Abstract
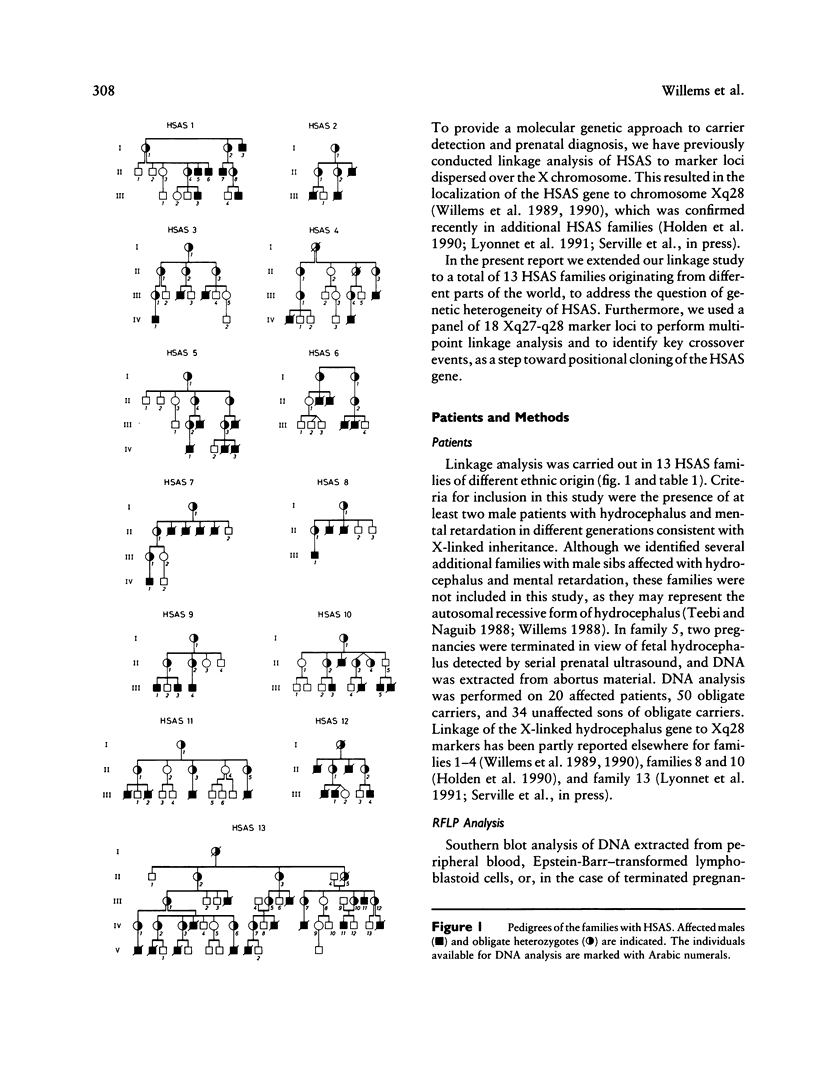
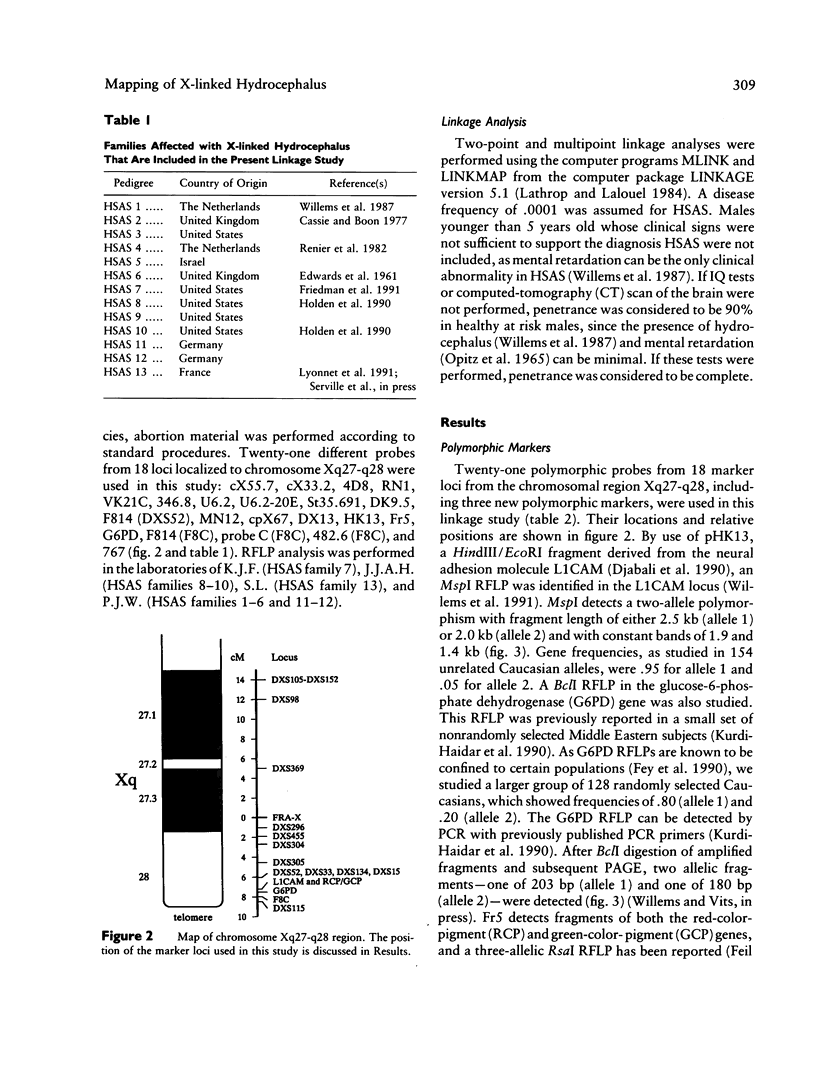
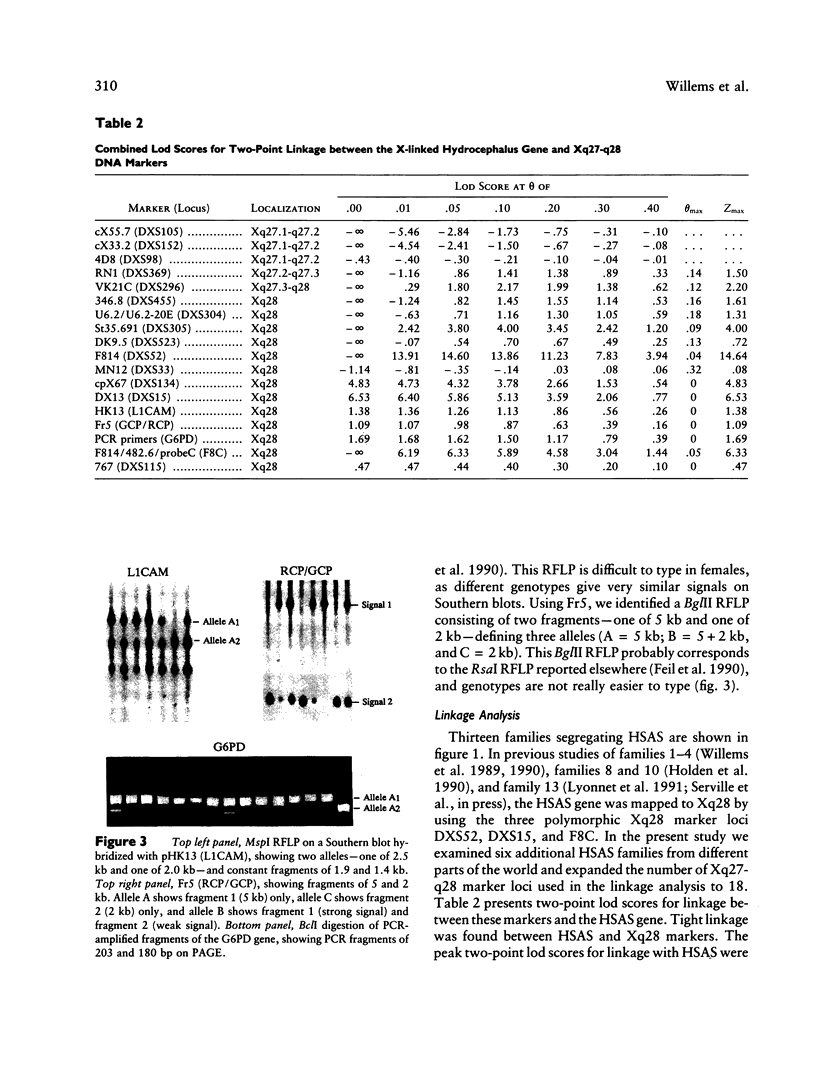
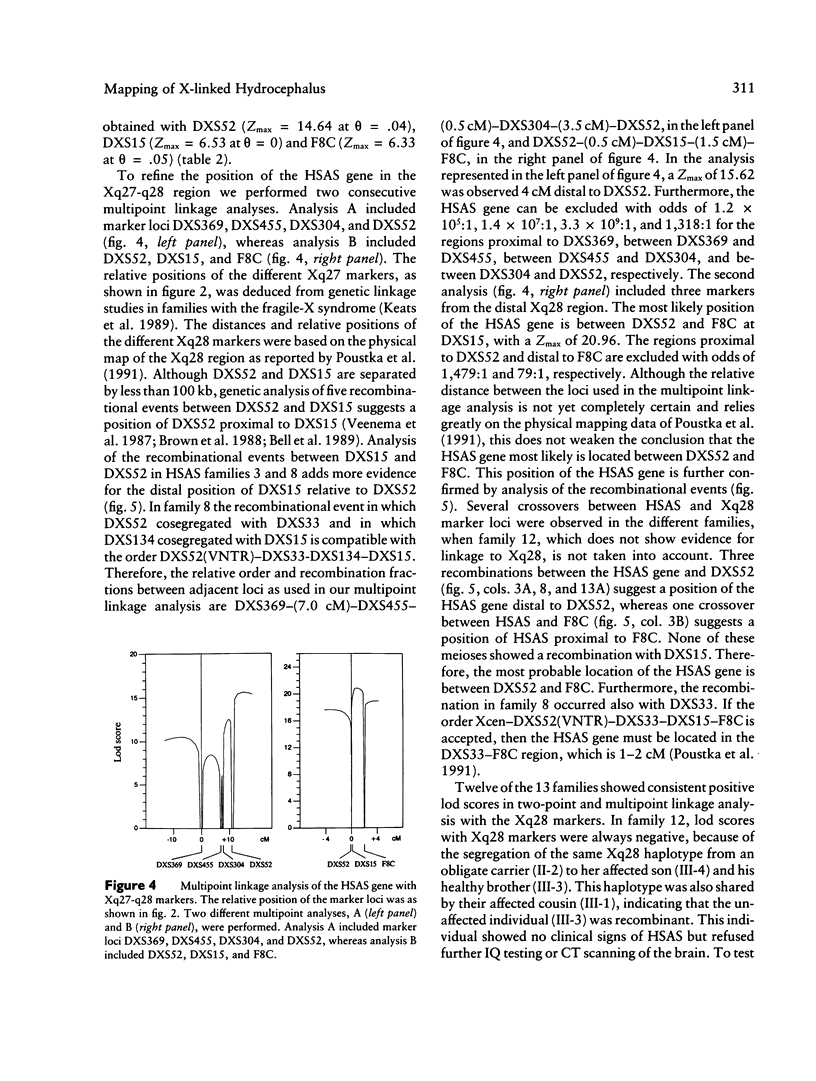
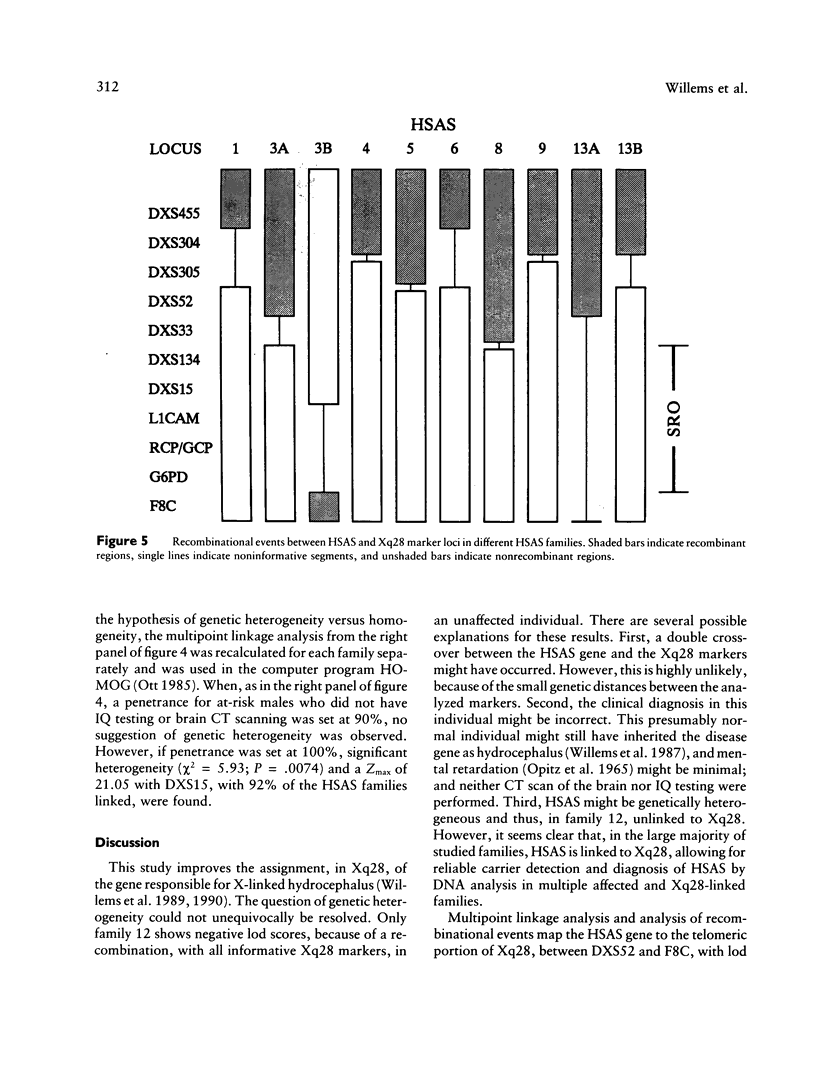
X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS) is the most frequent genetic form of hydrocephalus. Clinical symptoms of HSAS include hydrocephalus, mental retardation, clasped thumbs, and spastic paraparesis. Recently we have assigned the HSAS gene to Xq28 by linkage analysis. In the present study we used a panel of 18 Xq27-q28 marker loci to further localize the HSAS gene in 13 HSAS families of different ethnic origins. Among the Xq27-q28 marker loci used, DXS52, DXS15, and F8C gave the highest combined lod scores, of 14.64, 6.53 and 6.33, respectively, at recombination fractions of .04, 0, and .05, respectively. Multipoint linkage analysis localizes the HSAS gene in the telomeric part of the Xq28 region, with a maximal lod score of 20.91 at 0.5 cM distal to DXS52. Several recombinations between the HSAS gene and the Xq28 markers DXS455, DXS304, DXS305, and DXS52 confirm that the HSAS locus is distal to DXS52. One crossover between HSAS and F8C suggests the HSAS gene to be proximal to F8C. Therefore, data from multipoint linkage analysis and the localization of key crossovers indicate that the HSAS gene is most likely located between DXS52 and F8C. This high-resolution genetic mapping places the HSAS locus within a region of <2 Mb in length, which is now amenable to positional cloning.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell M. V., Patterson M. N., Dorkins H. R., Davies K. E. Physical mapping of DXS134 close to the DXS52 locus. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):27–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00288266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Gross A., Chan C., Jenkins E. C., Mandel J. L., Oberlé I., Arveiler B., Novelli G., Thibodeau S., Hagerman R. Multilocus analysis of the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;78(3):201–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00291662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton B. K. Recurrence risks for congenital hydrocephalus. Clin Genet. 1979 Jul;16(1):47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassie R., Boon A. R. Sex linked hydrocephalus. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):72–73. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djabali M., Mattei M. G., Nguyen C., Roux D., Demengeot J., Denizot F., Moos M., Schachner M., Goridis C., Jordan B. R. The gene encoding L1, a neural adhesion molecule of the immunoglobulin family, is located on the X chromosome in mouse and man. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS J. H., NORMAN R. M., ROBERTS J. M. Sex-linked hydrocephalus. Report of a family with 15 affected members. Arch Dis Child. 1961 Oct;36:481–485. doi: 10.1136/adc.36.189.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil R., Aubourg P., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. A 195-kb cosmid walk encompassing the human Xq28 color vision pigment genes. Genomics. 1990 Feb;6(2):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90578-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey M. F., Wainscoat J. S., Mukwala E. C., Falusi A. G., Vulliamy T. J., Luzzatto L. A PvuII restriction fragment length polymorphism of the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene is an African-specific marker. Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;84(5):471–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00195822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried K. X-linked mental retardation and-or hydrocephalus. Clin Genet. 1972;3(4):258–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Spaepen A., Cassiman J. J., van den Berghe H. X linked complicated spastic paraplegia, MASA syndrome, and X linked hydrocephalus owing to congenital stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius: variable expression of the same mutation at Xq28. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):429–431. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.429-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gareis F. J., Mason J. D. X-linked mental retardation associated with bilateral clasp thumb anomaly. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):333–338. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Gitschier J. A contiguous, 3-Mb physical map of Xq28 extending from the colorblindness locus to DXS15. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):873–882. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu G., Searby C., King A., Dubowitz M., Davies K. E. Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00401241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurdi-Haidar B., Mason P. J., Berrebi A., Ankra-Badu G., al-Ali A., Oppenheim A., Luzzatto L. Origin and spread of the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant (G6PD-Mediterranean) in the Middle East. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):1013–1019. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Tacke R., Scherer H., Teplow D., Früh K., Schachner M. Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):701–703. doi: 10.1038/334701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Grover H. J., Blanchette V. S., Giles A. R., Lillicrap D. P., Phillips A., Holden J. J., White B. N. Recombination between the factor VIII gene and the DXS52 locus gives the most probable genetic order as centromere-fra(X)-DXS15-DXS52-F8C-telomere. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;26(3):751–760. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Dietrich A., Langenstein G., Toniolo D., Warren S. T., Lehrach H. Physical map of human Xq27-qter: localizing the region of the fragile X mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8302–8306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renier W. O., Ter Haar B. G., Slooff J. L., Hustinx T. W., Gabreëls F. J. X-linked congenital hydrocephalus. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1982;84(2):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(82)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel M., Friedl W., Uhlhaas S., Neugebauer M., Heimann D., Zerres K. MASA syndrome: clinical variability and linkage analysis. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Oct 1;41(1):10–14. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. G., Danks D. M. Prenatal diagnosis of sex-linked hydrocephalus. Prenat Diagn. 1983 Jul;3(3):269–269. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970030316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C., Legius E., Fryns J. P., Cassiman J. J. MASA syndrome: new clinical features and linkage analysis using DNA probes. J Med Genet. 1990 Nov;27(11):688–692. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.11.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teebi A. S., Naguib K. K. Autosomal recessive nonsyndromal hydrocephalus. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Oct;31(2):467–470. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenema H., Carpenter N. J., Bakker E., Hofker M. H., Ward A. M., Pearson P. L. The fragile X syndrome in a large family. III. Investigations on linkage of flanking DNA markers with the fragile site Xq27. J Med Genet. 1987 Jul;24(7):413–421. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.7.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J., Brouwer O. F., Dijkstra I., Wilmink J. X-linked hydrocephalus. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Aug;27(4):921–928. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J., Dijkstra I., Van der Auwera B. J., Vits L., Coucke P., Raeymaekers P., Van Broeckhoven C., Consalez G. G., Freeman S. B., Warren S. T. Assignment of X-linked hydrocephalus to Xq28 by linkage analysis. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J. Heterogeneity in familial hydrocephalus. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Oct;31(2):471–473. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J., Vits L., De Boulle K. MspI RFLP in the L1 CAM gene in Xq28. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5448–5448. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5448-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Davies K. E., Bell M. V., Huson S. M., Patterson M. N. MASA syndrome: further clinical delineation and chromosomal localisation. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00273999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeatman G. W. Mental retardation-clasped thumb syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):339–344. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]