Abstract
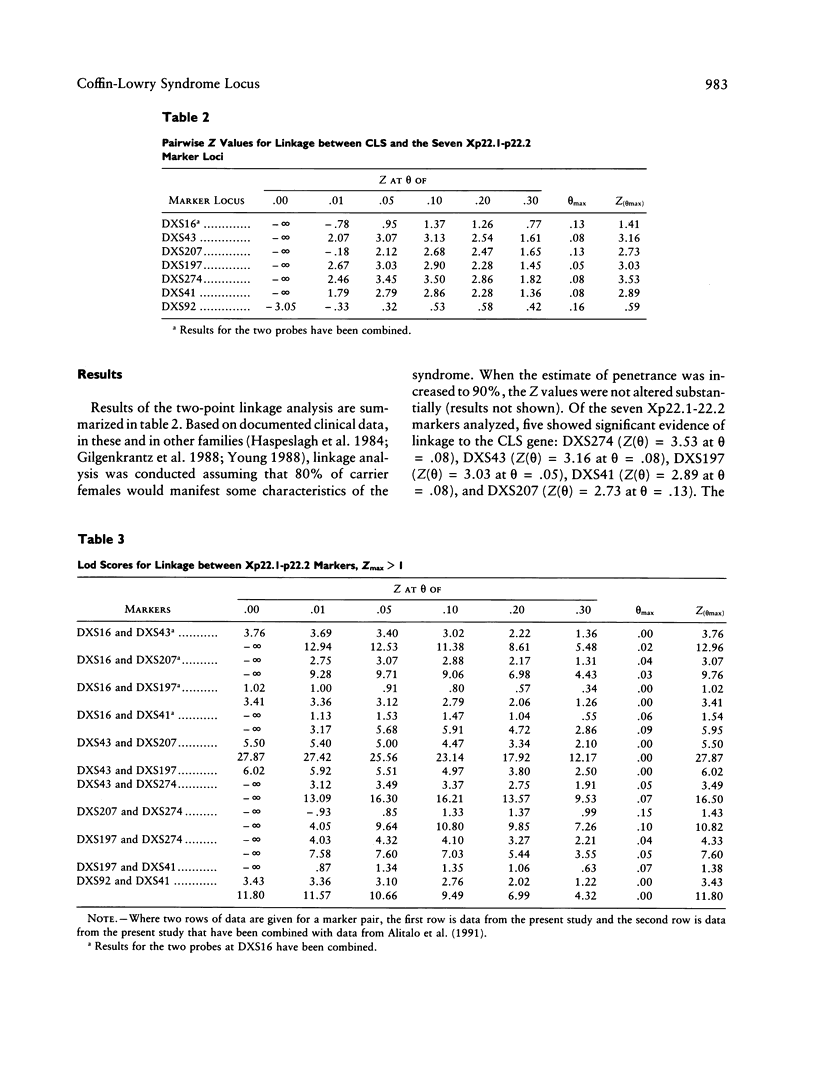
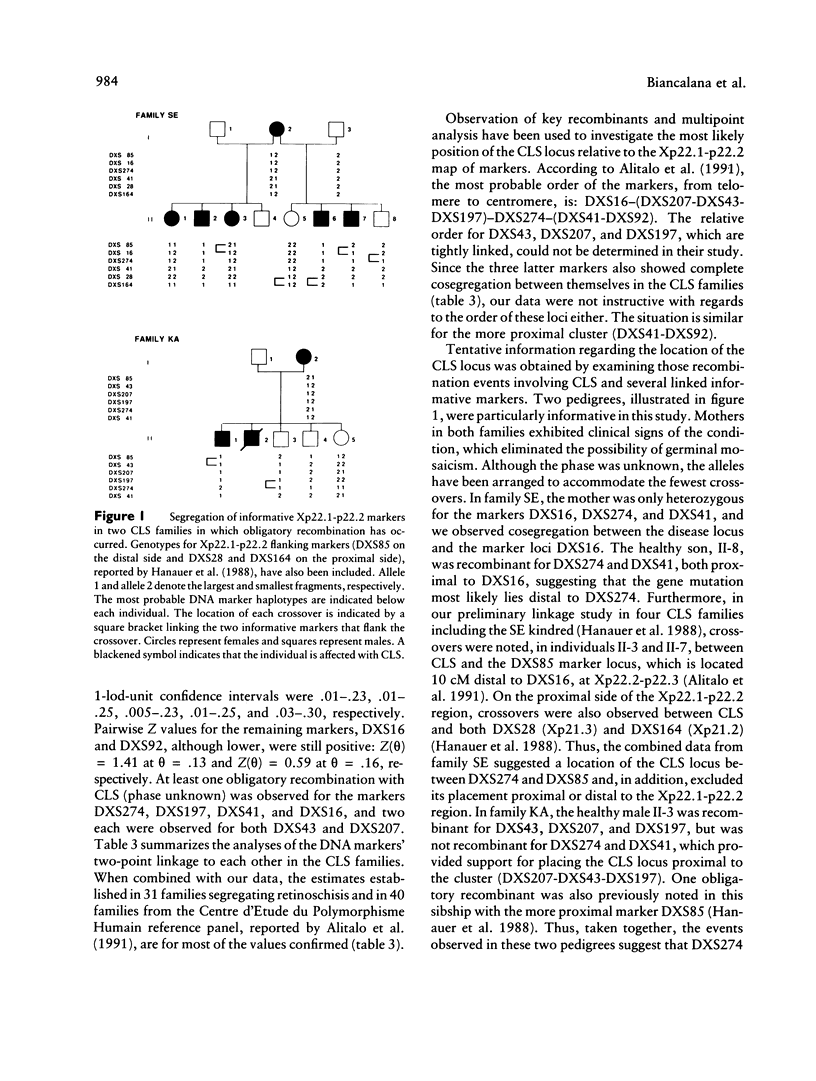
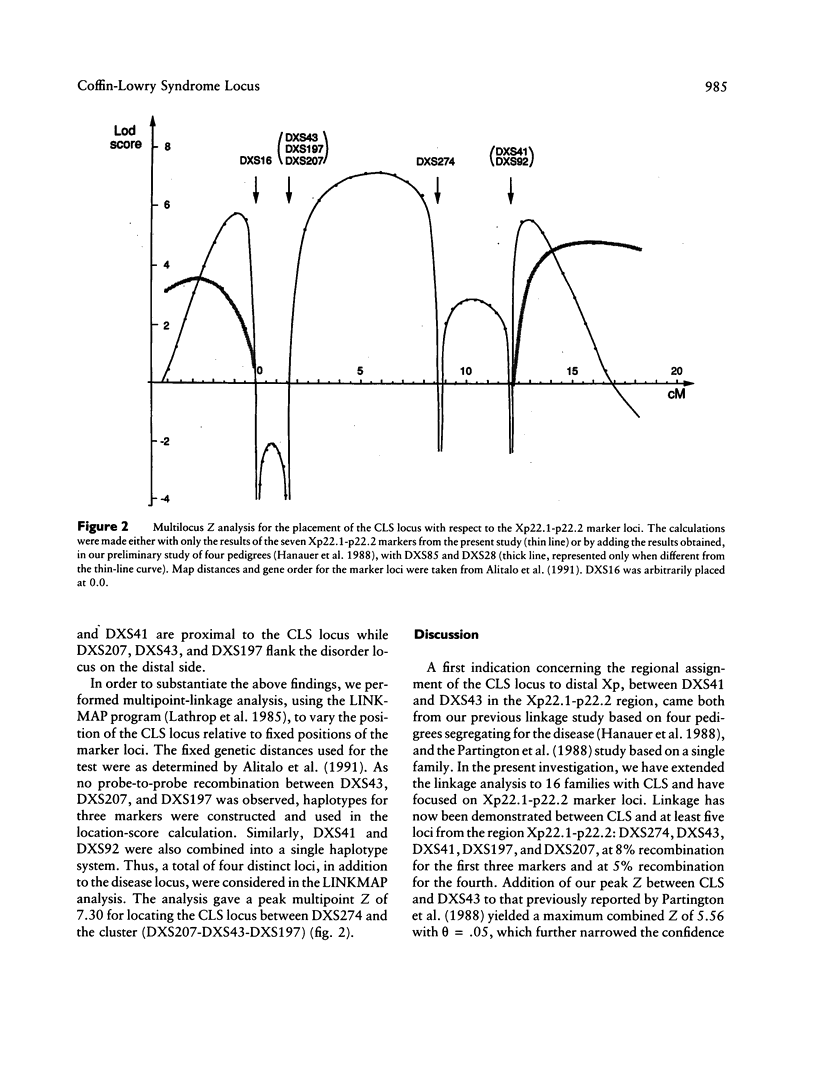
The Coffin-Lowry syndrome (CLS) is an X-linked inherited disease of unknown pathogenesis characterized by severe mental retardation, typical facial and digital anomalies, and progressive skeletal deformations. Our previous linkage analysis, based on four pedigrees with the disease, suggested a localization for the CLS locus in Xp22.1–p22.2, with the most likely position between the marker loci DXS41 and DXS43. We have now extended the study to 16 families by using seven RFLP marker loci spanning the Xp22.1–p22.2 region. Linkage has been established with five markers from this part of the X chromosome: DXS274 (lod score [Z] (θ) = 3.53 at θ = .08), DXS43 (Z(θ) = 3.16 at θ = .08), DXS197 (Z(θ) = 3.03 at θ = .05), DXS41 (Z(θ) = 2.89 at θ = .08), and DXS207 (Z(θ) = 2.73 at θ = .13). A multipoint linkage analysis further placed, with a maximum multipoint Z of 7.30, the mutation-causing CLS within a 7-cM interval defined by the cluster of tightly linked markers (DXS207-DXS43-DXS197) on the distal side and by DXS274 on the proximal side. Thus, these further linkage data confirm and refine the map location for the gene responsible for CLS in Xp22.1–p22.2. As no linkage heterogeneity was detected, this validates the use of the Xp22.1–p22.2 markers for carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis in CLS families.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo T., Kruse T. A., Ahrens P., Albertsen H. M., Eriksson A. W., de la Chapelle A. Genetic mapping of 12 marker loci in the Xp22.3-p21.2 region. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):599–603. doi: 10.1007/BF00201548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck M., Glössl J., Rüter R., Kresse H. Abnormal proteodermatan sulfate in three patients with Coffin-Lowry syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1983 Nov;17(11):926–929. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198311000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collacott R. A., Warrington J. S., Young I. D. Coffin-Lowry syndrome and schizophrenia: a family report. J Ment Defic Res. 1987 Jun;31(Pt 2):199–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1987.tb01356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilgenkrantz S., Mujica P., Gruet P., Tridon P., Schweitzer F., Nivelon-Chevallier A., Nivelon J. L., Couillault G., David A., Verloes A. Coffin-Lowry syndrome: a multicenter study. Clin Genet. 1988 Oct;34(4):230–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1988.tb02870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Alembik Y., Gilgenkrantz S., Mujica P., Nivelon-Chevallier A., Pembrey M. E., Young I. D., Mandel J. L. Probable localisation of the Coffin-Lowry locus in Xp22.2-p22.1 by multipoint linkage analysis. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):523–530. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspeslagh M., Fryns J. P., Beusen L., Van Dessel F., Vinken L., Moens E., Van den Berghe H. The Coffin-Lowry syndrome. A study of two new index patients and their families. Eur J Pediatr. 1984 Dec;143(2):82–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00445790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry B., Miller J. R., Fraser F. C. A new dominant gene mental retardation syndrome. Association with small stature, tapering fingers, characteristic facies, and possible hydrocephalus. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Jun;121(6):496–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Willard H. F., Nussbaum R. L., Romeo G., Puck J. M., Davies K. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):384–437. doi: 10.1159/000132801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Moisan J. P., Grzeschik K. H., Hellkuhl B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Van Cong N., Weil D., Mandel J. L. Characterization of a set of X-linked sequences and of a panel of somatic cell hybrids useful for the regional mapping of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00278816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partington M. W., Mulley J. C., Sutherland G. R., Thode A., Turner G. A family with the Coffin Lowry syndrome revisited: localization of CLS to Xp21-pter. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):509–521. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temtamy S. A., Miller J. D., Hussels-Maumenee I. The Coffin-Lowry syndrome: an inherited faciodigital mental retardation syndrome. J Pediatr. 1975 May;86(5):724–731. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Davies K. E., Read A. P., Tippett P., Wooding C., Flint T., Wood S., Kruse T. A., Whyte M. P., O'Riordan J. L. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences, DXS197 and DXS207, in hypophosphatemic rickets families. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90271-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D. The Coffin-Lowry syndrome. J Med Genet. 1988 May;25(5):344–348. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.5.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


