Abstract
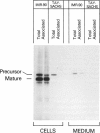
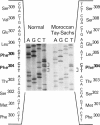
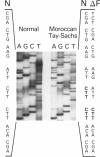
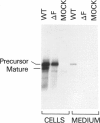
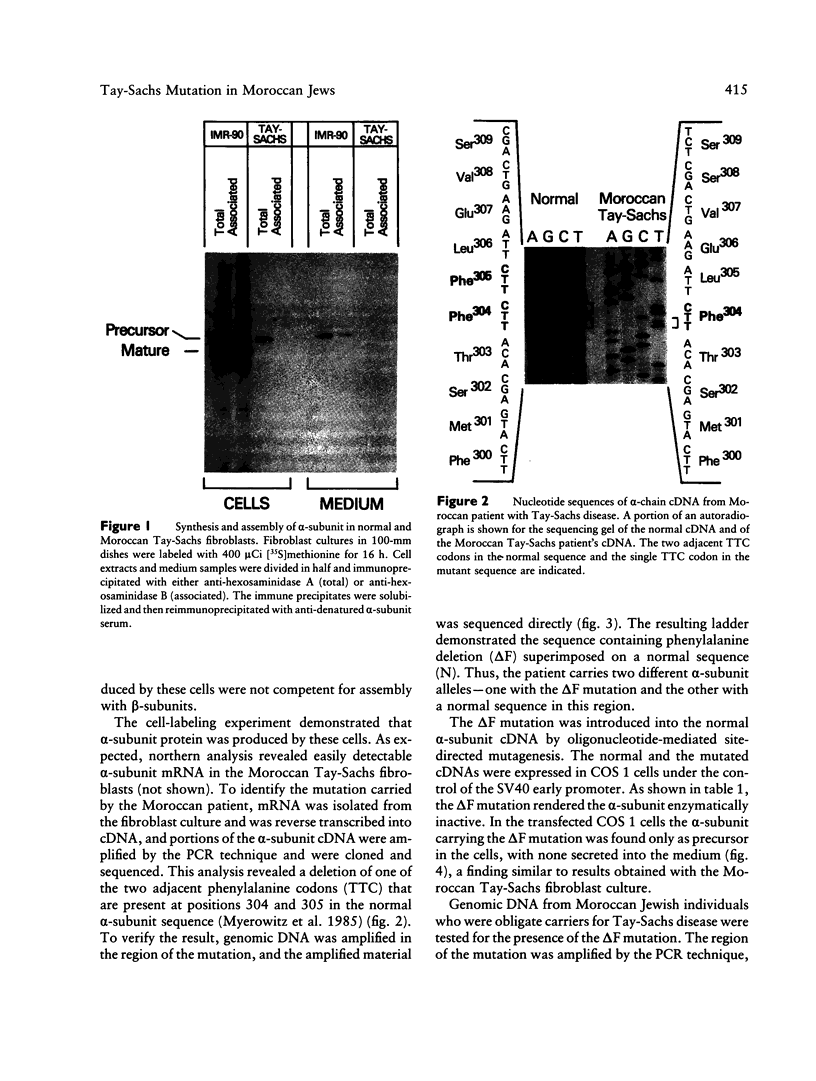
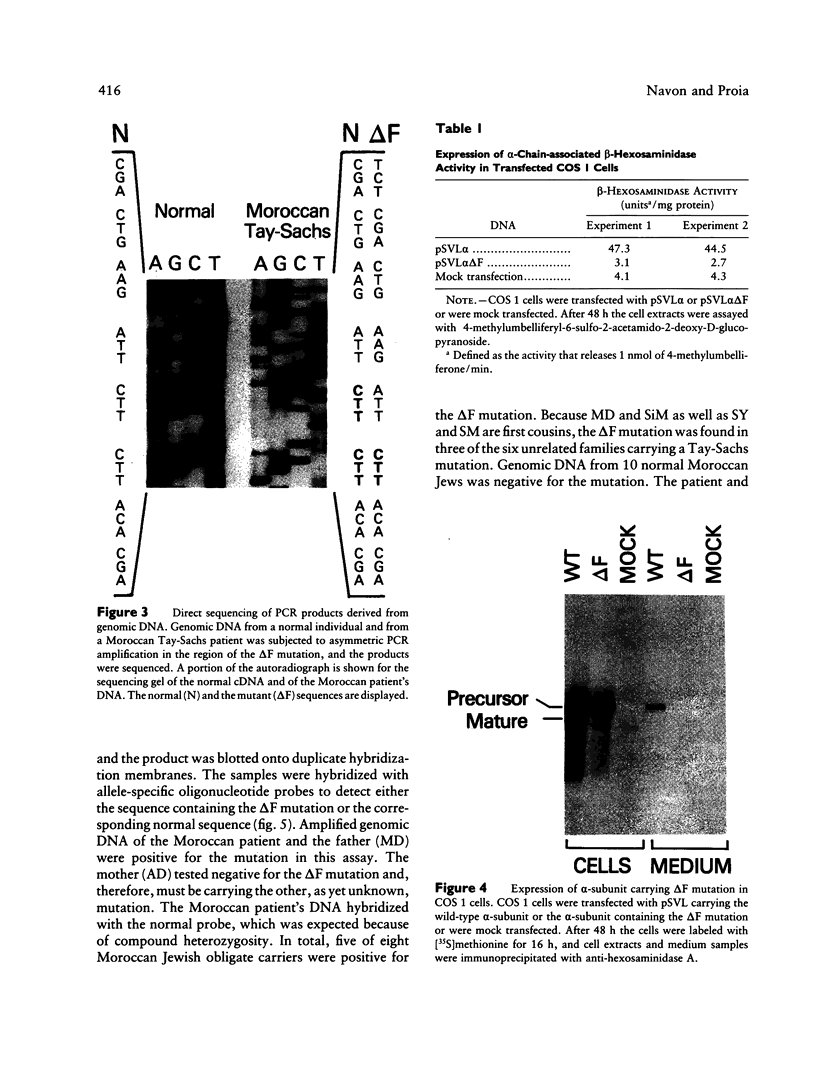
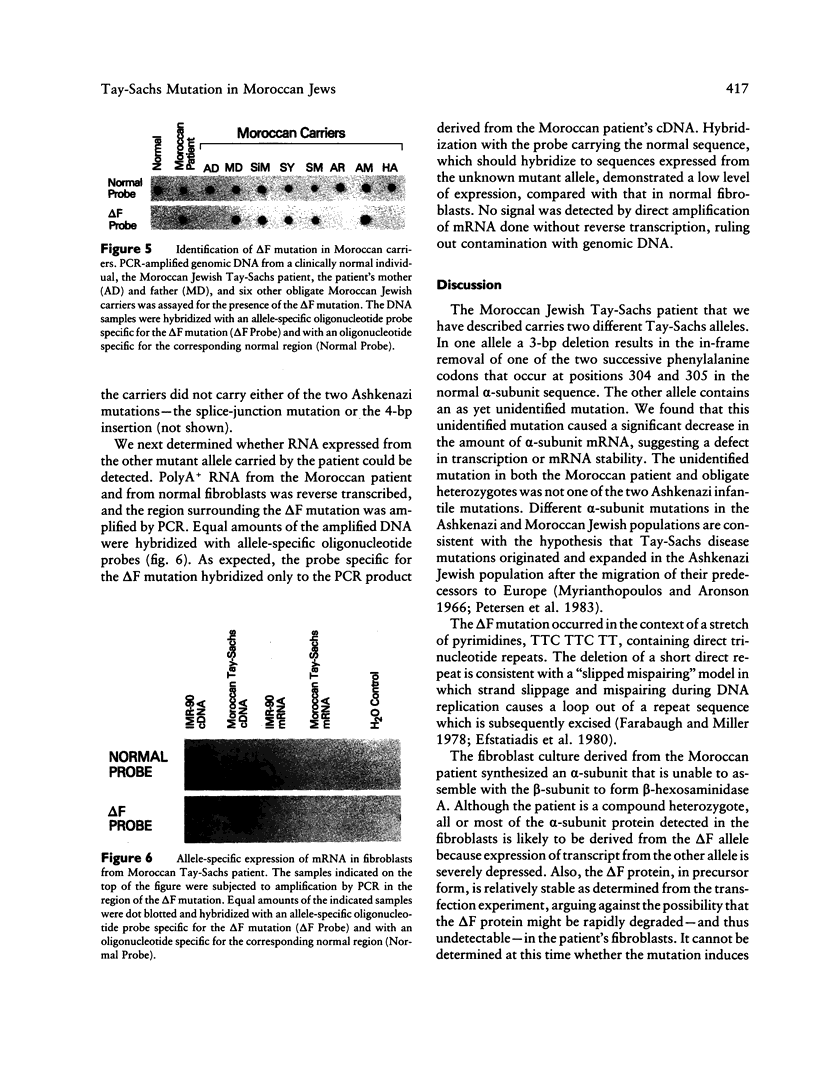
Tay-Sachs disease is an inherited lysosomal storage disorder caused by defects in the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-subunit gene. The carrier frequency for Tay-Sachs disease is significantly elevated in both the Ashkenazi Jewish and Moroccan Jewish populations but not in other Jewish groups. We have found that the mutations underlying Tay-Sachs disease in Ashkenazi and Moroccan Jews are different. Analysis of a Moroccan Jewish Tay-Sachs patient had revealed an in-frame deletion (delta F) of one of the two adjacent phenylalanine codons that are present at positions 304 and 305 in the alpha-subunit sequence. The mutation impairs the subunit assembly of beta-hexosaminidase A, resulting in an absence of enzyme activity. The Moroccan patient was found also to carry, in the other alpha-subunit allele, a different, and as yet unidentified, mutation which causes a deficit of mRNA. Analysis of obligate carriers from six unrelated Moroccan Jewish families showed that three harbor the delta F mutation, raising the possibility that this defect may be a prevalent mutation in this ethnic group.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andermann E., Scriver C. R., Wolfe L. S., Dansky L., Andermann F. Genetic variants of Tay-Sachs disease: Tay-Sachs disease and Sandhoff's disease in French Canadians, juvenile Tay-Sachs disease in Lebanese Canadians, and a Tay-Sachs screening program in the French-Canadian population. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1977;18:161–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpaia E., Dumbrille-Ross A., Maler T., Neote K., Tropak M., Troxel C., Stirling J. L., Pitts J. S., Bapat B., Lamhonwah A. M. Identification of an altered splice site in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs disease. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):85–86. doi: 10.1038/333085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach G., Navon R., Zeigler M., Beyth Y., Porter B., Cohen M. M. Tay-Sachs disease in a Moroccan Jewish family: a possible new mutation. Isr J Med Sci. 1976 Dec;12(12):1432–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bapat B., Ethier M., Neote K., Mahuran D., Gravel R. A. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding the beta-subunit of mouse beta-hexosaminidase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 12;237(1-2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. R., Zassenhaus H. P., Kaplan A. Molecular cloning of the cDNA which encodes beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase A from Dictyostelium discoideum. Complete amino acid sequence and homology with the human enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16823–16829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Taylor S. I. A nonsense mutation causing decreased levels of insulin receptor mRNA: detection by a simplified technique for direct sequencing of genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., Mahuran D. J., Neote K., Klavins M. H., O'Dowd B. F., Tropak M., Willard H. F., Anderson M. J., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the alpha-subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Extensive homology between the alpha- and beta-subunits and studies on Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8407–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Costigan F. C. The major defect in Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease is an insertion in the gene for the alpha-chain of beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18587–18589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. A deletion involving Alu sequences in the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain gene of French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15396–15399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Piekarz R., Neufeld E. F., Shows T. B., Suzuki K. Human beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain: coding sequence and homology with the beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7830–7834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. Splice junction mutation in some Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease: evidence against a single defect within this ethnic group. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3955–3959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrianthopoulos N. C., Aronson S. M. Population dynamics of Tay-Sachs disease. I. Reproductive fitness and selection. Am J Hum Genet. 1966 Jul;18(4):313–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Proia R. L. The mutations in Ashkenazi Jews with adult GM2 gangliosidosis, the adult form of Tay-Sachs disease. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1471–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.2522679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F. Natural history and inherited disorders of a lysosomal enzyme, beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):10927–10930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Suzuki K. A splicing defect due to an exon-intron junctional mutation results in abnormal beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain mRNAs in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with Tay-Sachs disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):463–469. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paw B. H., Tieu P. T., Kaback M. M., Lim J., Neufeld E. F. Frequency of three Hex A mutant alleles among Jewish and non-Jewish carriers identified in a Tay-Sachs screening program. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;47(4):698–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G. M., Rotter J. I., Cantor R. M., Field L. L., Greenwald S., Lim J. S., Roy C., Schoenfeld V., Lowden J. A., Kaback M. M. The Tay-Sachs disease gene in North American Jewish populations: geographic variations and origin. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Nov;35(6):1258–1269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L. Gene encoding the human beta-hexosaminidase beta chain: extensive homology of intron placement in the alpha- and beta-chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1883–1887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., d'Azzo A., Neufeld E. F. Association of alpha- and beta-subunits during the biosynthesis of beta-hexosaminidase in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3350–3354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggs-Raine B. L., Feigenbaum A. S., Natowicz M., Skomorowski M. A., Schuster S. M., Clarke J. T., Mahuran D. J., Kolodny E. H., Gravel R. A. Screening for carriers of Tay-Sachs disease among Ashkenazi Jews. A comparison of DNA-based and enzyme-based tests. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):6–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht J., Zeigler M., Segal M., Bach G. Tay-Sachs disease among Moroccan Jews. Isr J Med Sci. 1983 Jan;19(1):67–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]