Abstract
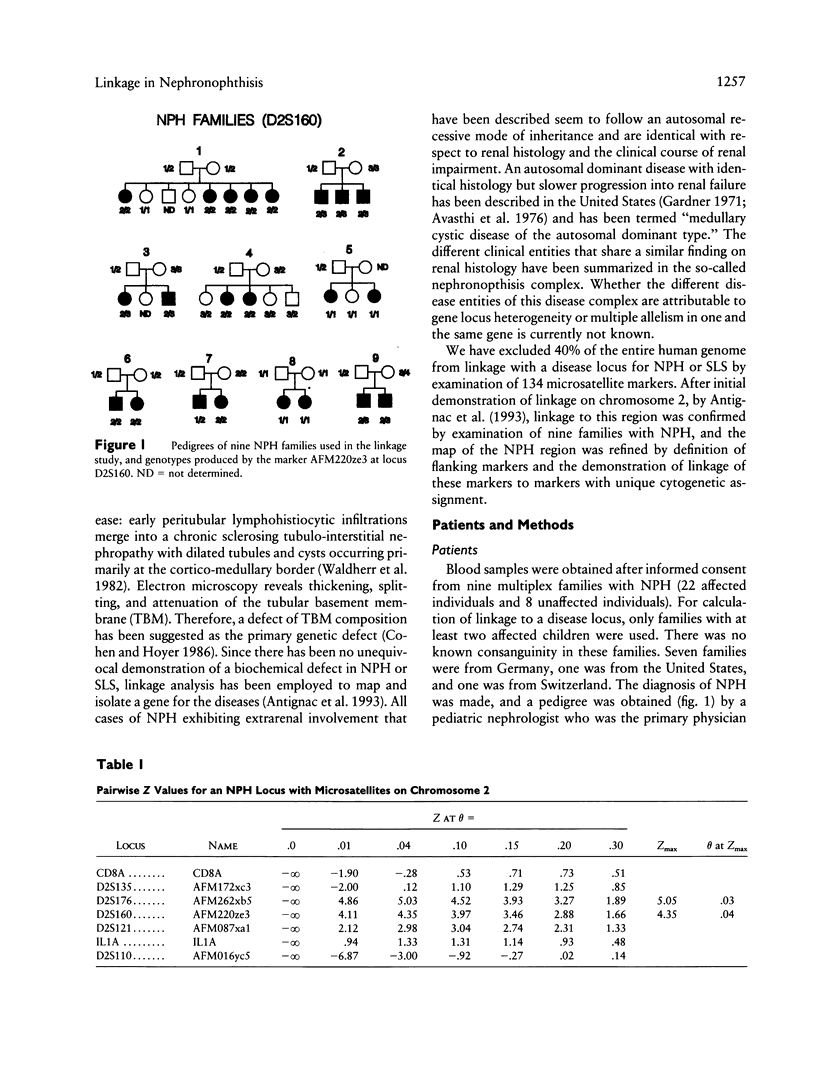
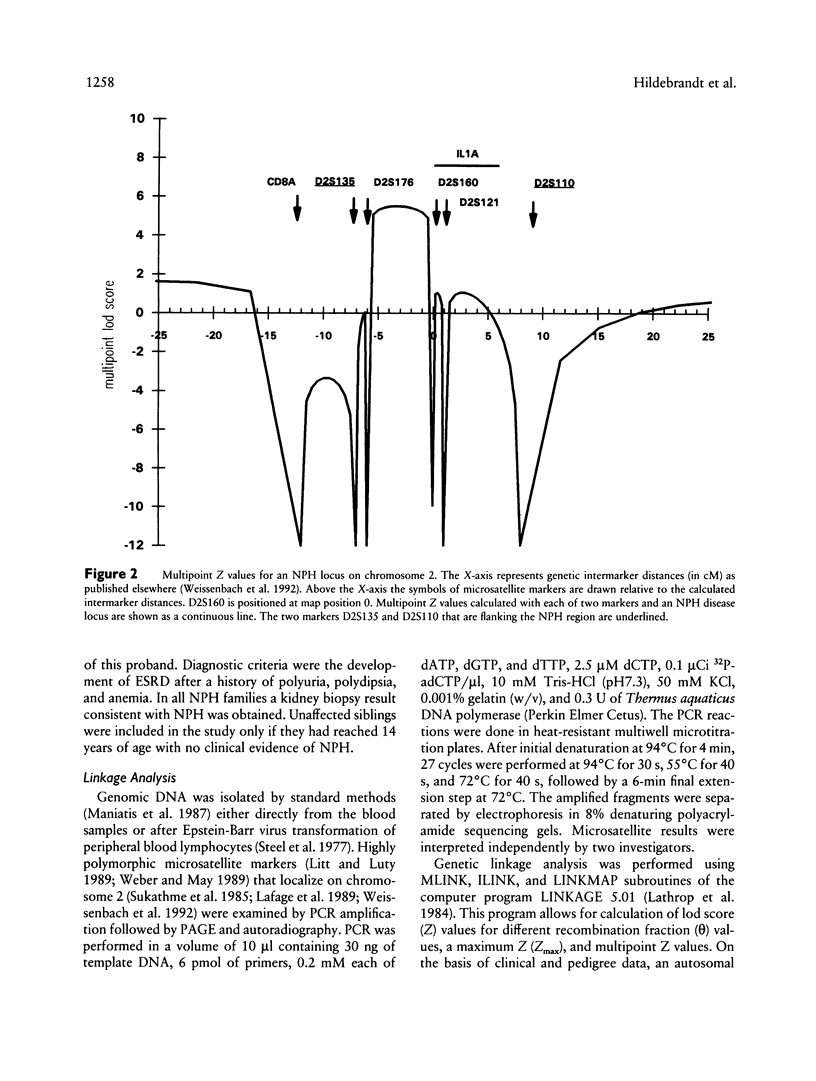
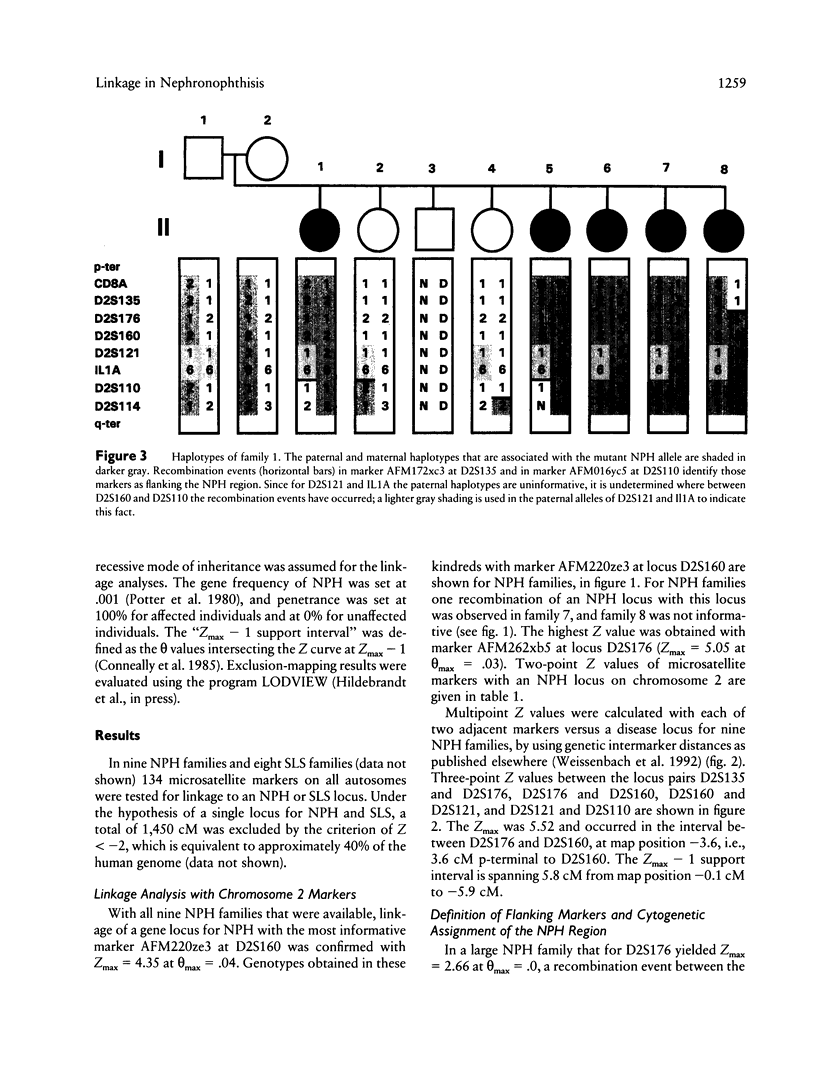
Familial juvenile nephronophthisis (NPH) is an autosomal recessive kidney disease that leads to end-stage renal failure in adolescence and is associated with the formation of cysts at the cortico-medullary junction of the kidneys. NPH is responsible for about 15% of end-stage renal disease in children, as shown by Kleinknecht and Habib. NPH in combination with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa is known as the Senior-Løken syndrome (SLS) and exhibits renal pathology that is identical to NPH. We had excluded 40% of the human genome from linkage with a disease locus for NPH or SLS when antignac et al. first demonstrated linkage for an NPH locus on chromosome 2. We present confirmation of linkage of an NPH locus to microsatellite markers on chromosome 2 in nine families with NPH. By linkage analysis with marker AFM262xb5 at locus D2S176, a maximum lod score of 5.05 at a θmax = .03 was obtained. In a large NPH family that yielded at D2S176 a maximum lod score of 2.66 at θmax = .0, markers AFM172xc3 and AFM016yc5, representing loci D2S135 and D2S110, respectively, were identified as flanking markers, thereby defining the interval for an NPH locus to a region of approximately 15 cM. Furthermore, the cytogenetic assignment of the NPH region was specified to 2p12-(2q13 or adjacent bands) by calculation of linkage between these flanking markers and markers with known unique cytogenetic assignment. The refined map may serve as a genetic framework for additional genetic and physical mapping of the region.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antignac C., Arduy C. H., Beckmann J. S., Benessy F., Gros F., Medhioub M., Hildebrandt F., Dufier J. L., Kleinknecht C., Broyer M. A gene for familial juvenile nephronophthisis (recessive medullary cystic kidney disease) maps to chromosome 2p. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):342–345. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avasthi P. S., Erickson D. G., Gardner K. D. Hereditary renal-retinal dysplasia and the medullary cystic disease-nephronophthisis complex. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Feb;84(2):157–161. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-2-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boichis H., Passwell J., David R., Miller H. Congenital hepatic fibrosis and nephronophthisis. A family study. Q J Med. 1973 Jan;42(165):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. H., Hoyer J. R. Nephronophthisis. A primary tubular basement membrane defect. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):564–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANCONI G., HANHART E., von ALBERTINI A., UHLINGER E., DOLIVO G., PRADER A. Die familiäre juvenile Nephronophthise (die idiopathische parenchymatöse Schrumpfniere). Helv Paediatr Acta. 1951 Feb;6(1):1–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner K. D., Jr Evolution of clinical signs in adult-onset cystic disease of the renal medulla. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Jan;74(1):47–54. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOKEN A. C., HANSSEN O., HALVORSEN S., JOLSTER N. J. Hereditary renal dysplasia and blindness. Acta Paediatr. 1961 Mar;50:177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1961.tb08037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafage M., Maroc N., Dubreuil P., de Waal Malefijt R., Pébusque M. J., Carcassonne Y., Mannoni P. The human interleukin-1 alpha gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 2 at band q13. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):104–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):397–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainzer F., Saldino R. M., Ozonoff M. B., Minagi H. Familial nephropathy associatdd with retinitis pigmentosa, cerebellar ataxia and skeletal abnormalities. Am J Med. 1970 Oct;49(4):556–562. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter D. E., Holliday M. A., Piel C. F., Feduska N. J., Belzer F. O., Salvatierra O., Jr Treatment of end-stage renal disease in children: a 15-year experience. Kidney Int. 1980 Jul;18(1):103–109. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENIOR B., FRIEDMANN A. I., BRAUDO J. L. Juvenile familial nephropathy with tapetoretinal degeneration. A new oculorenal dystrophy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961 Nov;52:625–633. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(61)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel C. M., Philipson J., Arthur E., Gardiner S. E., Newton M. S., McIntosh R. V. Possibility of EB virus preferentially transforming a subpopulation of human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):729–731. doi: 10.1038/270729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Vollmer A. C., Erikson J., Isobe M., Croce C., Parnes J. R. Gene for the human T cell differentiation antigen Leu-2/T8 is closely linked to the kappa light chain locus on chromosome 2. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):429–434. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldherr R., Lennert T., Weber H. P., Födisch H. J., Schärer K. The nephronophthisis complex. A clinicopathologic study in children. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1982;394(3):235–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00430668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


