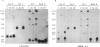Abstract
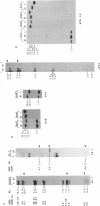
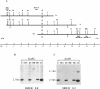
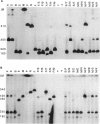
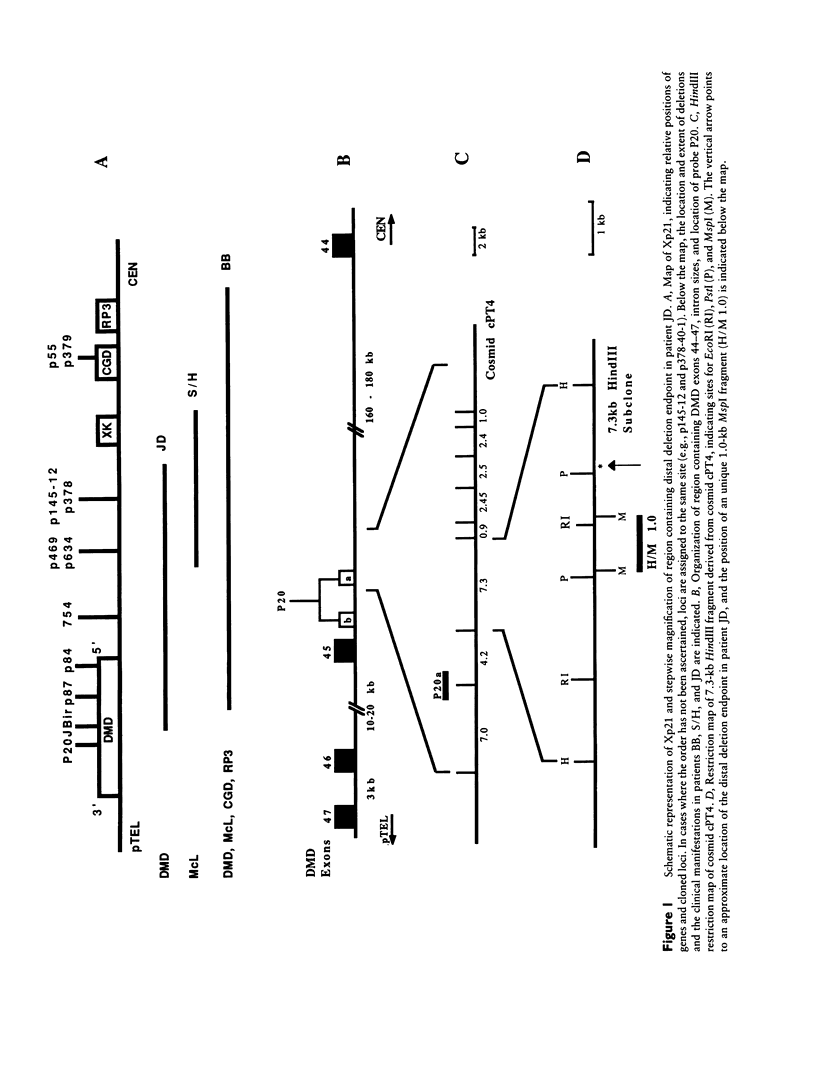
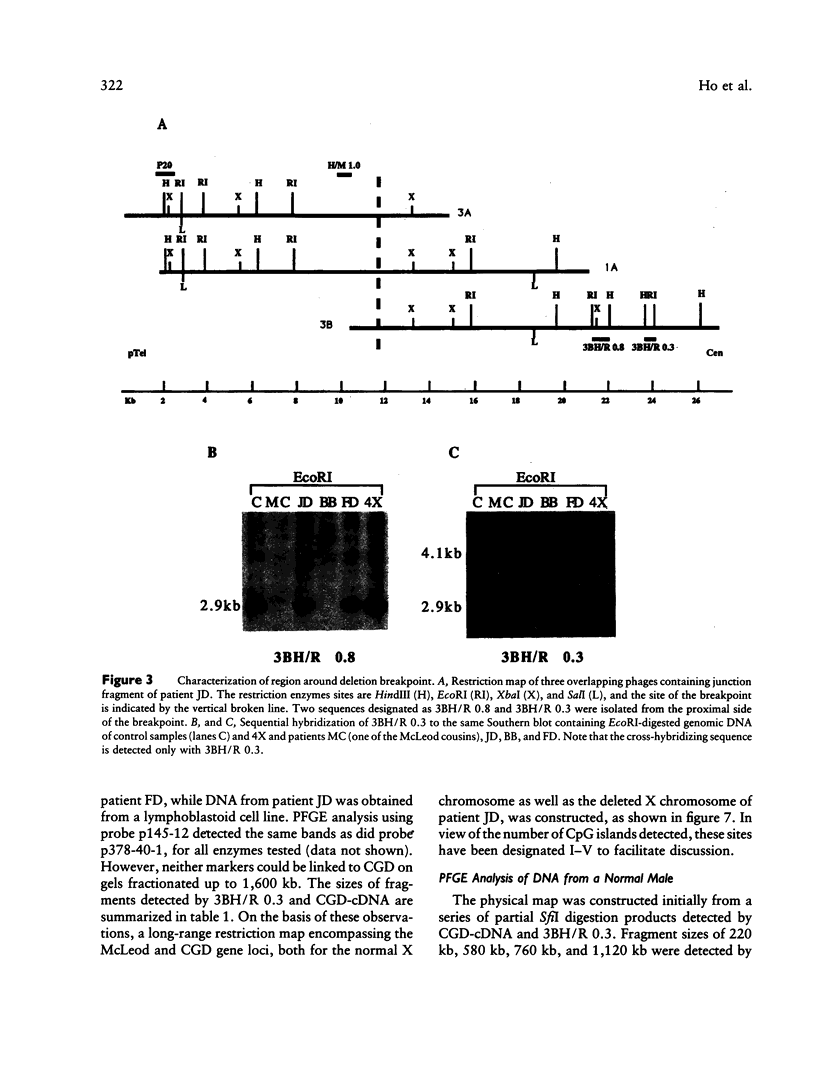
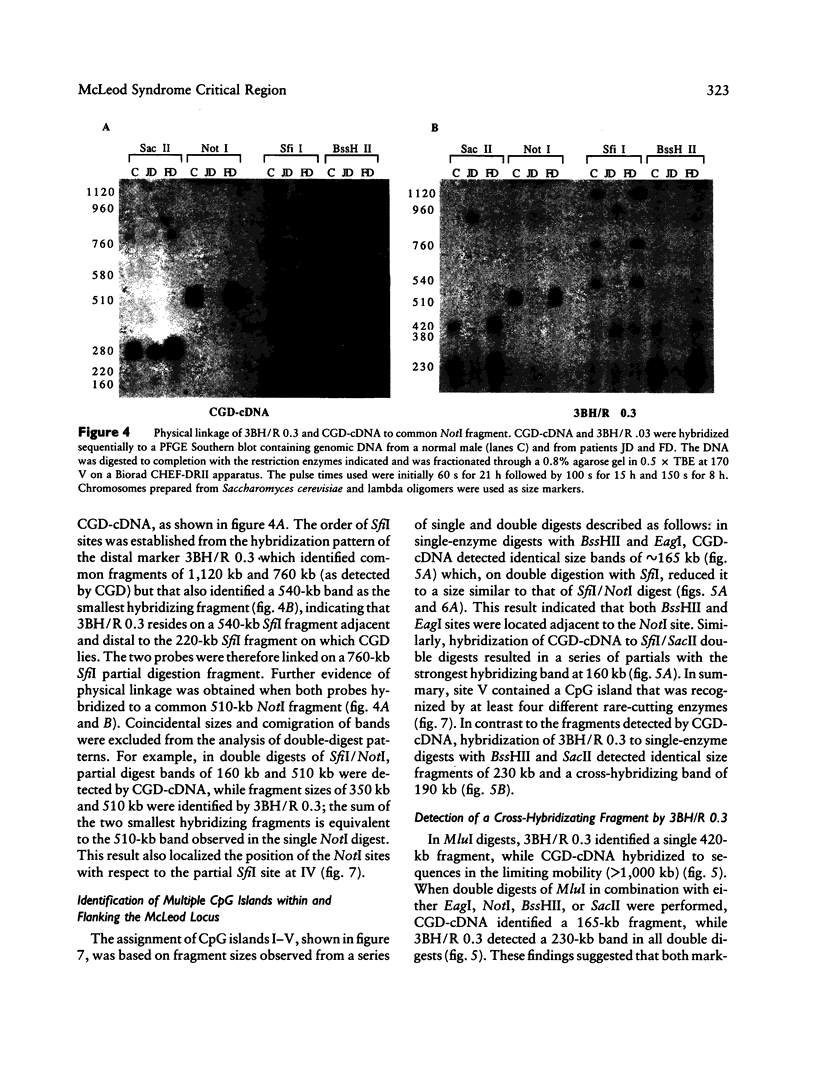
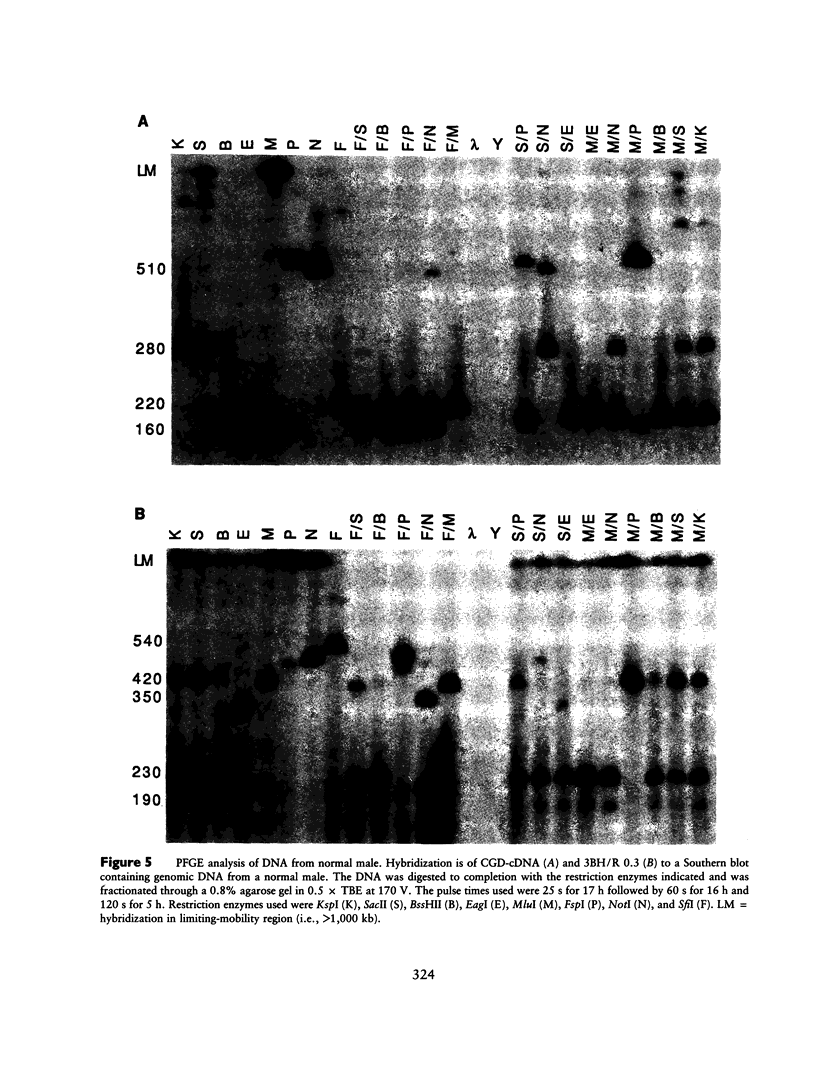
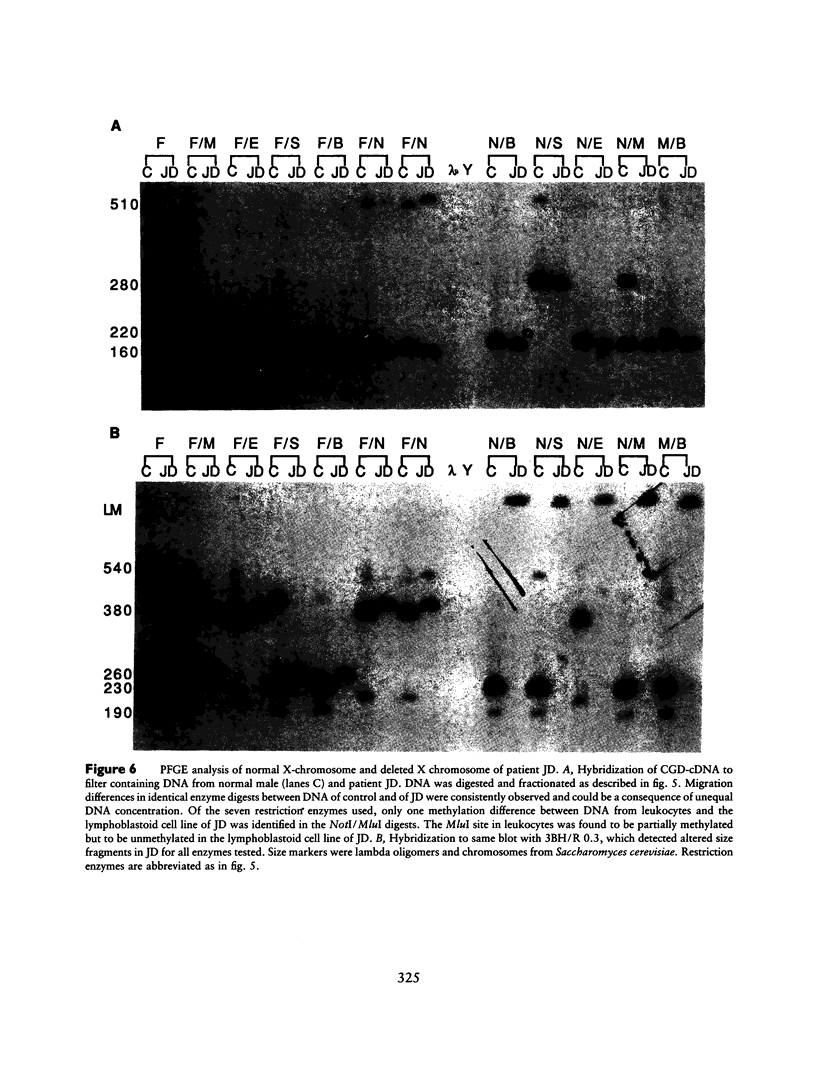
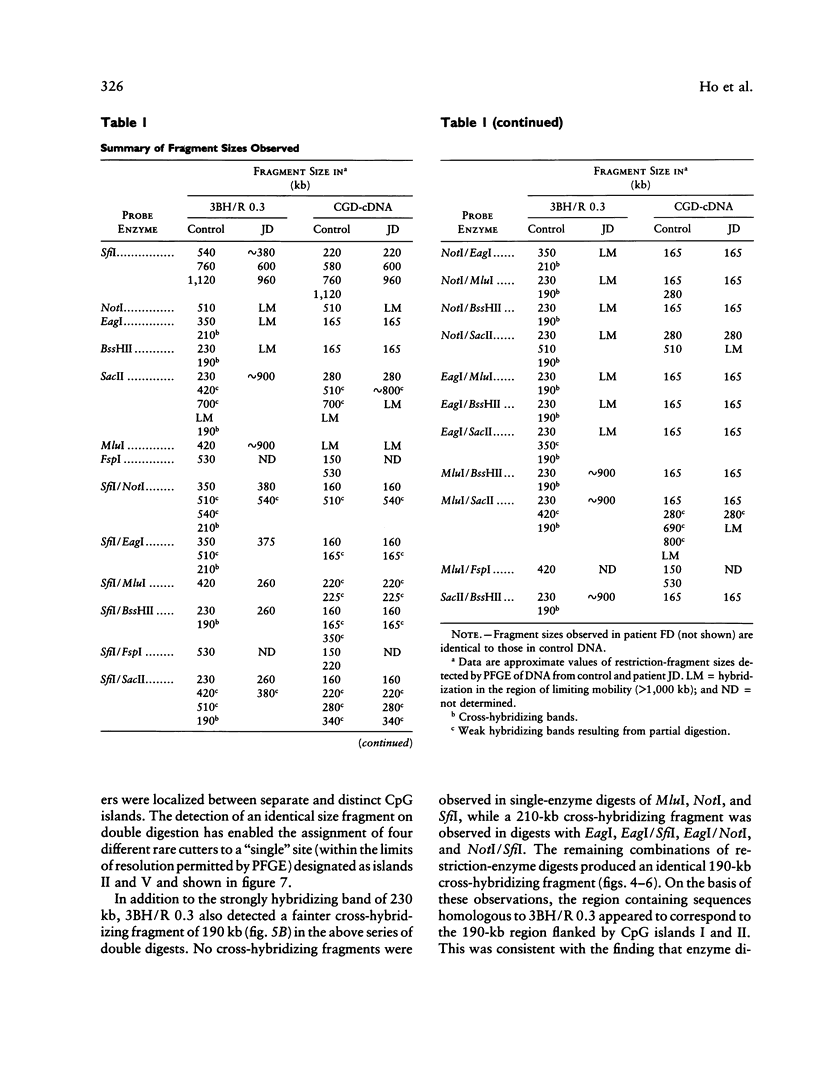
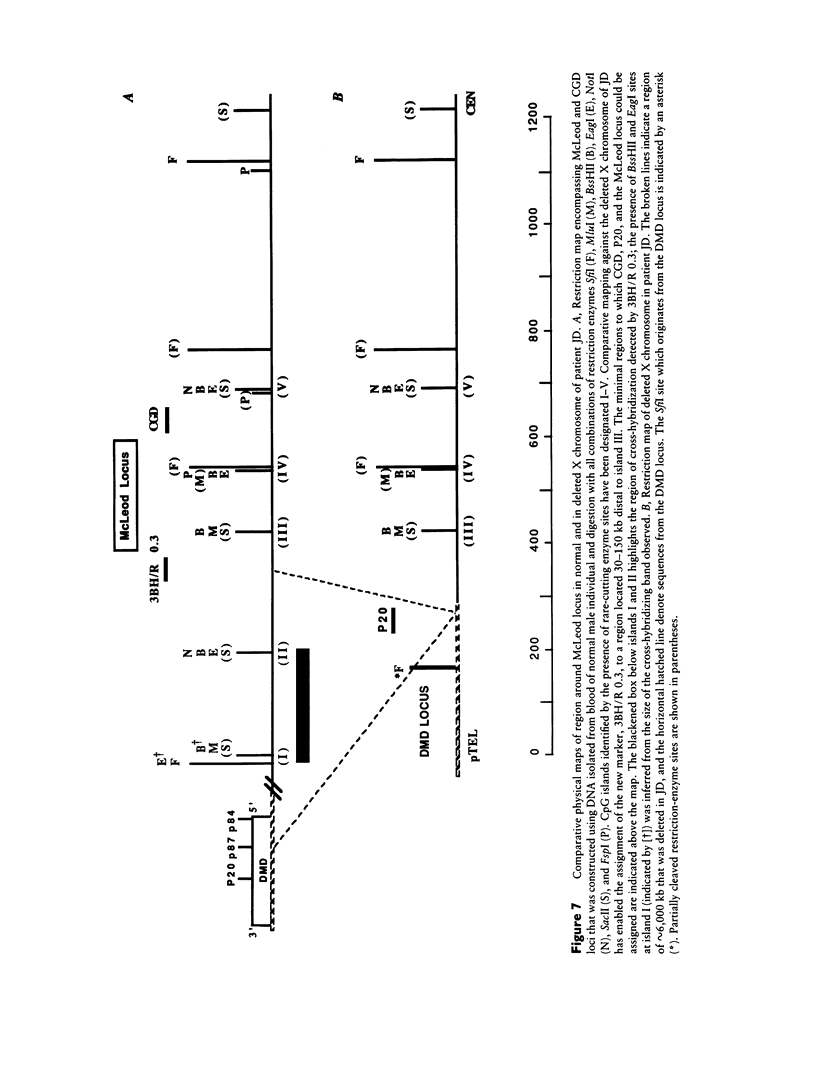
McLeod syndrome, characterized by acanthocytosis and the absence of a red-blood-cell Kell antigen (Kx), is a multisystem disorder involving a late-onset myopathy, splenomegaly, and neurological defects. The locus for this syndrome has been mapped, by deletion analysis, to a region between the loci for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). In this study, we describe a new marker, 3BH/R 0.3 (DXS 709), isolated by cloning the deletion breakpoint of a DMD patient. A long-range restriction map of Xp21, encompassing the gene loci for McLeod and CGD, was constructed, and multiple CpG islands were found clustered in a 700-kb region. Using the new marker, we have limited the McLeod syndrome critical region to 150-380-kb. Within this interval, two CpG-rich islands which may represent candidate sites for the McLeod gene were identified.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertelson C. J., Pogo A. O., Chaudhuri A., Marsh W. L., Redman C. M., Banerjee D., Symmans W. A., Simon T., Frey D., Kunkel L. M. Localization of the McLeod locus (XK) within Xp21 by deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):703–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blonden L. A., den Dunnen J. T., van Paassen H. M., Wapenaar M. C., Grootscholten P. M., Ginjaar H. B., Bakker E., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. High resolution deletion breakpoint mapping in the DMD gene by whole cosmid hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5611–5621. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter N. D., Morgan J. E., Monaco A. P., Schwartz M. S., Jeffery S. Dystrophin expression and genotypic analysis of two cases of benign X linked myopathy (McLeod's syndrome). J Med Genet. 1990 Jun;27(6):345–347. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.6.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Dunnen J. T., Grootscholten P. M., Bakker E., Blonden L. A., Ginjaar H. B., Wapenaar M. C., van Paassen H. M., van Broeckhoven C., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Topography of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene: FIGE and cDNA analysis of 194 cases reveals 115 deletions and 13 duplications. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):835–847. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elvin P., Slynn G., Black D., Graham A., Butler R., Riley J., Anand R., Markham A. F. Isolation of cDNA clones using yeast artificial chromosome probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3913–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey D., Mächler M., Seger R., Schmid W., Orkin S. H. Gene deletion in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease and McLeod syndrome: fine mapping of the Xk gene locus. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):252–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M. Construction and characterization of a genomic library in lambda. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:190–199. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Barlow D. P., Lehrach H. A large inverted duplication allows homologous recombination between chromosomes heterozygous for the proximal t complex inversion. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):813–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Frischauf A. M. Isolation of genomic DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:180–183. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Colletti-Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Localization and cloning of Xp21 deletion breakpoints involved in muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00281063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Aldridge J., Fischbeck K. H., Bartlett R., Pericak-Vance M. A., Roses A. D., Kunkel L. M. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):842–845. doi: 10.1038/316842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Molecular genetics of chronic granulomatous disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Avellino G., Pfeffer S. R., Mukherjee T. K., Nichols M., Rubinstein P., Marsh W. L. Kell blood group antigens are part of a 93,000-dalton red cell membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9521–9525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Marsh W. L., Scarborough A., Johnson C. L., Rabin B. I., Overbeeke M. Biochemical studies on McLeod phenotype red cells and isolation of Kx antigen. Br J Haematol. 1988 Jan;68(1):131–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb04191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symmans W. A., Shepherd C. S., Marsh W. L., Oyen R., Shohet S. B., Linehan B. J. Hereditary acanthocytosis associated with the McLeod phenotype of the Kell blood group system. Br J Haematol. 1979 Aug;42(4):575–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang L. L., Redman C. M., Williams D., Marsh W. L. Biochemical studies on McLeod phenotype erythrocytes. Vox Sang. 1981 Jan;40(1):17–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1981.tb00664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wapenaar M. C., Kievits T., Hart K. A., Abbs S., Blonden L. A., den Dunnen J. T., Grootscholten P. M., Bakker E., Verellen-Dumoulin C., Bobrow M. A deletion hot spot in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Genomics. 1988 Feb;2(2):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90090-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. E., Cooke A., Colgan J., Boyd E., Aitken D. A., Sinclair L., Glasgow L., Stephenson J. B., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Duchenne muscular dystrophy due to familial Xp21 deletion detectable by DNA analysis and flow cytometry. Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;73(2):175–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00291610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimer B. M., Marsh W. L., Taswell H. F., Galey W. R. Haematological changes associated with the McLeod phenotype of the Kell blood group system. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jun;36(2):219–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint-Basile G., Bohler M. C., Fischer A., Cartron J., Dufier J. L., Griscelli C., Orkin S. H. Xp21 DNA microdeletion in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod phenotype. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00451463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Bakker E., Breteler E. G., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Direct detection of more than 50% of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations by field inversion gels. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):640–642. doi: 10.1038/329640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ommen G. J., Verkerk J. M., Hofker M. H., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M., Ray P., Worton R., Wieringa B., Bakker E., Pearson P. L. A physical map of 4 million bp around the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene on the human X-chromosome. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]