Abstract
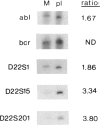
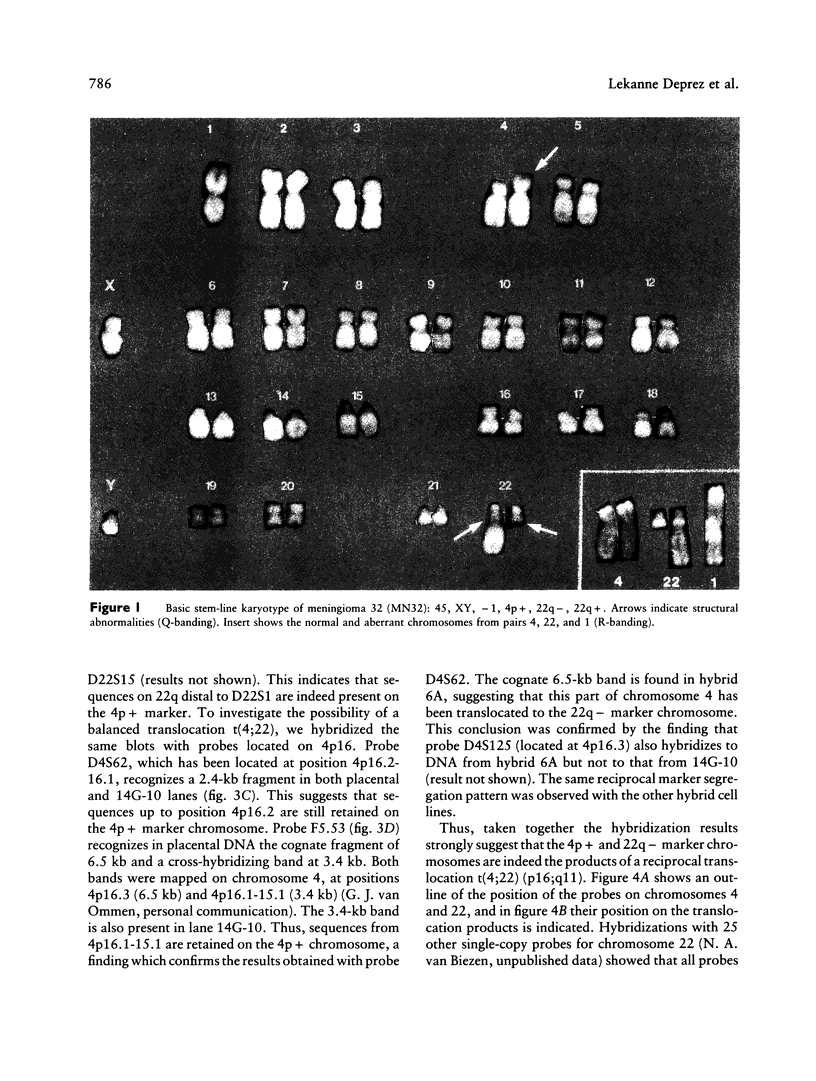
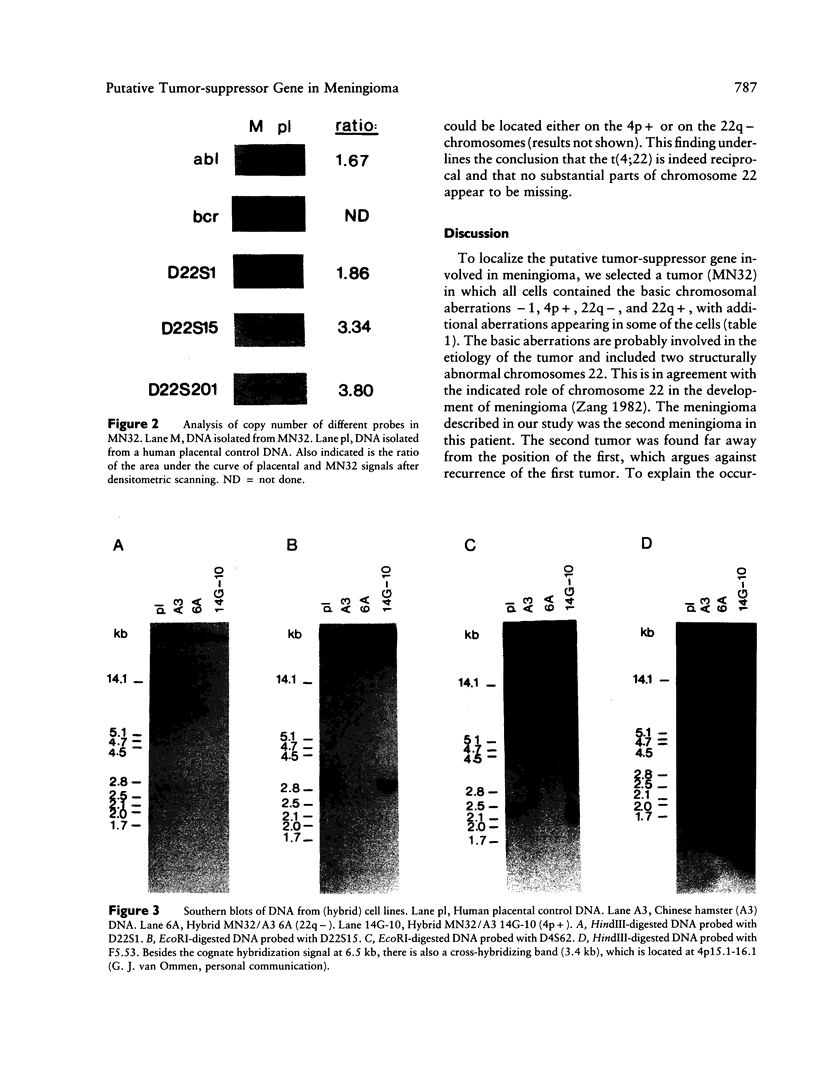
Cytogenetic analysis of meningioma cells from one particular patient (MN32) displayed the stem-line karyo-type 45, XY, -1, 4p+, 22q-, 22q+, which thus had rearrangements of both chromosomes 22. The 22q+ marker appeared as a dicentric: 22 pter----q11::1p11----qter. The reciprocal product of this translocation has presumably been lost because it lacked a centromere. The 22q- chromosome also appeared to have lost sequences distal to band q11. We assumed that this marker could have been the result of a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 4 and 22. To investigate the 4p+ and 22q- chromosomes in more detail, human-hamster somatic cell hybrids were constructed that segregated the 22q- and 4p+ chromosomes. Southern blot analysis with DNA from these hybrids showed that sequences from 22q were indeed translocated to 4p+ and that reciprocally sequences from 4p were translocated to 22q-, demonstrating a balanced t(4;22)(p16;q11). On the basis of these results we presume that in this tumor a tumor-suppressor gene is deleted in the case of the 22q+ marker and that the t(4;22) disrupts the second allele of this gene. The latter translocation was mapped between D22S1 and D22S15, a distance of 1 cM on the linkage map of this chromosome. The area in which we have located the translocation is within the region where the gene predisposing to neurofibromatosis 2 has been mapped.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al Saadi A., Latimer F., Madercic M., Robbins T. Cytogenetic studies of human brain tumors and their clinical significance. II. Meningioma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 May;26(1):127–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Skraastad M. I., Fisser-Groen Y. M., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Two additional RFLPs at the D4S10 locus, useful for Huntington's disease (HD)-family studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9100–9100. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bućan M., Zimmer M., Whaley W. L., Poustka A., Youngman S., Allitto B. A., Ormondroyd E., Smith B., Pohl T. M., MacDonald M. Physical maps of 4p16.3, the area expected to contain the Huntington disease mutation. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90442-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casalone R., Granata P., Simi P., Tarantino E., Butti G., Buonaguidi R., Faggionato F., Knerich R., Solero L. Recessive cancer genes in meningiomas? An analysis of 31 cases. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Jul;27(1):145–159. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casartelli C., Rogatto S. R., Barbieri Neto J. Karyotypic evolution of human meningioma. Progression through malignancy. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Jul 1;40(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Koufos A., Hansen M. F. Recessive mutant genes predisposing to human cancer. Mutat Res. 1986 Jul;168(1):3–14. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(86)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. V., Martin G. R., Nadeau J. H., Haines J. L., Bucan M., Kozak C. A., MacDonald M. E., Lockyer J. L., Ledley F. D., Woo S. L. Synteny on mouse chromosome 5 of homologs for human DNA loci linked to the Huntington disease gene. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumanski J. P., Carlbom E., Collins V. P., Nordenskjöld M. Deletion mapping of a locus on human chromosome 22 involved in the oncogenesis of meningioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9275–9279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessler M., Poustka A., Cavenee W., Neve R. L., Orkin S. H., Bruns G. A. Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):774–778. doi: 10.1038/343774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geurts van Kessel A. H., ten Brinke H., Boere W. A., den Boer W. C., de Groot P. G., Hagemeijer A., Meera Khan P., Pearson P. L. Characterization of the Philadelphia chromosome by gene mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1981;30(2):83–91. doi: 10.1159/000131595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Stephenson J. R. The human v-abl cellular homologue. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):57–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stam K., Groffen J., de Klein A., Grosveld G. Structural organization of the bcr gene and its role in the Ph' translocation. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):758–761. doi: 10.1038/315758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julier C., Lathrop G. M., Reghis A., Szajnert M. F., Lalouel J. M., Kaplan J. C. A linkage and physical map of chromosome 22, and some applications to gene mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):297–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuyama J., Papenhausen P. R., Herz F., Gazivoda P., Hirano A., Koss L. G. Chromosome abnormalities in meningiomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 May;22(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koper J. W., Foekens J. A., Braakman R., Lamberts S. W. Effects of progesterone on the response to epidermal growth factor and other growth factors in cultured human meningioma cells. Cancer Res. 1990 May 1;50(9):2604–2607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltby E. L., Ironside J. W., Battersby R. D. Cytogenetic studies in 50 meningiomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Apr;31(2):199–210. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon C., Thiele C. J., Ross R. A., Kwan M., Triche T. J., Miser J. S., Israel M. A. Indistinguishable patterns of protooncogene expression in two distinct but closely related tumors: Ewing's sarcoma and neuroepithelioma. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 1;48(15):4307–4311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meese E., Blin N., Zang K. D. Loss of heterozygosity and the origin of meningioma. Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;77(4):349–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00291425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Culver M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pYNZ32) on chromosome 4p [D4S125]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4186–4186. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsgård L., Rønne M., Schrøder H. D. Cytogenetic studies of 19 meningiomas and their clinical significance. I. Anticancer Res. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston-Martin S., Paganini-Hill A., Henderson B. E., Pike M. C., Wood C. Case-control study of intracranial meningiomas in women in Los Angeles County, California. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Jul;65(1):67–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston-Martin S., Yu M. C., Henderson B. E., Roberts C. Risk factors for meningiomas in men in Los Angeles County. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 May;70(5):863–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey J. A., Bello M. J., de Campos J. M., Kusak E., Moreno S. Chromosomal involvement secondary to -22 in human meningiomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jul 15;33(2):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose E. A., Glaser T., Jones C., Smith C. L., Lewis W. H., Call K. M., Minden M., Champagne E., Bonetta L., Yeger H. Complete physical map of the WAGR region of 11p13 localizes a candidate Wilms' tumor gene. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90600-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G. A., Haines J. L., Bazanowski A., Colella-Crowley A., Trofatter J. A., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. A genetic linkage map of the long arm of human chromosome 22. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G. A., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L., Bazanowsky A., Patterson D., Gusella J. F. D22S15--a fetal brain cDNA with BanII and SacI RFLP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1646–1646. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G. A., Seizinger B. R., Wertelecki W., Haines J. L., Superneau D. W., Martuza R. L., Gusella J. F. Flanking markers bracket the neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) gene on chromosome 22. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):323–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Martuza R. L., Gusella J. F. Loss of genes on chromosome 22 in tumorigenesis of human acoustic neuroma. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):644–647. doi: 10.1038/322644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Rouleau G., Ozelius L. J., Lane A. H., St George-Hyslop P., Huson S., Gusella J. F., Martuza R. L. Common pathogenetic mechanism for three tumor types in bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):317–319. doi: 10.1126/science.3105060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Harper M. E., Sawyer J., Singer M. F., McBride O. W. Localization of a unique DNA sequence to band p16 of human chromosome 4. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;45(2):75–79. doi: 10.1159/000132433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turc-Carel C., Aurias A., Mugneret F., Lizard S., Sidaner I., Volk C., Thiery J. P., Olschwang S., Philip I., Berger M. P. Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. I. An evaluation of 85 cases of remarkable consistency of t(11;22)(q24;q12). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jun;32(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Xu G., Cawthon R. M., Stevens J., Wolff R. K., Culver M., Carey J. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90252-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Oncogenes, antioncogenes, and the molecular bases of multistep carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 15;49(14):3713–3721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P., Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Blanchetot A. Organization of the human myoglobin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):439–446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertelecki W., Rouleau G. A., Superneau D. W., Forehand L. W., Williams J. P., Haines J. L., Gusella J. F. Neurofibromatosis 2: clinical and DNA linkage studies of a large kindred. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 4;319(5):278–283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808043190505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zang K. D. Cytological and cytogenetical studies on human meningioma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1982 Jul;6(3):249–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(82)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F. R., Delattre O., Rouleau G., Couturier J., Lefrançois, Thomas G., Aurias A. The neuroepithelioma breakpoint on chromosome 22 is proximal to the meningioma locus. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):174–177. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90463-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]