Abstract
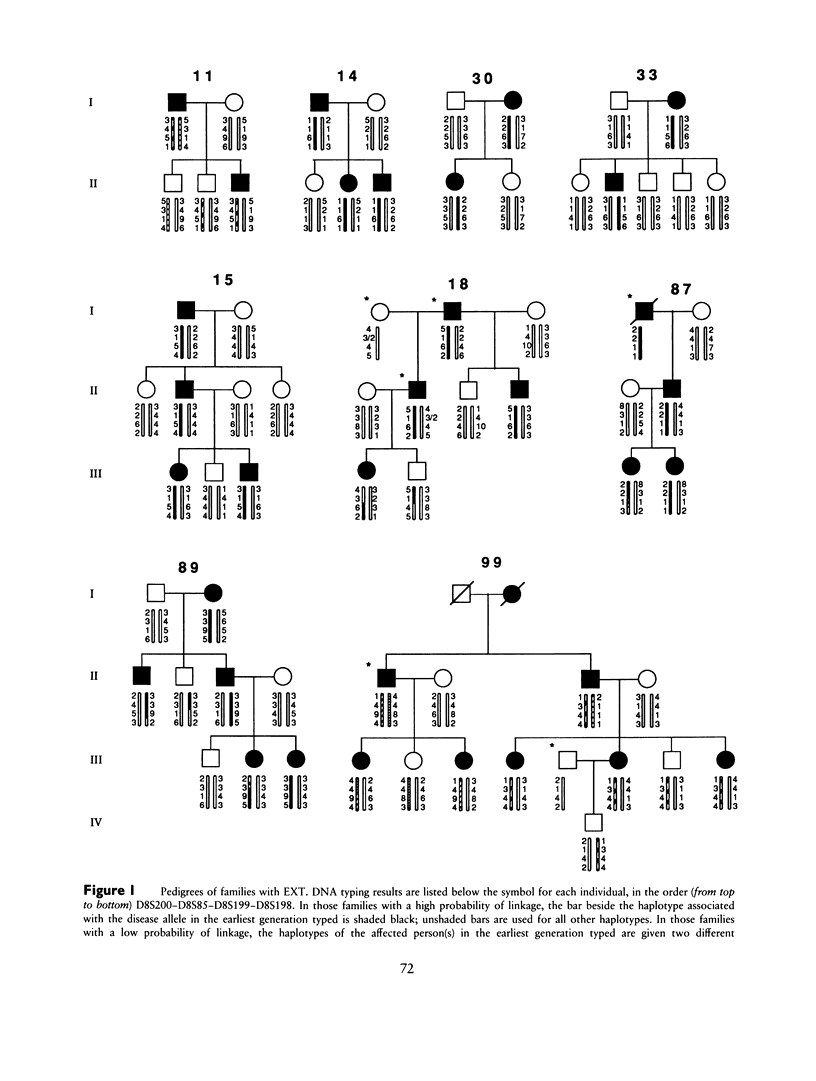
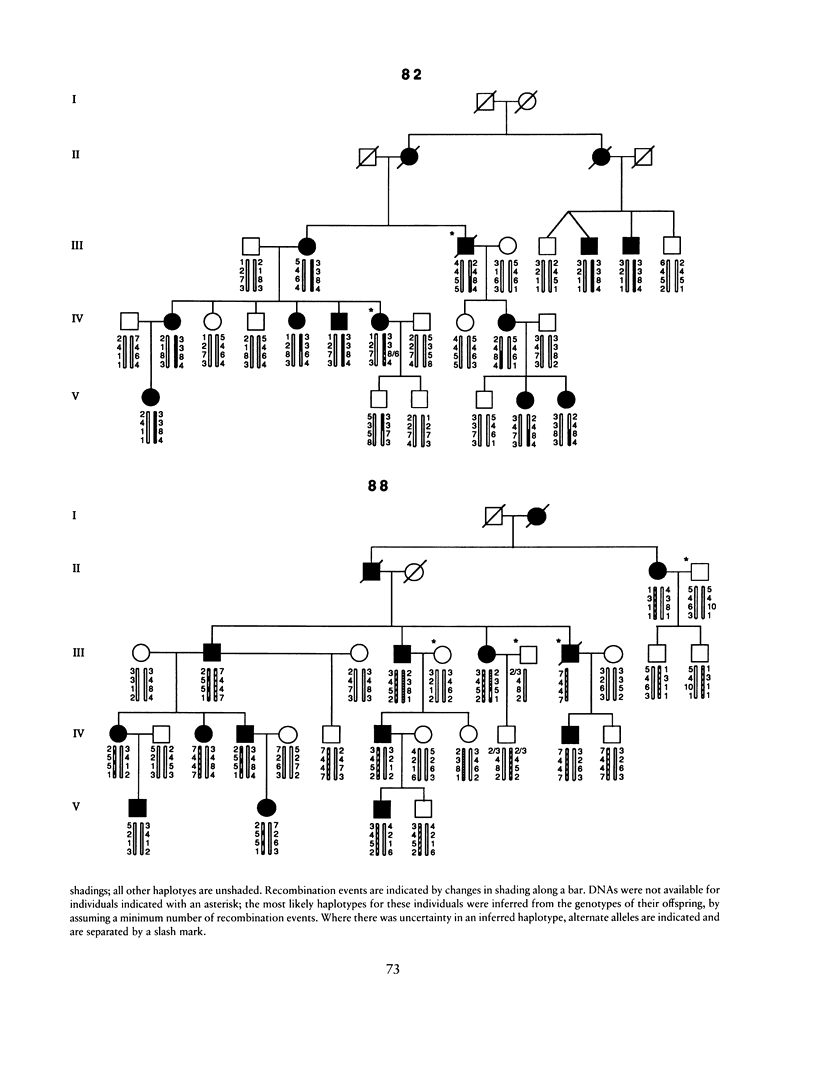
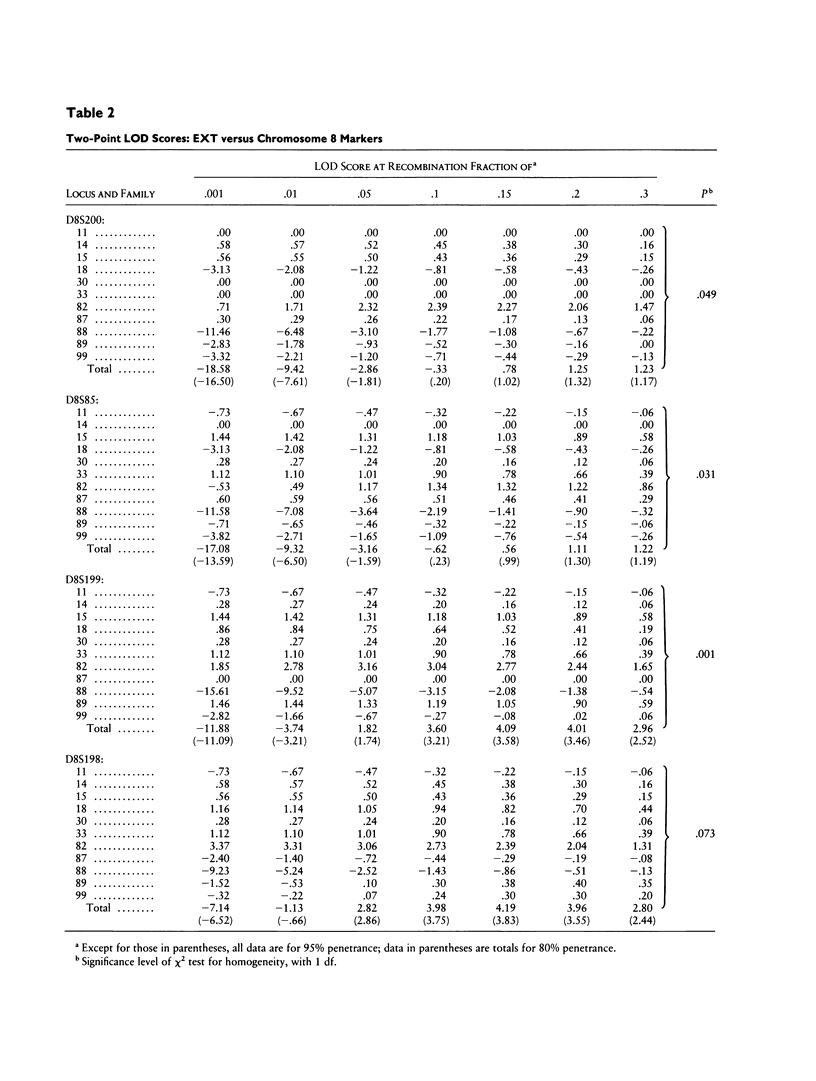
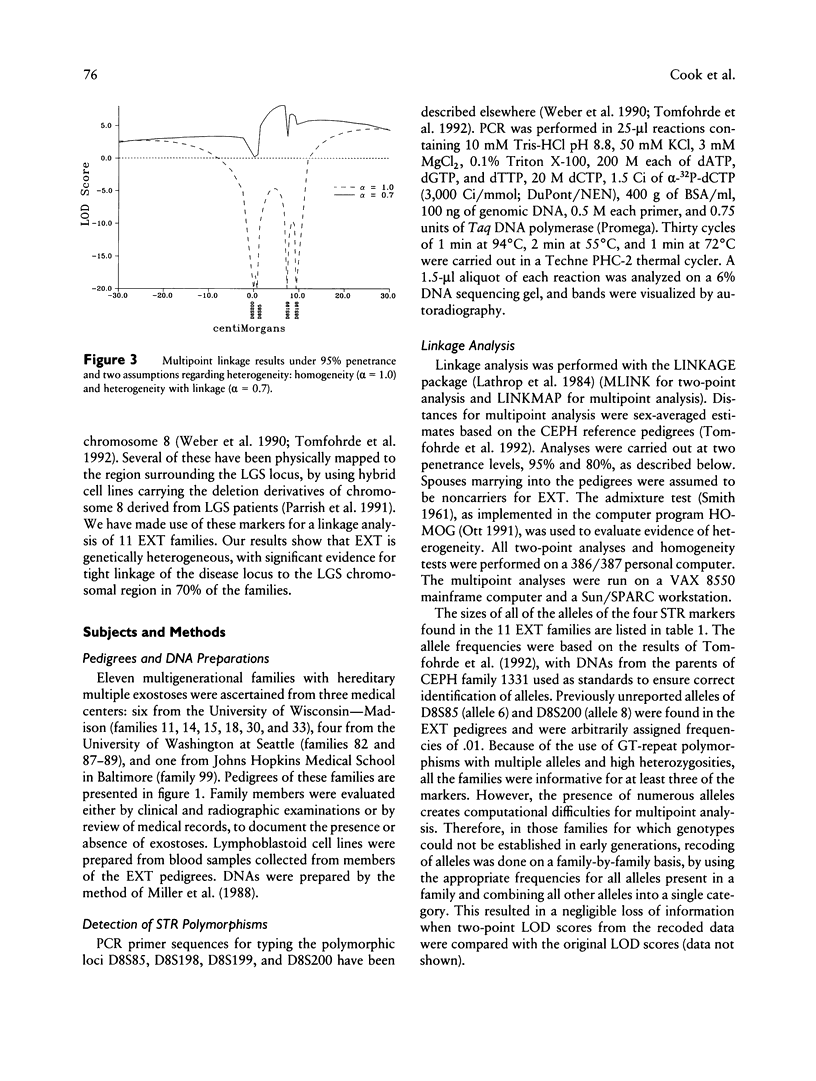
We have carried out a linkage analysis on 11 families segregating gene(s) for hereditary multiple exostoses (EXT). Four highly informative, short tandem-repeat (STR) markers that have been physically mapped to an interval surrounding the Langer-Giedion chromosomal region (8q24.11-q24.13) were used in a multipoint linkage analysis. Significant evidence for linkage of EXT with genetic heterogeneity was found. A model of heterogeneity with linkage of the disease gene to the STR markers in 70% of the families (with a 95% confidence interval of 26%–96%) produced a maximum LOD score of 8.11, with the most likely position of EXT between D8S85 and D8S199. Thus there are at least two genes that are capable of causing hereditary multiple exostoses, one in the Langer-Giedion region and one at another, unlinked location.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bühler E. M., Malik N. J. The tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome(s): chromosome 8 long arm deletion: is there a shortest region of overlap between reported cases? TRP I and TRP II syndromes: are they separate entities? Am J Med Genet. 1984 Sep;19(1):113–119. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Van den Berghe H. 8q24.12 Interstitial deletion in trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type I. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):188–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00282091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennekam R. C. Hereditary multiple exostoses. J Med Genet. 1991 Apr;28(4):262–266. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.4.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROOTH R. S., MACKLIN M. T., HILBISH T. F. Diaphysial aclasis (multiple exostoses) on Guam. Am J Hum Genet. 1961 Sep;13:340–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Merrer M., Ben Othmane K., Stanescu V., Lyonnet S., Van Maldergem L., Royer G., Munnich A., Maroteaux P. The gene for hereditary multiple exostoses does not map to the Langer-Giedion region (8q23-q24). J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):713–715. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone N. C., Shupe J. L., Gardner E. J., Millar E. A., Olson A. E., Phillips E. C. Hereditary multiple exostosis. A comparative human-equine-epidemiologic study. J Hered. 1987 May-Jun;78(3):171–177. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle R. F., Dalzell P., Turner G., Wass D., Yip M. Y. Multiple exostoses in a patient with t(8;11)(q24.11;p15.5). J Med Genet. 1991 Dec;28(12):881–883. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.12.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish J. E., Wagner M. J., Hecht J. T., Scott C. I., Jr, Wells D. E. Molecular analysis of overlapping chromosomal deletions in patients with Langer-Giedion syndrome. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):54–61. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90101-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON L. HEREDITARY MULTIPLE EXOSTOSIS. Am J Hum Genet. 1964 Sep;16:351–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura Y., Sugiura I., Iwata H. Hereditary multiple exostosis: diaphyseal aclasis. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1976 Dec;21(3):149–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomfohrde J., Wood S., Schertzer M., Wagner M. J., Wells D. E., Parrish J., Sadler L. A., Blanton S. H., Daiger S. P., Wang Z. Human chromosome 8 linkage map based on short tandem repeat polymorphisms: effect of genotyping errors. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):144–152. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutsinas S., Wynne-Davies R. The infrequency of malignant disease in diaphyseal aclasis and neurofibromatosis. J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;20(5):345–349. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.5.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Patterson D., Drabkin H. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the D8S85, D8S87, and D8S88 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4038–4038. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


