Abstract
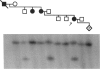
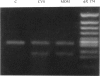
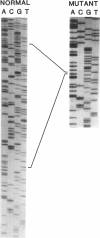
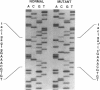
The Marfan syndrome, an autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder, is manifested by abnormalities in the cardiovascular, skeletal, and ocular systems. Recently, fibrillin, an elastin-associated microfibrillar glycoprotein, has been linked to the Marfan syndrome, and fibrillin mutations in affected individuals have been documented. In this study, genetic linkage analysis with fibrillin specific markers was used to establish the prenatal diagnosis in an 11-wk-gestation fetus in a four-generation Marfan kindred. At birth, skeletal changes suggestive of the Marfan syndrome were observed. Reverse transcription–PCR amplification of the fibrillin gene mRNA detected a deletion of 123 bp in one allele in affected relatives. This deletion corresponds to an exon encoding an epidermal growth factor–like motif. Examination of genomic DNA showed a G→C transversion at the +1 consensus donor splice site.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arpaia E., Dumbrille-Ross A., Maler T., Neote K., Tropak M., Troxel C., Stirling J. L., Pitts J. S., Bapat B., Lamhonwah A. M. Identification of an altered splice site in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs disease. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):85–86. doi: 10.1038/333085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh G. F., Wong C., Reed R., Antonarakis S. E., Zhu D., Ghosh P. K., Maniatis T., Forget B. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr A new mutation in IVS-1 of the human beta globin gene causing beta thalassemia due to abnormal splicing. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonadio J., Ramirez F., Barr M. An intron mutation in the human alpha 1(I) collagen gene alters the efficiency of pre-mRNA splicing and is associated with osteogenesis imperfecta type II. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2262–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botkin J. R., Alemagno S. Carrier screening for cystic fibrosis: a pilot study of the attitudes of pregnant women. Am J Public Health. 1992 May;82(5):723–725. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.5.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges A. B., Faed M., Boxer M., Gray J. R., Bundy C., Murray A. Marfan syndrome in a large family: response of family members to a screening programme. J Med Genet. 1992 Feb;29(2):81–85. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.2.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chimienti G., Capurso A., Resta F., Pepe G. A G----C change at the donor splice site of intron 1 causes lipoprotein lipase deficiency in a southern-Italian family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):620–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91240-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole W. G., Chiodo A. A., Lamande S. R., Janeczko R., Ramirez F., Dahl H. H., Chan D., Bateman J. F. A base substitution at a splice site in the COL3A1 gene causes exon skipping and generates abnormal type III procollagen in a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17070–17077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decruyenaere M., Evers-Kiebooms G., Denayer L., Van den Berghe H. Cystic fibrosis: community knowledge and attitudes towards carrier screening and prenatal diagnosis. Clin Genet. 1992 Apr;41(4):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denayer L., Evers-Kiebooms G., De Boeck K., Van den Berghe H. Reproductive decision making of aunts and uncles of a child with cystic fibrosis: genetic risk perception and attitudes toward carrier identification and prenatal diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Sep 1;44(1):104–111. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Cutting G. R., Pyeritz R. E., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Corson G. M., Puffenberger E. G., Hamosh A., Nanthakumar E. J., Curristin S. M. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):337–339. doi: 10.1038/352337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Pyeritz R. E., Puffenberger E. G., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Corson G. M., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Francomano C. A., Cutting G. R. Marfan phenotype variability in a family segregating a missense mutation in the epidermal growth factor-like motif of the fibrillin gene. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1674–1680. doi: 10.1172/JCI115766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Saraiva J. M., Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R., Francomano C. A. Clustering of fibrillin (FBN1) missense mutations in Marfan syndrome patients at cysteine residues in EGF-like domains. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(5):366–374. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Valle D., Francomano C. A., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):680–683. doi: 10.1126/science.8430317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., Drugan A., Koppitch F. C., 3rd, Zador I. E., Sacks A. J., Sokol R. J. Genetic diagnosis in the first trimester: the norm for the 1990s. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Jun;160(6):1332–1339. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90852-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo S. S., Beisiegel U., Beil U., Higuchi K., Bojanovski M., Gregg R. E., Greten H., Brewer H. B., Jr Donor splice site mutation in the apolipoprotein (Apo) C-II gene (Apo C-IIHamburg) of a patient with Apo C-II deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1489–1494. doi: 10.1172/JCI113756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Menashe V., Weleber R. G., Koler R. D., Bigley R. H., Lovrien E., Zonana J., Hollister D. W. Cosegregation of elastin-associated microfibrillar abnormalities with the Marfan phenotype in families. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):652–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Redondo J. M., Stoming T. A., Kutlar F., Kutlar A., McKie V. C., McKie K. M., Huisman T. H. Severe Hb S-beta zero-thalassaemia with a T----C substitution in the donor splice site of the first intron of the beta-globin gene. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jan;71(1):113–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb06283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoda T., Yamada N., Kawamura M., Kozaki K., Mori N., Ishibashi S., Shimano H., Takaku F., Yazaki Y., Furuichi Y. Heterogeneous mutations in the human lipoprotein lipase gene in patients with familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1856–1864. doi: 10.1172/JCI115507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoda T., Yamada N., Murase T., Inaba T., Ishibashi S., Shimano H., Koga S., Yazaki Y., Furuichi Y., Takaku F. Occurrence of multiple aberrantly spliced mRNAs upon a donor splice site mutation that causes familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24757–24762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Godfrey M., Sakai L. Y., Pyeritz R. E. Immunohistologic abnormalities of the microfibrillar-fiber system in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):152–159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M., Gallinaro H. The 5' splice site: phylogenetic evolution and variable geometry of association with U1RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2159–2180. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Sakai L. Y., Child A., Pope F. M., Puhakka L., Ryhänen L., Palotie A., Kaitila I., Peltonen L. Two mutations in Marfan syndrome resulting in truncated fibrillin polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5917–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberg M., Factor S., Cho S., Herskowitz A., Nitowsky H., Morecki R. Fetal Marfan syndrome: prenatal ultrasound diagnosis with pathological confirmation of skeletal and aortic lesions. Prenat Diagn. 1981 Oct;1(4):241–247. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970010403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuivaniemi H., Kontusaari S., Tromp G., Zhao M. J., Sabol C., Prockop D. J. Identical G+1 to A mutations in three different introns of the type III procollagen gene (COL3A1) produce different patterns of RNA splicing in three variants of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. IV. An explanation for exon skipping some mutations and not others. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):12067–12074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landels E. C., Green P. M., Ellis I. H., Fensom A. H., Bobrow M. Beta-hexosaminidase splice site mutation has a high frequency among non-Jewish Tay-Sachs disease carriers from the British Isles. J Med Genet. 1992 Aug;29(8):563–567. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.8.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Godfrey M., Vitale E., Hori H., Mattei M. G., Sarfarazi M., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F., Hollister D. W. Linkage of Marfan syndrome and a phenotypically related disorder to two different fibrillin genes. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):330–334. doi: 10.1038/352330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Vitale E., Superti-Furga A., Steinmann B., Ramirez F. G to T transversion at position +5 of a splice donor site causes skipping of the preceding exon in the type III procollagen transcripts of a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5256–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddalena A., Bick D. P., Schulman J. D. Molecular diagnosis of genetic disease. J Reprod Med. 1992 May;37(5):437–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. R., Schwartz R. H. Attitudes toward genetic testing of Amish, Mennonite, and Hutterite families with cystic fibrosis. Am J Public Health. 1992 Feb;82(2):236–242. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.2.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mononen I., Heisterkamp N., Kaartinen V., Mononen T., Williams J. C., Groffen J. Aspartylglycosaminuria in a non-Finnish patient caused by a donor splice mutation in the glycoasparaginase gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3196–3199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope F. M., Nicholls A. C., Palan A., Kwee M. L., De Groot W. P., Hausmann R. Clinical features of an affected father and daughter with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIB. Br J Dermatol. 1992 Jan;126(1):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb08409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton V. R., Kienzle B. K., Knowles R. W. An altered splice site is found in the DRB4 gene that is not expressed in HLA-DR7,Dw11 individuals. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(5):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00352841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Del Mastro R., Sarfarazi M., Lee B., Vitale E., Child A. H., Godfrey M., Devereux R. B., Hewett D., Steinmann B. Genetic linkage of the Marfan syndrome, ectopia lentis, and congenital contractural arachnodactyly to the fibrillin genes on chromosomes 15 and 5. The International Marfan Syndrome Collaborative Study. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 2;326(14):905–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204023261401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasan N. S., Kuivaniemi H., Vogel B. E., Minor R. R., Wootton J. A., Tromp G., Weksberg R., Prockop D. J. A mutation in the pro alpha 2(I) gene (COL1A2) for type I procollagen in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII: evidence suggesting that skipping of exon 6 in RNA splicing may be a common cause of the phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Feb;48(2):305–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. K., Marchant J., Bush A., Williamson B. Attitudes towards prenatal diagnosis and carrier screening for cystic fibrosis among the parents of patients in a paediatric cystic fibrosis clinic. J Med Genet. 1992 Jul;29(7):490–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Bernard M., Combates N., Wirtz M. K., Hollister D. W., Steinmann B., Ramirez F. Identification of a mutation that causes exon skipping during collagen pre-mRNA splicing in an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome variant. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8561–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., D'Alessio M., Ramirez F., Eyre D. R. Structural and functional characterization of a splicing mutation in the pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene of an Ehlers-Danlos type VII patient. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):16007–16011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz D. C., Janes S. R., Rosenfield J. M., Erbe R. W. Attitudes toward the prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: factors in decision making among affected families. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):1077–1085. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer M., Bolscher B. G., Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Smith C. I., Ahlin A., Weening R. S., Roos D. Splice site mutations are a common cause of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1992 Sep 15;80(6):1553–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]