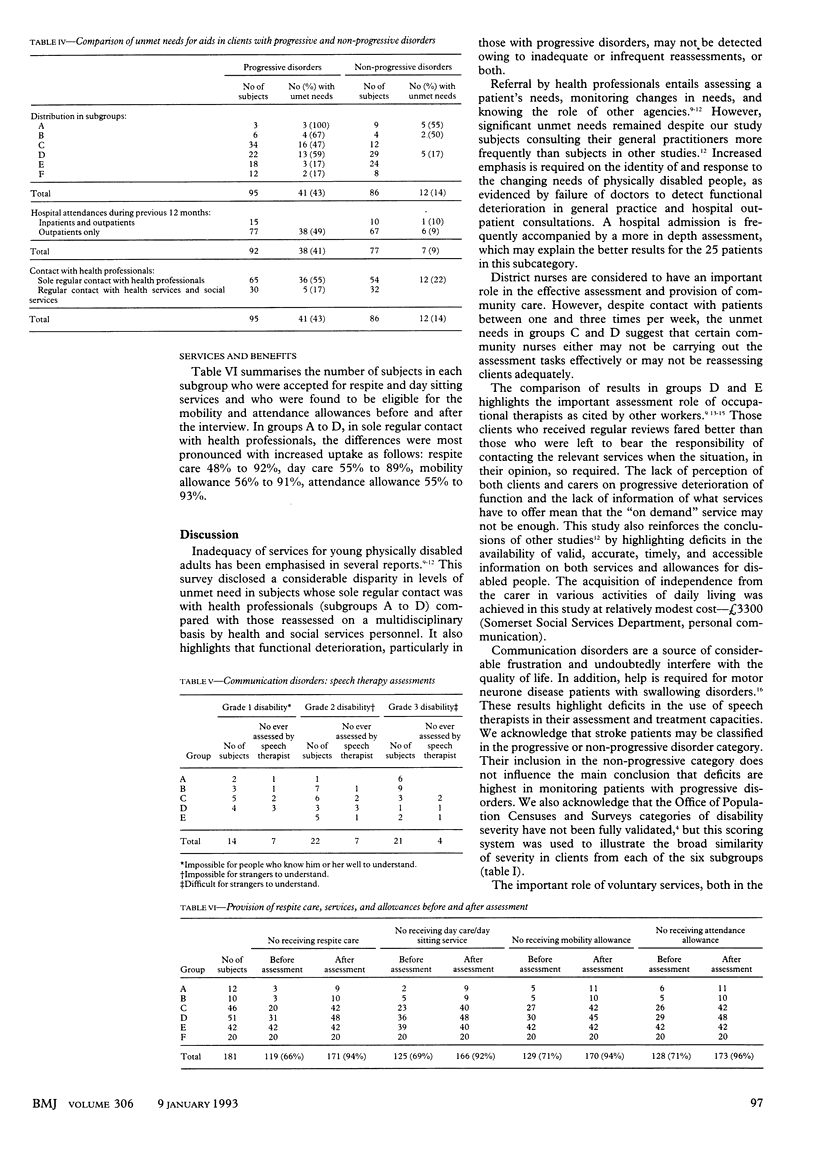
OBJECTIVE--To identify unmet needs in the care of severely disabled people aged 16-64. DESIGN--Detailed personal interview and physical assessment of physically disabled adults; personal or telephone interview with carers. SETTING--Somerset Health District. SUBJECTS--181 severely disabled adults and their carers. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Independence in activities of daily living; identity of requirements for assessing communication disorders; appropriate provision of services and allowances. RESULTS--53 (29.3%) of the 181 disabled subjects had unmet needs for aids to allow independence in activities of daily living-namely, 43% of subjects (41/95) with progressive disorders and 14% of subjects (12/86) with non-progressive disorders. The prevalence of unmet need was higher among subjects whose sole regular professional contact was with health services personnel (48 (40.3%) of 119 subjects). Only 18 (31.6%) of the 57 subjects with communication disorders had ever been assessed by a speech therapist. CONCLUSIONS--This study shows that the needs of severely physically disabled adults in the community--especially those with progressive disorders--are being monitored inadequately by health professionals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchan H., Gray M., Hill A., Coulter A. Needs assessment made simple. Health Serv J. 1990 Feb 15;100(5188):240–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. J., Enderby P. Management of motor neurone disease. J Neurol Sci. 1984 Apr;64(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(84)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick D. L., Peach H., Gregg I. Disablement and care: a comparison of patient views and general practitioner knowledge. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1982 Jul;32(240):429–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


