Full text
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini A., Ward D. C. In situ hybridization banding of human chromosomes with Alu-PCR products: a simultaneous karyotype for gene mapping studies. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):770–774. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilovsky D., Share J. The ITPA and Down's syndrome: an exploratory study. Am J Ment Defic. 1965 Jul;70(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin J. L., Rahmani Z., Chettouh Z., Prieur M., Fermanian J., Poissonnier M., Leonard C., Nicole A., Mattei J. F., Sinet P. M. Slot blot method for the quantification of DNA sequences and mapping of chromosome rearrangements: application to chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):518–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolling D. R., Borgaonkar D. S., Herr H. M., Davis M. Evaluation of dermal patterns in Down's syndrome by predictive discrimination. II. Composite score based on the combination of left and right pattern areas. Clin Genet. 1971;2(3):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgaonkar D. S., Davis M., Bolling D. R., Herr H. M. Evaluation of dermal patterns in Down's syndrome by predictive discrimination. I. Preliminary analysis based on frequencies of patterns. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1971 Mar;128(3):141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carritt B., Litt M. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 20 and 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):358–371. doi: 10.1159/000132799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Shimizu N. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):235–244. doi: 10.1159/000133017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronk C., Crocker A. C., Pueschel S. M., Shea A. M., Zackai E., Pickens G., Reed R. B. Growth charts for children with Down syndrome: 1 month to 18 years of age. Pediatrics. 1988 Jan;81(1):102–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosley P. A., Dowling S. The relationship between cluster and liquid simplification and sentence length, age, and IQ in Down's syndrome children. J Commun Disord. 1989 Jun;22(3):151–168. doi: 10.1016/0021-9924(89)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. The development of language abilities in mongols: a correlational study. J Ment Defic Res. 1977 Jun;21(2):103–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1977.tb00030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Horisberger M., Kraus J., Tantravahi U., Korenberg J., Rao V., Reddy S., Patterson D. Analysis of human chromosome 21: correlation of physical and cytogenetic maps; gene and CpG island distributions. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B., Schapiro M. B., Grady C. L., Rapoport S. I. Cerebral metabolic pattern in young adult Down's syndrome subjects: altered intercorrelations between regional rates of glucose utilization. J Ment Defic Res. 1990 Jun;34(Pt 3):237–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1990.tb01535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
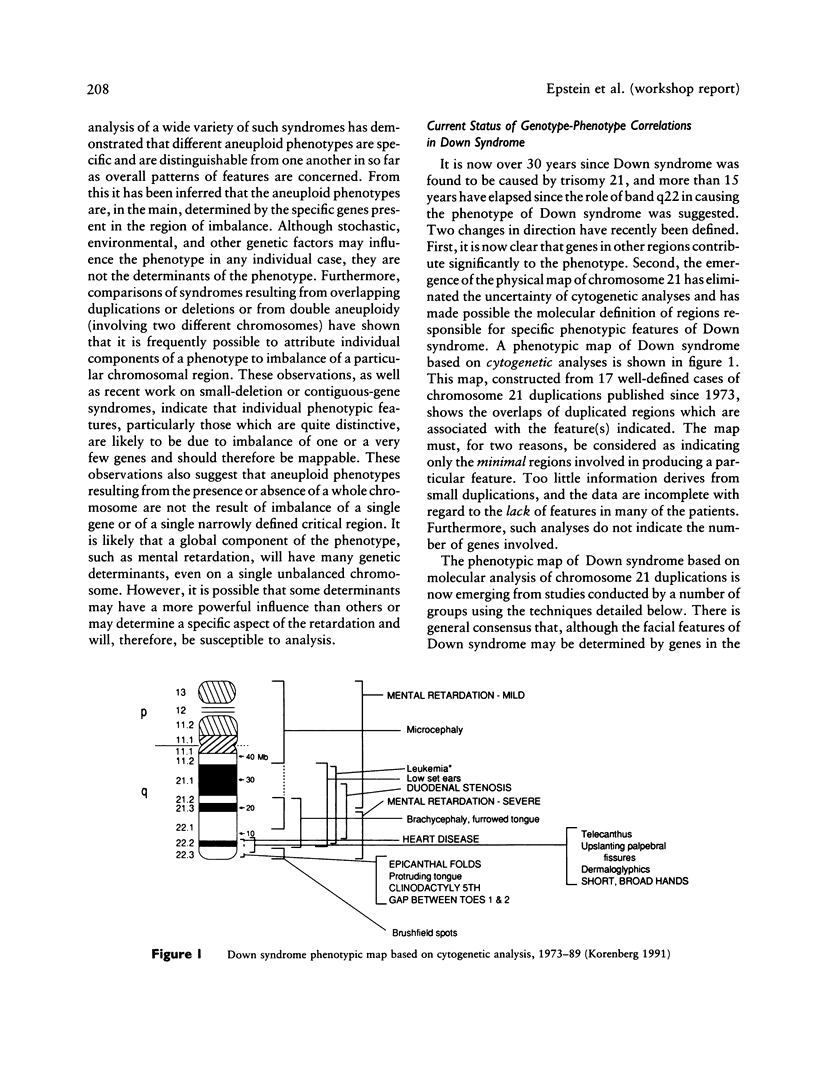
- Korenberg J. R., Kawashima H., Pulst S. M., Ikeuchi T., Ogasawara N., Yamamoto K., Schonberg S. A., West R., Allen L., Magenis E. Molecular definition of a region of chromosome 21 that causes features of the Down syndrome phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):236–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln A. J., Courchesne E., Kilman B. A., Galambos R. Neuropsychological correlates of information-processing by children with Down syndrome. Am J Ment Defic. 1985 Jan;89(4):403–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lott I. T. Down's syndrome, aging, and Alzheimer's disease: a clinical review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;396:15–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb26840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick M. K., Schinzel A., Petersen M. B., Stetten G., Driscoll D. J., Cantu E. S., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Watkins P. C., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular genetic approach to the characterization of the "Down syndrome region" of chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir W. J., Squire I., Blackwood D. H., Speight M. D., St Clair D. M., Oliver C., Dickens P. Auditory P300 response in the assessment of Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome: a 2-year follow-up study. J Ment Defic Res. 1988 Dec;32(Pt 6):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1988.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver C., Holland A. J. Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: a review. Psychol Med. 1986 May;16(2):307–322. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700009120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 27 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preus M., Aymé S. Formal analysis of dysmorphism: objective methods of syndrome definition. Clin Genet. 1983 Jan;23(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb00430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preus M., Schinzel A., Aymé S., Kaijser K. Trisomy 9 (pter----q1 to q3): the phenotype as an objective aid to karyotypic interpretation. Clin Genet. 1984 Jul;26(1):52–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueschel S. M., Findley T. W., Furia J., Gallagher P. L., Scola F. H., Pezzullo J. C. Atlantoaxial instability in Down syndrome: roentgenographic, neurologic, and somatosensory evoked potential studies. J Pediatr. 1987 Apr;110(4):515–521. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80541-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueschel S. M., Scola F. H. Atlantoaxial instability in individuals with Down syndrome: epidemiologic, radiographic, and clinical studies. Pediatrics. 1987 Oct;80(4):555–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani Z., Blouin J. L., Creau-Goldberg N., Watkins P. C., Mattei J. F., Poissonnier M., Prieur M., Chettouh Z., Nicole A., Aurias A. Critical role of the D21S55 region on chromosome 21 in the pathogenesis of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5958–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani Z., Blouin J. L., Créau-Goldberg N., Watkins P. C., Mattei J. F., Poissonnier M., Prieur M., Chettouh Z., Nicole A., Aurias A. Down syndrome critical region around D21S55 on proximal 21q22.3. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:98–103. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. H., Galaburda A. M., Kemper T. L. Down's syndrome: is there a decreased population of neurons? Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):909–916. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapiro M. B., Ball M. J., Grady C. L., Haxby J. V., Kaye J. A., Rapoport S. I. Dementia in Down's syndrome: cerebral glucose utilization, neuropsychological assessment, and neuropathology. Neurology. 1988 Jun;38(6):938–942. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.6.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapiro M. B., Creasey H., Schwartz M., Haxby J. V., White B., Moore A., Rapoport S. I. Quantitative CT analysis of brain morphometry in adult Down's syndrome at different ages. Neurology. 1987 Aug;37(8):1424–1427. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.8.1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapiro M. B., Luxenberg J. S., Kaye J. A., Haxby J. V., Friedland R. P., Rapoport S. I. Serial quantitative CT analysis of brain morphometrics in adult Down's syndrome at different ages. Neurology. 1989 Oct;39(10):1349–1353. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.10.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer D. Simultaneous fluorescent staining of R bands and specific heterochromatic regions (DA-DAPI bands) in human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(2-3):190–193. doi: 10.1159/000131482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriberg L. D., Kwiatkowski J., Best S., Hengst J., Terselic-Weber B. Characteristics of children with phonologic disorders of unknown origin. J Speech Hear Disord. 1986 May;51(2):140–161. doi: 10.1044/jshd.5102.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokal R. R. Classification: purposes, principles, progress, prospects. Science. 1974 Sep 27;185(4157):1115–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4157.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommers R. K., Starkey K. L. Dichotic verbal processing in Down's syndrome children having qualitatively different speech and language skills. Am J Ment Defic. 1977 Jul;82(1):44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Bird E. D., Latt S. A., Neve R. L. The amyloid beta protein gene is not duplicated in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.2890207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski K. E., Wisniewski H. M., Wen G. Y. Occurrence of neuropathological changes and dementia of Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):278–282. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


