Abstract
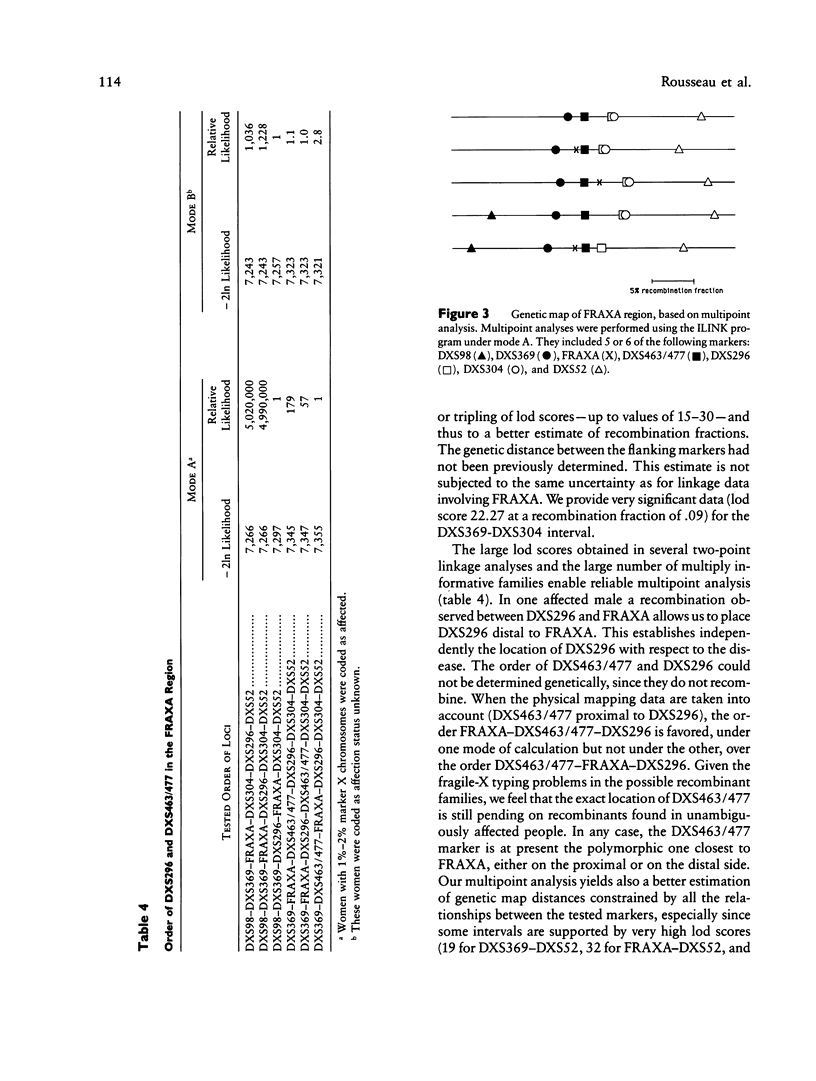
We report the validation and use of a cell hybrid panel which allowed us a rapid physical localization of new DNA probes in the vicinity of the fragile-X locus (FRAXA). Seven regions are defined by this panel, two of which lie between DXS369 and DXS296, until now the closest genetic markers that flank FRAXA. Of those two interesting regions, one is just distal to DXS369 and defined by probe 2-71 (DXS476), which is not polymorphic. The next one contains probes St677 (DXS463) and 2-34 (DXS477), which are within 130 kb and both detect TaqI RFLPs. The combined informativeness of these two probes is 30%. We cloned from an irradiation-reduced hybrid line another new polymorphic probe, Do33 (DXS465; 42% heterozygosity). This probe maps to the DXS296 region, proximal to a chromosomal breakpoint that corresponds to the Hunter syndrome locus (IDS). The physical order is thus Cen–DXS369–DXS476–(DXS463,DXS477)–(DXS296,DXS465)–IDS–DXS304–tel. We performed a linkage analysis for five of these markers in both the Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain families and in a large set of fragile-X families. This establishes that DXS296 is distal to FRAXA. The relative position of DXS463 and DXS477 with respect to FRAXA remains uncertain, but our results place them genetically halfway between DXS369 and DXS304. Thus the DXS463–DXS477 cluster defines presently either the closest proximal or the closest distal polymorphic marker with respect to FRAXA. The three new polymorphic probes described here have a combined heterozygosity of 60% and represent a major improvement for genetic analysis of fragile-X families, in particular for diagnostic applications.
Full text
PDF


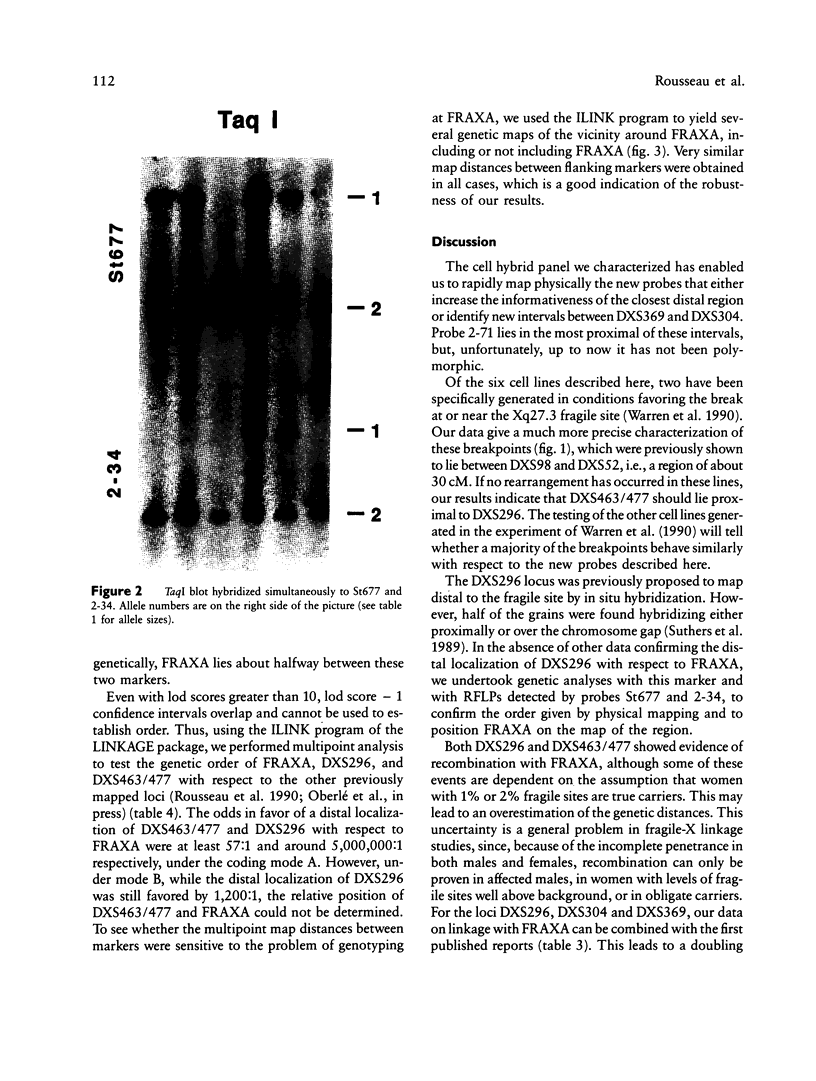
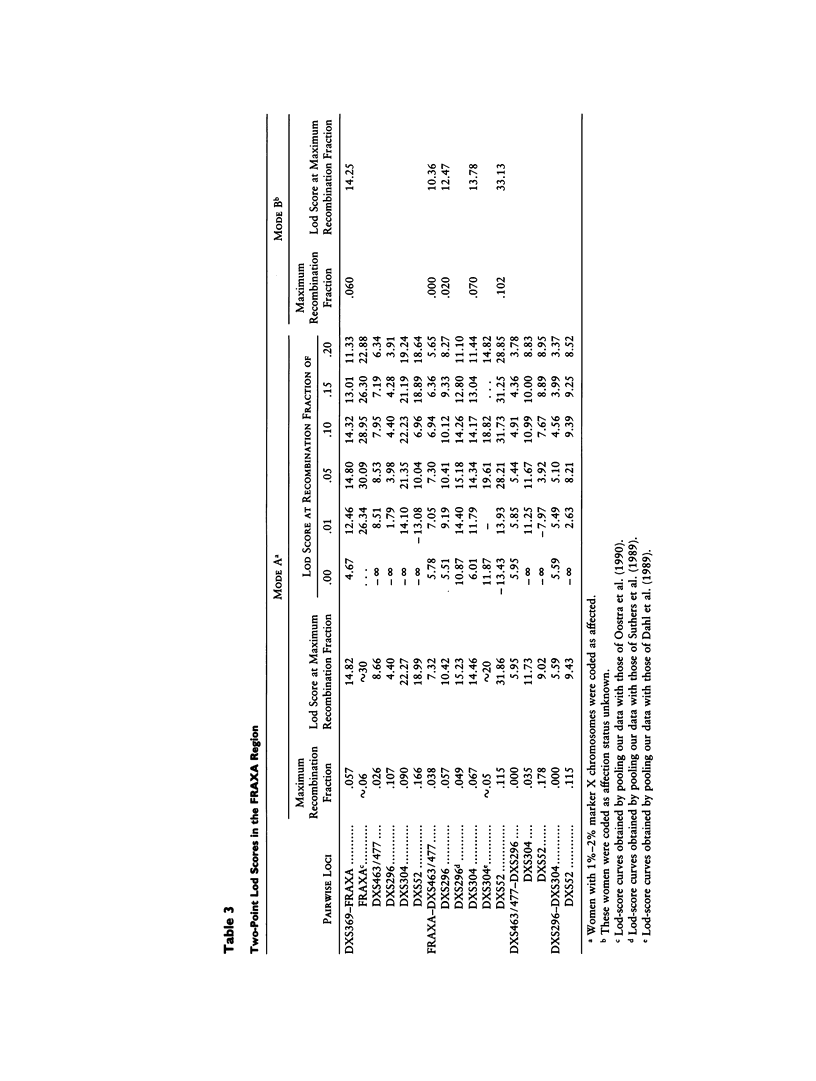


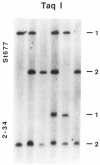
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham F., Hart K., Crolla J., Bobrow M., Francavilla M., Goodfellow P. N. A method for generating hybrids containing nonselected fragments of human chromosomes. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier J., Dutrillaux B., Garber P., Raoul O., Croquette M. F., Fourlinnie J. C., Maillard E. Evidence for a correlation between late replication and autosomal gene inactivation in a familial translocation t(X;21). Hum Genet. 1979 Jul 18;49(3):319–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00569351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Pritchard C. A., Uglum E., Casher D., Kobori J., Myers R. M. Segregation of the Huntington disease region of human chromosome 4 in a somatic cell hybrid. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Goonewardena P., Malmgren H., Gustavson K. H., Holmgren G., Seemanova E., Annerén G., Flood A., Pettersson U. Linkage analysis of families with fragile-X mental retardation, using a novel RFLP marker (DXS 304). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):304–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Smith T. A fundamental division in the Alu family of repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4775–4778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Ledbetter S. A., Corbo L., Victoria M. F., Ramírez-Solis R., Webster T. D., Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Alu polymerase chain reaction: a method for rapid isolation of human-specific sequences from complex DNA sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6686–6690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Ledbetter D. H. Fragile X syndrome: a unique mutation in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:109–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra B. A., Hupkes P. E., Perdon L. F., van Bennekom C. A., Bakker E., Halley D. J., Schmidt M., Du Sart D., Smits A., Wieringa B. New polymorphic DNA marker close to the fragile site FRAXA. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90457-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau F., Vincent A., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. New informative polymorphism at the DXS304 locus, a close distal marker for the fragile X locus. Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;84(3):263–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00200572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Callen D. F., Hyland V. J., Kozman H. M., Baker E., Eyre H., Harper P. S., Roberts S. H., Hors-Cayla M. C., Davies K. E. A new DNA marker tightly linked to the fragile X locus (FRAXA). Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1298–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.2573953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Hyland V. J., Callen D. F., Oberle I., Rocchi M., Thomas N. S., Morris C. P., Schwartz C. E., Schmidt M., Ropers H. H. Physical mapping of new DNA probes near the fragile X mutation (FRAXA) by using a panel of cell lines. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):187–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Dahl N., Oberlé I., Hanauer A., Mandel J. L., Malmgren H., Pettersson U. The polymorphic marker DXS304 is within 5 centimorgans of the fragile X locus. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):797–801. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Knight S. J., Peters J. F., Stayton C. L., Consalez G. G., Zhang F. P. Isolation of the human chromosomal band Xq28 within somatic cell hybrids by fragile X site breakage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3856–3860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]