Abstract
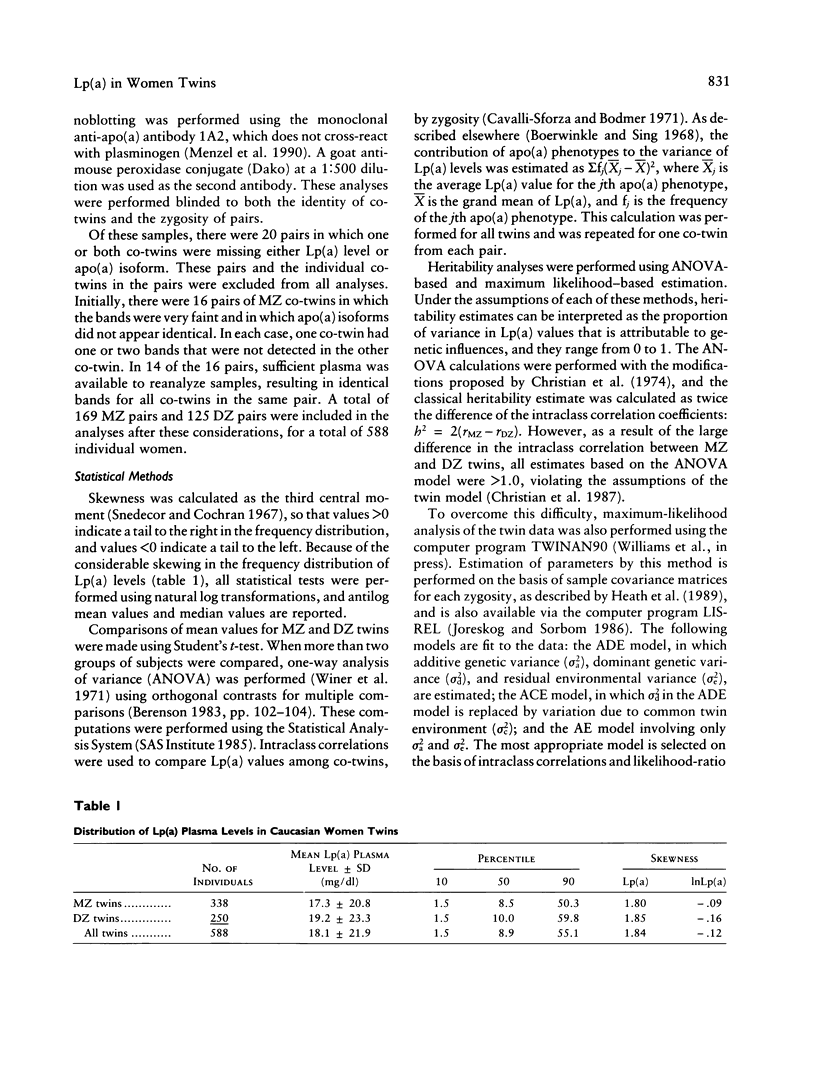
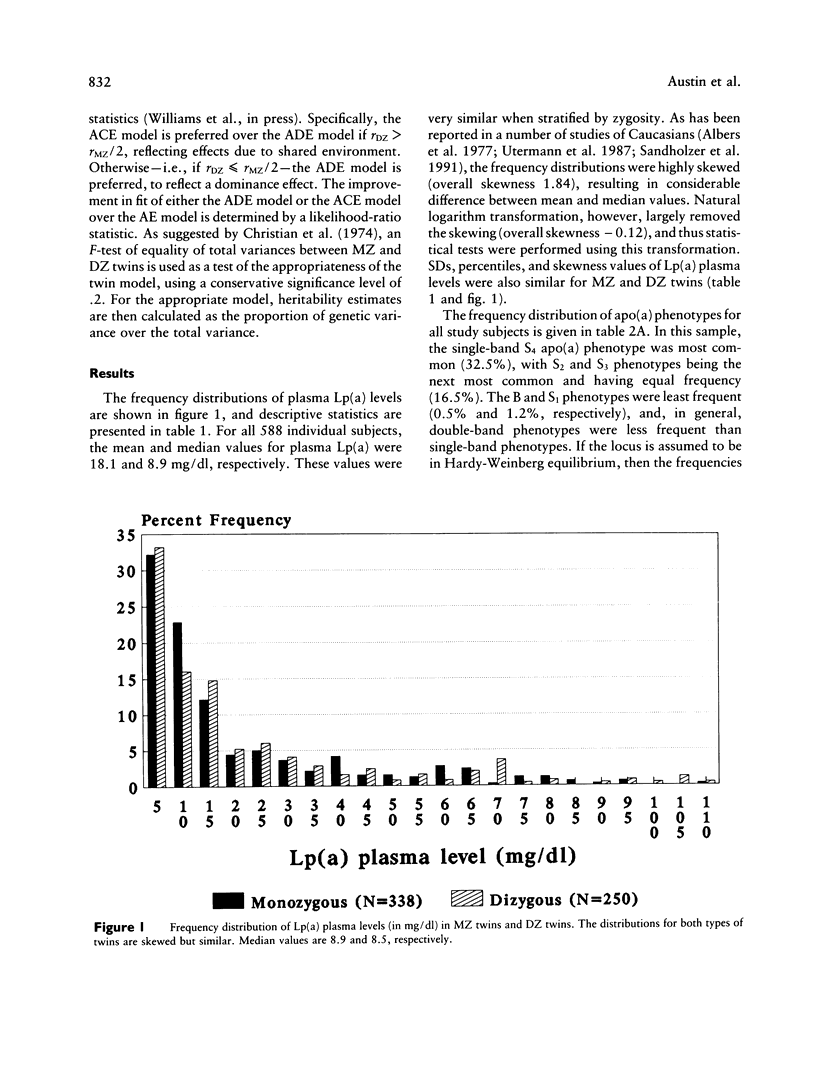
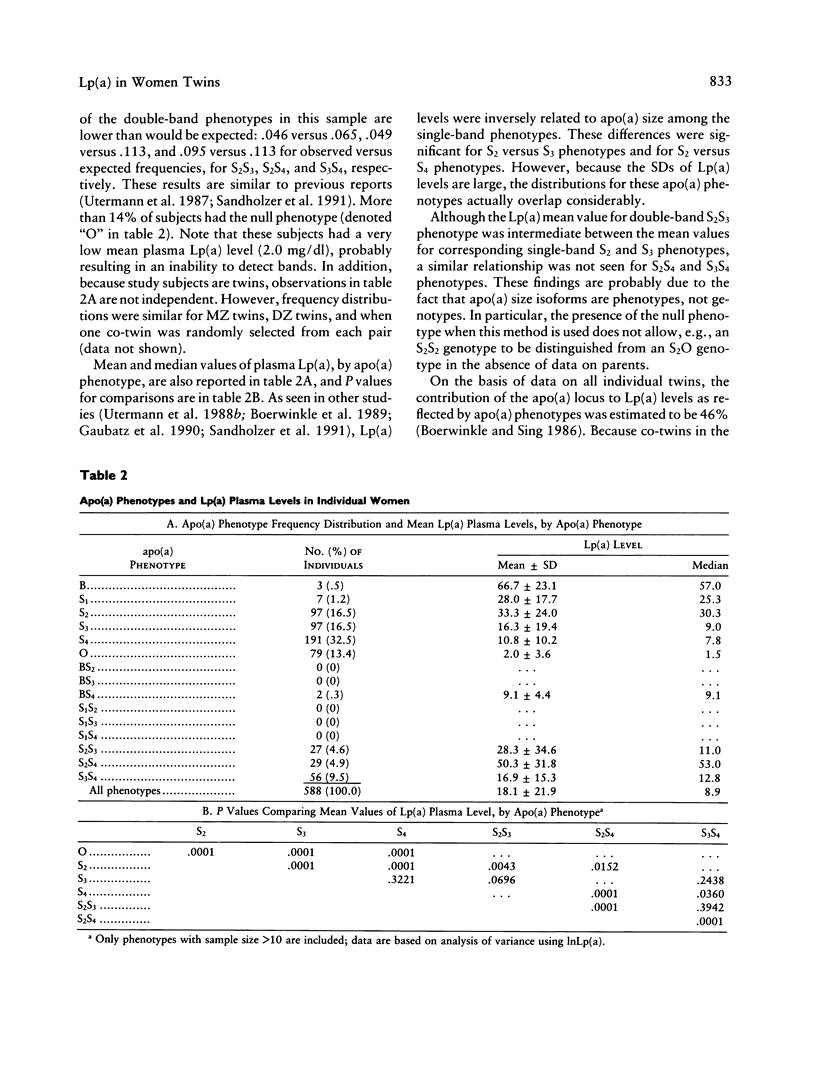
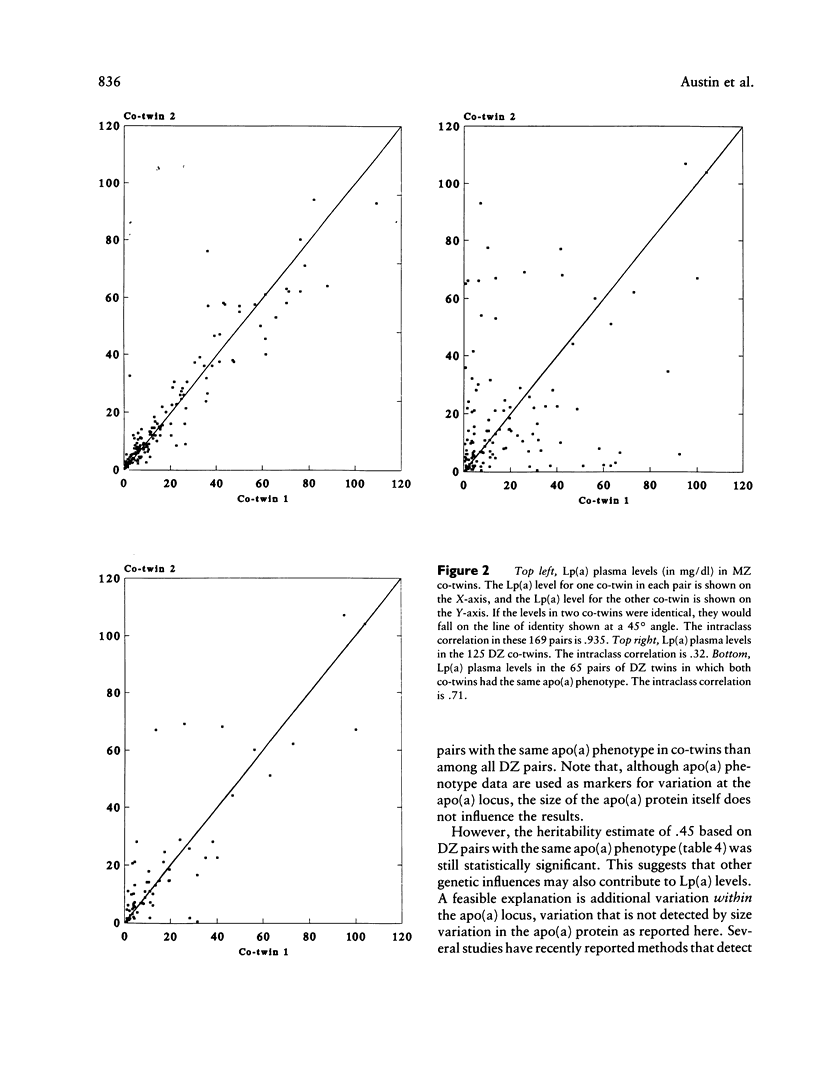
Lp(a) is a unique lipoprotein consisting of an LDL-like particle and a characteristic protein, apo(a). Increased levels of Lp(a) constitute a risk factor for coronary heart disease. Variation in the size of the apo(a) protein is a phenotype controlled by the apo(a) gene on chromosome 6 and is related to Lp(a) plasma levels. Based on 169 MZ and 125 DZ adult female twin pairs, this study's purpose was to estimate the proportion of the variation in Lp(a) levels that is due to genetic influences and to determine the extent to which the apo(a) locus explains this heritability. Lp(a) levels were significantly more similar in MZ twins than in DZ twins: mean co-twin differences were 3.9 +/- 5.7 mg/dl and 16.0 +/- 19.9 mg/dl (P less than .001), respectively. Intraclass correlations were .94 in MZ twins and .32 in DZ twins, resulting in a heritability estimate of .94 (P less than .001). Heritability was then calculated using only co-twins with the same apo(a) phenotype: the heritability estimate decreased to .45 but was still highly significant (P less than .001). Therefore, on the basis of heritability analysis of women twins, Lp(a) levels are almost entirely genetically controlled. Variation at the apo(a) locus contributes to this heritability, although other genetic factors could be involved.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Adolphson J. L., Hazzard W. R. Radioimmunoassay of human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. J., Wahl P., Hazzard W. R. Quantitative genetic studies of the human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. Biochem Genet. 1974 Jun;11(6):475–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00486079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin M. A., King M. C., Bawol R. D., Hulley S. B., Friedman G. D. Risk factors for coronary heart disease in adult female twins. Genetic heritability and shared environmental influences. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Feb;125(2):308–318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrolan N., Gavish D., Breslow J. L. Plasma lipoprotein(a) concentration is controlled by apolipoprotein(a) (apo(a)) protein size and the abundance of hepatic apo(a) mRNA in a cynomolgus monkey model. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13866–13872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K., Dahlén G., Børresen A. L. Lp(a) phenotypes, other lipoprotein parameters, and a family history of coronary heart disease in middle-aged males. Clin Genet. 1979 Nov;16(5):347–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Utermann G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00288277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Sing C. F. Bias of the contribution of single-locus effects to the variance of a quantitative trait. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;39(1):137–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Hamsten A., Asplund A. Pronounced lowering of serum levels of lipoprotein Lp(a) in hyperlipidaemic subjects treated with nicotinic acid. J Intern Med. 1989 Oct;226(4):271–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1989.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. C., Kang K. W., Norton J. J., Jr Choice of an estimate of genetic variance from twin data. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Mar;26(2):154–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsetti J. P., Sterry J. A., Sparks J. D., Sparks C. E., Weintraub M. Effect of weight loss on serum lipoprotein(a) concentrations in an obese population. Clin Chem. 1991 Jul;37(7):1191–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D. T., Hegele R. A., Hass P. E., Emi M., Wu L. L., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M., Williams R. R., White R. L., Lalouel J. M. Genetic linkage between lipoprotein(a) phenotype and a DNA polymorphism in the plasminogen gene. Genomics. 1988 Oct;3(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrington P. N., Ishola M., Hunt L., Arrol S., Bhatnagar D. Apolipoproteins (a), AI, and B and parental history in men with early onset ischaemic heart disease. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1070–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91895-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. L., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Tomlinson J. E., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M., Lusis A. J. The apolipoprotein(a) gene resides on human chromosome 6q26-27, in close proximity to the homologous gene for plasminogen. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):352–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00282175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz J. W., Ghanem K. I., Guevara J., Jr, Nava M. L., Patsch W., Morrisett J. D. Polymorphic forms of human apolipoprotein[a]: inheritance and relationship of their molecular weights to plasma levels of lipoprotein[a]. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):603–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurakar A., Hoeg J. M., Kostner G., Papadopoulos N. M., Brewer H. B., Jr Levels of lipoprotein Lp(a) decline with neomycin and niacin treatment. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Nov;57(2-3):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Wilson D. E., Edwards C. Q., Cannon W. N., Carmelli D., Williams R. R. The genetics of quantitative plasma Lp(a): analysis of a large pedigree. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):179–188. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath A. C., Neale M. C., Hewitt J. K., Eaves L. J., Fulker D. W. Testing structural equation models for twin data using LISREL. Behav Genet. 1989 Jan;19(1):9–35. doi: 10.1007/BF01065881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt D., Milner J., Owen A. R., Breckenridge W. C., Maguire G. F., Jones G. J., Little J. A. The inheritance of sinking-pre-beta lipoprotein and its relation to the Lp(a) antigen. Clin Genet. 1982 May;21(5):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. C., Hasstedt S. J., Kuida H., Stults B. M., Hopkins P. N., Williams R. R. Genetic heritability and common environmental components of resting and stressed blood pressures, lipids, and body mass index in Utah pedigrees and twins. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Mar;129(3):625–638. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iselius L., Dahlén G., de Faire U., Lundman T. Complex segregation analysis of the Lp(a)/pre-beta 1-lipoprotein trait. Clin Genet. 1981 Aug;20(2):147–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb01820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauhiainen M., Koskinen P., Ehnholm C., Frick M. H., Mänttäri M., Manninen V., Huttunen J. K. Lipoprotein (a) and coronary heart disease risk: a nested case-control study of the Helsinki Heart Study participants. Atherosclerosis. 1991 Jul;89(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90007-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauhiainen M., Metso J., Koskinen P., Ehnholm C. Characterization of the enzyme activity of human plasma lipoprotein (a) using synthetic peptide substrates. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):491–496. doi: 10.1042/bj2740491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamboh M. I., Ferrell R. E., Kottke B. A. Expressed hypervariable polymorphism of apolipoprotein (a). Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):1063–1074. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Avogaro P., Cazzolato G., Marth E., Bittolo-Bon G., Qunici G. B. Lipoprotein Lp(a) and the risk for myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jan-Feb;38(1-2):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner C., Boerwinkle E., Leffert C. C., Rahmig T., Hobbs H. H. Molecular basis of apolipoprotein (a) isoform size heterogeneity as revealed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2153–2161. doi: 10.1172/JCI115248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamon-Fava S., Jimenez D., Christian J. C., Fabsitz R. R., Reed T., Carmelli D., Castelli W. P., Ordovas J. M., Wilson P. W., Schaefer E. J. The NHLBI Twin Study: heritability of apolipoprotein A-I, B, and low density lipoprotein subclasses and concordance for lipoprotein(a). Atherosclerosis. 1991 Nov;91(1-2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Gersdorf E., Menzel H. J., Duba C., Cleve H., Humphries S., Utermann G. The gene for the Lp(a)-specific glycoprotein is closely linked to the gene for plasminogen on chromosome 6. Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;81(2):149–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00293891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Dieplinger H., Lackner C., Hoppichler F., Lloyd J. K., Muller D. R., Labeur C., Talmud P. J., Utermann G. Abetalipoproteinemia with an ApoB-100-lipoprotein(a) glycoprotein complex in plasma. Indication for an assembly defect. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):981–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Fless G. M., Levin E. G., Scanu A. M., Plow E. F. A potential basis for the thrombotic risks associated with lipoprotein(a). Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):301–303. doi: 10.1038/339301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Berg K., Dahlen G., Ferrell R. E., Rhoads G. G. Genetics of the Lp lipoprotein in Japanese-Americans. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai A., Miyahara T., Fujimoto N., Matsuda M., Kameyama M. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Feb;59(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepin J. M., O'Neil J. A., Hoff H. F. Quantification of apo[a] and apoB in human atherosclerotic lesions. J Lipid Res. 1991 Feb;32(2):317–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath M., Niendorf A., Reblin T., Dietel M., Krebber H. J., Beisiegel U. Detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall of 107 coronary bypass patients. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):579–592. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Dahlen G., Berg K., Morton N. E., Dannenberg A. L. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1986 Nov 14;256(18):2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengren A., Wilhelmsen L., Eriksson E., Risberg B., Wedel H. Lipoprotein (a) and coronary heart disease: a prospective case-control study in a general population sample of middle aged men. BMJ. 1990 Dec 1;301(6763):1248–1251. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6763.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouy D., Grailhe P., Nigon F., Chapman J., Anglés-Cano E. Lipoprotein(a) impairs generation of plasmin by fibrin-bound tissue-type plasminogen activator. In vitro studies in a plasma milieu. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):629–638. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Jauhiainen M., Zardi L., Vaheri A., Ehnholm C. Lipoprotein(a) binds to fibronectin and has serine proteinase activity capable of cleaving it. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4035–4040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandholzer C., Hallman D. M., Saha N., Sigurdsson G., Lackner C., Császár A., Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Effects of the apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein(a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):607–614. doi: 10.1007/BF00201550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandkamp M., Funke H., Schulte H., Köhler E., Assmann G. Lipoprotein(a) is an independent risk factor for myocardial infarction at a young age. Clin Chem. 1990 Jan;36(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI114625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing C. F., Schultz J. S., Shreffler D. C. The genetics of the Lp antigen. II. A family study and proposed models of genetic control. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;38(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundell I. B., Nilsson T. K., Hallmans G., Hellsten G., Dahlén G. H. Interrelationships between plasma levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor, tissue plasminogen activator, lipoprotein (a), and established cardiovascular risk factors in a north Swedish population. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Nov;80(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Duba C., Menzel H. J. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. II. Inheritance of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):47–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00291233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Kraft H. G., Menzel H. J., Hopferwieser T., Seitz C. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. I. Relation of LP(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00291232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a). Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):904–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2530631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W., Hitchens J., Magnani H. N., Khan M. A study of methods of identification and estimation of Lp(a) lipoprotein and of its significance in health, hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1974 Sep-Oct;20(2):323–346. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(74)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., Guttormsen S. A., Schultz J. S. Linkage between the loci for the Lp(a) lipoprotein (LP) and plasminogen (PLG). Hum Genet. 1988 May;79(1):80–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00291716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenker G., Költringer P., Boné G., Niederkorn K., Pfeiffer K., Jürgens G. Lipoprotein(a) as a strong indicator for cerebrovascular disease. Stroke. 1986 Sep-Oct;17(5):942–945. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.5.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


