Abstract
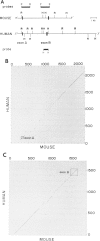
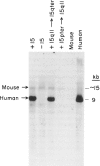
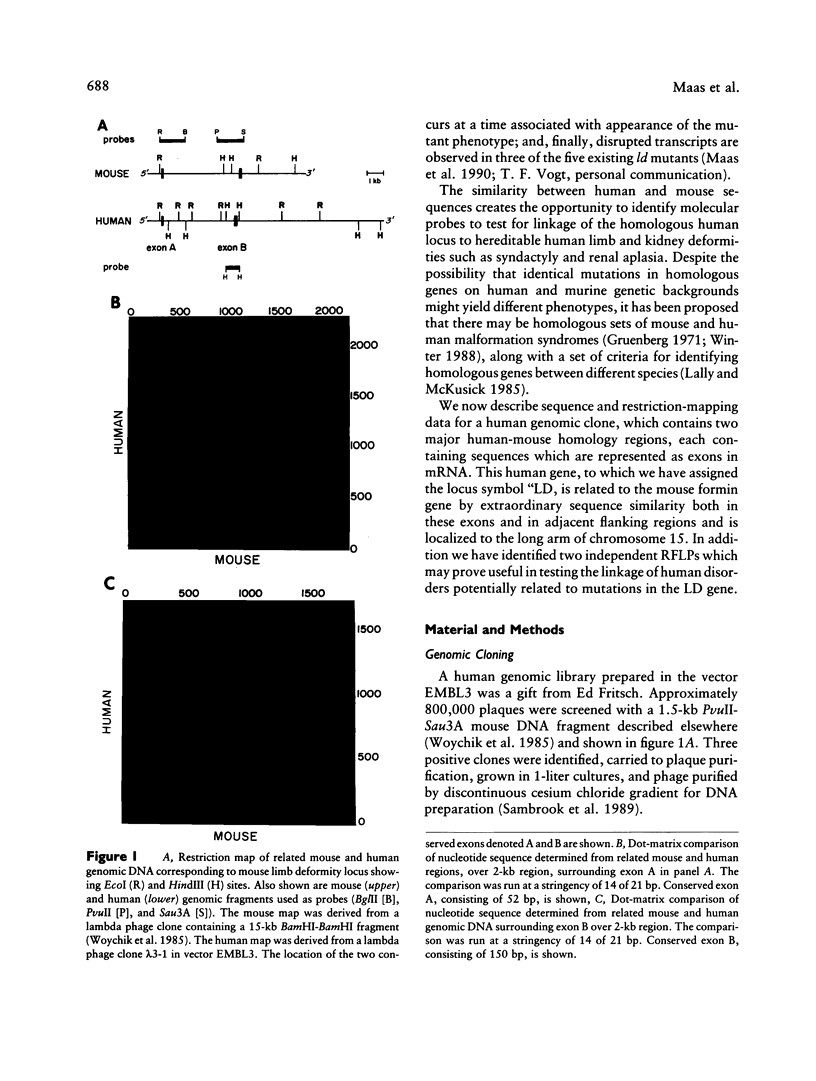
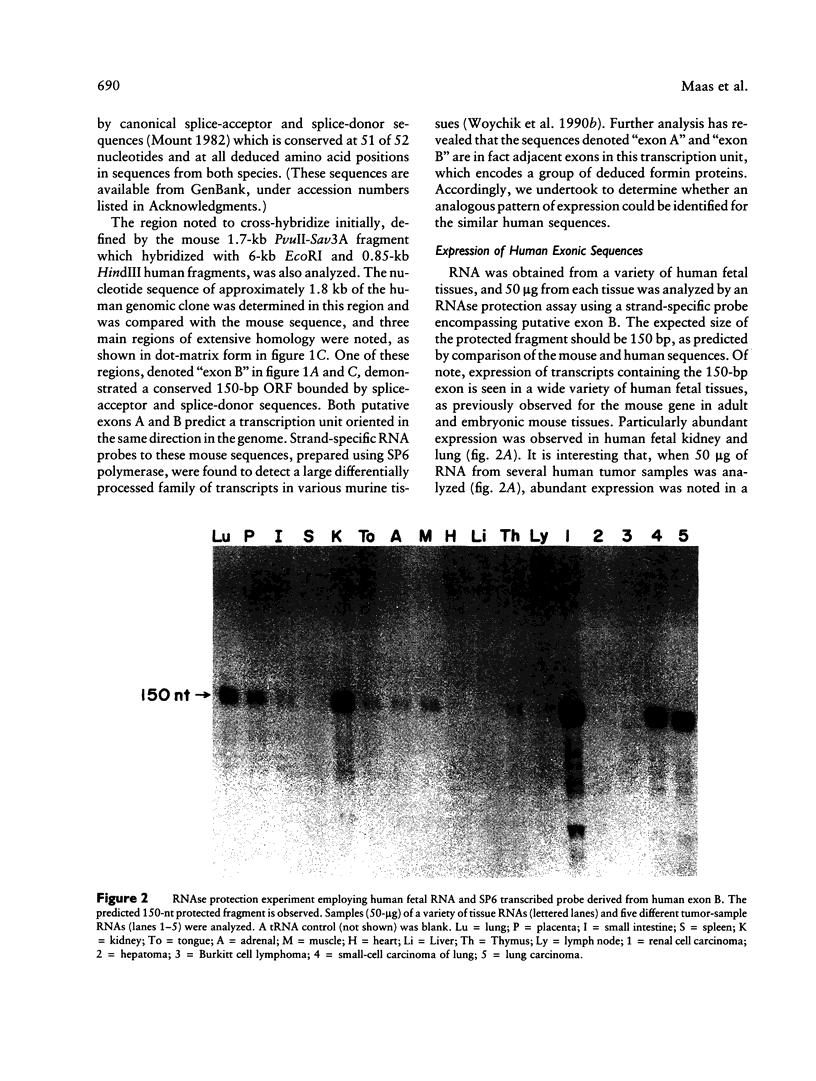
The murine limb deformity (ld) locus resides on mouse chromosome 2 and gives rise to a recessively inherited, characteristic limb deformity/renal aplasia phenotype. In this locus in the mouse, a gene, termed the "formin" gene, has been identified which encodes an array of differentially processed transcripts in both adult and embryonic tissues. A set of these transcripts are disrupted in independent mutant mouse ld alleles. We wish to report the isolation of a human genomic clone which is homologous to the mouse formin gene by virtue of sequence comparison and expression of conserved exons. Among human fetal tissues analyzed, the kidney appears to be a major site of expression. This human gene, LD, maps to chromosome 15q11----qter in mouse human somatic cell hybrids and, specifically, to 15q13----q14 by chromosomal in situ hybridization. This localization establishes both LD and beta 2-microglobulin as syntenic genes on mouse chromosome 2 and human chromosome 15 and implies the interspecies conservation of the region between them. In addition, we identify in the human locus two frequently occurring DNA polymorphisms which can be used to test the linkage of LD to known human dysmorphoses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde F., Gómez S., Massa C. Asociación malformativa acra y renal (polisindactilia dominante y duplicidad pieloureteral). An Esp Pediatr. 1978 Mar;11(3):237–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Donlon T. A. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 14 and 15. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):280–298. doi: 10.1159/000132795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel B., Nachman R., Aronson N., Weiss H. Congenital solitary kidney: a review of 74 cases. J Urol. 1974 Mar;111(3):394–397. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59974-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T., Lane J., Housman D. A mouse model of the aniridia-Wilms tumor deletion syndrome. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):823–827. doi: 10.1126/science.2173141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinebrecht J., Selow J., Winkler W. The mouse mutant limb-deformity (ld). Anat Anz. 1982;152(4):313–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., McKusick V. A. Report of the Committee on Comparative Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):536–566. doi: 10.1159/000132187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lurie I. W., Cherstvoy E. D. Renal agenesis as a diagnostic feature of the cryptophthalmos-syndactyly syndrome. Clin Genet. 1984 Jun;25(6):528–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mass R. L., Zeller R., Woychik R. P., Vogt T. F., Leder P. Disruption of formin-encoding transcripts in two mutant limb deformity alleles. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):853–855. doi: 10.1038/346853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai H., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Taggart R. T. Assignment of the pepsinogen gene complex (PGA) to human chromosome region 11q13 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(3-4):215–217. doi: 10.1159/000132324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. A., Meisel-Stosiek M. Present nosology of the Cenani-Lenz type of syndactyly. Clin Genet. 1982 Jan;21(1):74–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb02083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A., Haley L. L., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Cooper E. S., Goggin A. P. Assignment of the beta-glucuronidase structural gene to the pter leads to q22 region of chromosome 7 in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;21(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1159/000130882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B. Human genome organization of enzyme loci and metabolic diseases. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1983;10:323–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. Mapping the human genome, cloned genes, DNA polymorphisms, and inherited disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1982;12:341–452. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8315-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T., Eddy R., Haley L., Byers M., Henry M., Fujita T., Matsui H., Taniguchi T. Interleukin 2 (IL2) is assigned to human chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 May;10(3):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01535253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M. Malformation syndromes: a review of mouse/human homology. J Med Genet. 1988 Jul;25(7):480–487. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.7.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Generoso W. M., Russell L. B., Cain K. T., Cacheiro N. L., Bultman S. J., Selby P. B., Dickinson M. E., Hogan B. L., Rutledge J. C. Molecular and genetic characterization of a radiation-induced structural rearrangement in mouse chromosome 2 causing mutations at the limb deformity and agouti loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2588–2592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Maas R. L., Zeller R., Vogt T. F., Leder P. 'Formins': proteins deduced from the alternative transcripts of the limb deformity gene. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):850–853. doi: 10.1038/346850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Stewart T. A., Davis L. G., D'Eustachio P., Leder P. An inherited limb deformity created by insertional mutagenesis in a transgenic mouse. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):36–40. doi: 10.1038/318036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Jackson-Grusby L., Leder P. The limb deformity gene is required for apical ectodermal ridge differentiation and anteroposterior limb pattern formation. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1481–1492. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]