Abstract
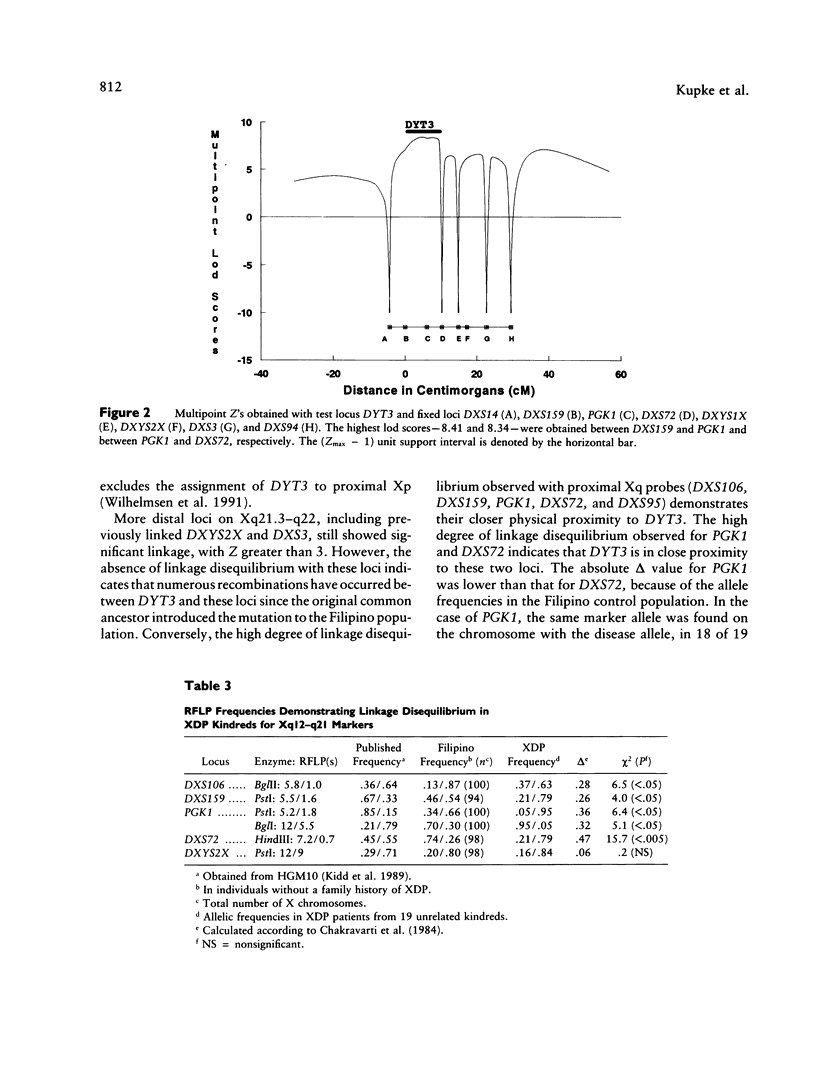
The study of rare genetic forms of dystonia and parkinsonism permits positional cloning of genes potentially involved in more common, multifactorial forms of these diseases. One movement disorder amenable to molecular genetic analysis is the X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome (XDP). This disease is endemic to the Philippines where it originated by a genetic founder effect. Linkage analysis was performed with DNA from 14 XDP kindreds by using 12 polymorphic DNA sequences in Xp11-Xq22. Two-point analysis demonstrated maximum lod scores of 5.45, 4.95, 4.28, and 5.99 for DXS106, DXS159, PGK1, and DXS72, respectively, at recombination fractions of zero (DXS106 and DXS159), .01 (PGK1), and .04 (DXS72). Multipoint analysis resulted in a maximum-likelihood score (Zmax) of 8.41 with a (Zmax - 1) support interval of 9 cM between DXS159 and DXS72 (Xq12-q21.1). In 19 XDP kindreds significant linkage disequilibrium was found for loci DXS72 (delta = .47), PGK1 (delta = .36), DXS95 (delta = .30), DXS106 (delta = .28), and DXS159 (delta = .26). These data indicate that the gene mutated in XDP (locus DYT3) is located in Xq12-q21.1.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arveiler B., Hofker M. H., Bergen A. A., Mandel J. L. A PstI RFLP detected by probe cpX73 (DXS159) in Xq11-q12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5903–5903. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers F. P., van de Pol D. J., van Kerkhoff L. P., Wieringa B., Ropers H. H. Cloning of a gene that is rearranged in patients with choroideraemia. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):674–677. doi: 10.1038/347674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessler M., Poustka A., Cavenee W., Neve R. L., Orkin S. H., Bruns G. A. Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):774–778. doi: 10.1038/343774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golbe L. I., Di Iorio G., Bonavita V., Miller D. C., Duvoisin R. C. A large kindred with autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1990 Mar;27(3):276–282. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Bergen A. A., Skraastad M. I., Carpenter N. J., Veenema H., Connor J. M., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Efficient isolation of X chromosome-specific single-copy probes from a cosmid library of a human X/hamster hybrid-cell line: mapping of new probes close to the locus for X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;40(4):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B. J., Sherman S. L., Ott J. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):387–394. doi: 10.1159/000133023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. L., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Risch N., Bressman S. B., Brin M. F., Schuback D. E., Burke R. E., Kwiatkowski D. J., Shale H. Dystonia gene in Ashkenazi Jewish population is located on chromosome 9q32-34. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):114–120. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Lee L. V., Müller U. Assignment of the X-linked torsion dystonia gene to Xq21 by linkage analysis. Neurology. 1990 Sep;40(9):1438–1442. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.9.1438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Lee L. V., Viterbo G. H., Arancillo J., Donlon T., Müller U. X-linked recessive torsion dystonia in the Philippines. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jun;36(2):237–242. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320360219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. V., Kupke K. G., Caballar-Gonzaga F., Hebron-Ortiz M., Müller U. The phenotype of the X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome. An assessment of 42 cases in the Philippines. Medicine (Baltimore) 1991 May;70(3):179–187. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199105000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. V., Pascasio F. M., Fuentes F. D., Viterbo G. H. Torsion dystonia in Panay, Philippines. Adv Neurol. 1976;14:137–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermot K. D., Morgan S. H., Cheshire J. K., Wilson T. M. Anderson Fabry disease, a close linkage with highly polymorphic DNA markers DXS17, DXS87 and DXS88. Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;77(3):263–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00284482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D. Parkinson's disease in twins. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Jan;50(1):105–106. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marttila R. J., Kaprio J., Koskenvuo M., Rinne U. K. Parkinson's disease in a nationwide twin cohort. Neurology. 1988 Aug;38(8):1217–1219. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.8.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G., Itagaki S., Mizukawa K. Anatomy and pathology of the basal ganglia. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;14(3 Suppl):363–372. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Kupke K. G. The genetics of primary torsion dystonia. Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;84(2):107–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00208922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Lalande M., Donlon T., Latt S. A. Moderately repeated DNA sequences specific for the short arm of the human Y chromosome are present in XX males and reduced in copy number in an XY female. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1325–1340. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard T. G., Marsden C. D., Duvoisin R. C. Dopa-responsive dystonia. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L., Kramer P. L., Moskowitz C. B., Kwiatkowski D. J., Brin M. F., Bressman S. B., Schuback D. E., Falk C. T., Risch N., de Leon D. Human gene for torsion dystonia located on chromosome 9q32-q34. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1427–1434. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D., de Martinville B., Barker D., Wyman A., White R., Francke U., Botstein D. Single-copy sequence hybridizes to polymorphic and homologous loci on human X and Y chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5352–5356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Davis J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. An anonymous single-copy X-chromosome RFLP for DXS72 from Xq13-Xq22 [HGM8 provisional no. DXS72]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5724–5724. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Yang H. M., Niebuhr E., Rosenberg T., Page D. C. Regional localization of polymorphic DNA loci on the proximal long arm of the X chromosome using deletions associated with choroideremia. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):156–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00278188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa M., Nomura Y., Kase M. Hereditary progressive dystonia with marked diurnal fluctuation: clinicopathophysiological identification in reference to juvenile Parkinson's disease. Adv Neurol. 1987;45:227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smead D. L., Nussbaum R. L., Puck J. M. RFLPs in human X-linked PGK1: a new probe for the PstI RFLP demonstrates strong linkage disequilibrium with the BgII RFLP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7551–7551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Willard H. F., Michelson A. M., Riggs A. D., Orkin S. H. Clonal analysis using recombinant DNA probes from the X-chromosome. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4806–4813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. D., Duvoisin R. C., Ince S. E., Nutt J. D., Eldridge R., Calne D. B. Parkinson's disease in 65 pairs of twins and in a set of quadruplets. Neurology. 1983 Jul;33(7):815–824. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.7.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Weeks D. E., Nygaard T. G., Moskowitz C. B., Rosales R. L., dela Paz D. C., Sobrevega E. E., Fahn S., Gilliam T. C. Genetic mapping of "Lubag" (X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism) in a Filipino kindred to the pericentromeric region of the X chromosome. Ann Neurol. 1991 Feb;29(2):124–131. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


