Abstract
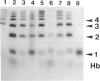
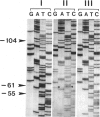
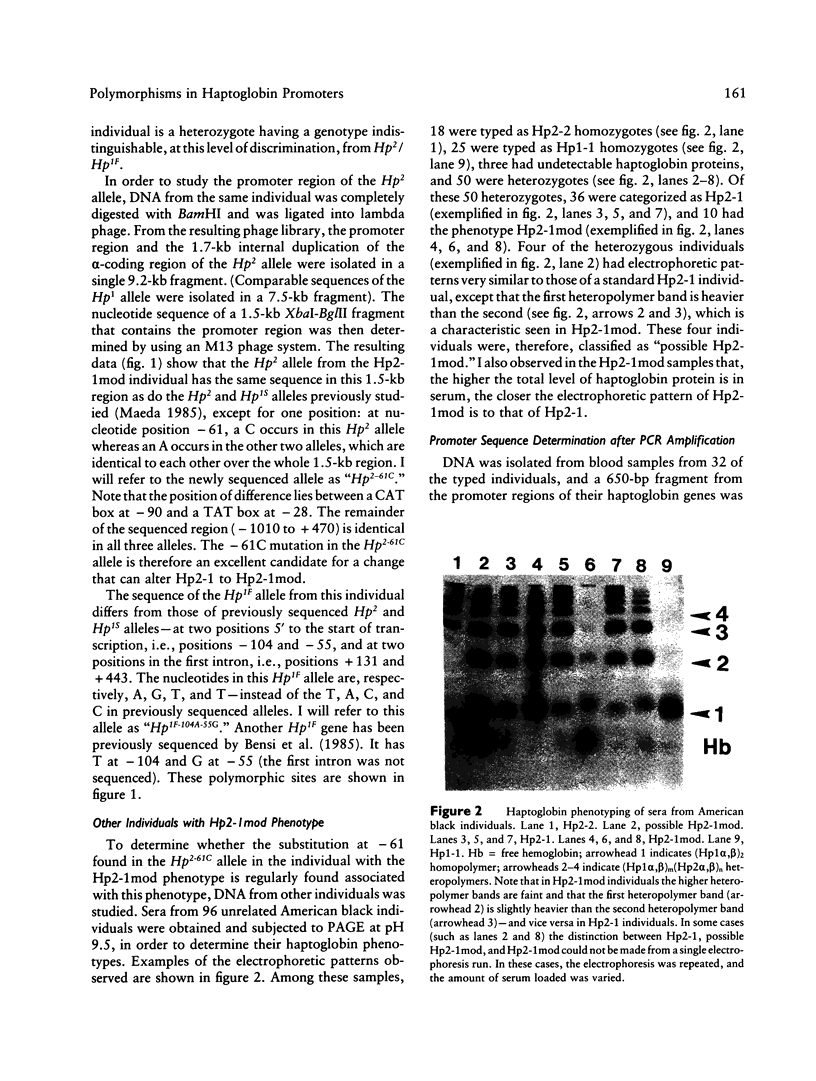
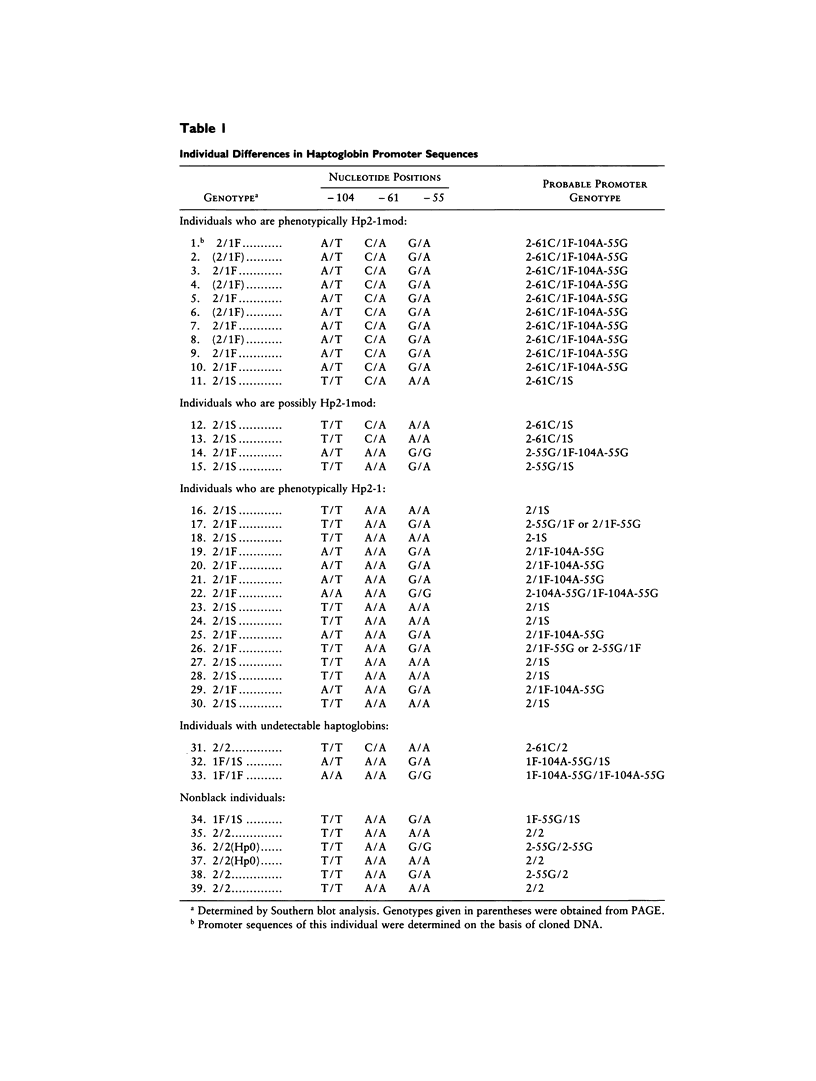
A haptoglobin 2-1 modified (Hp2-1mod) phenotype results when the amount of Hp2 polypeptide synthesized in Hp2/Hp1 heterozygotes is less than that of Hp1 polypeptide. Cloned Hp2 DNA from an individual with the Hp2-1mod phenotype is here shown to have a C in place of the normal A at nucleotide position -61 in one of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) responsive elements of the haptoglobin promoter region. Direct sequencing of the haptoglobin promoter region, amplified by PCR, from DNA from unrelated American blacks showed a C at -61 in all of 10 individuals with the Hp2-1mod phenotype, in two of four with a "possible Hp2-1mod" phenotype, but in none of 15 with the Hp2-1 phenotype. Thus the -61C mutation in the Hp2-61C allele is strongly associated with the Hp2-1mod phenotype. Sequencing results also show that there are three other promoter sequences in the population studied; each can be associated with either Hp2 or Hp1. The variability seen in the Hp2-1mod phenotype, a variability which ranges from close to Hp2-1 to close to Hp1-1, can be explained, in part, by the existence of several Hp2 alleles differing in their promoters--and possibly, in part, by differences in the promoters of the accompanying Hp1 allele. A further part of the variability may be the consequence of differences in the way that the Hp2-61C and the Hp2 alleles respond to the IL-6-dependent factor during an acute-phase response.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azevedo E., Krieger H., Morton N. E. Ahaptoglobinemia in northeastern Brazil. Hum Hered. 1969;19(6):609–612. doi: 10.1159/000152275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensi G., Raugei G., Klefenz H., Cortese R. Structure and expression of the human haptoglobin locus. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):119–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. A., Chan G. F., Hew C. L., Dixon G. H. Gene action in the human haptoglobins. 3. Isolation of the alpha-chains as single gene products. Isolation, molecular weight, and amino acid composition of alpha and beta chains. Can J Biochem. 1970 Jan;48(1):123–132. doi: 10.1139/o70-019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. H., Kurosky A. Haptoglobin: the evolutionary product of duplication, unequal crossing over, and point mutation. Adv Hum Genet. 1982;12:189-261, 453-4. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8315-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL G. E., SMITHIES O. Human haptoglobins: estimation and purification. Biochem J. 1959 May;72(1):115–121. doi: 10.1042/bj0720115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBLETT E. R., BROOKS L. E. Haptoglobin sub-types in three racial groups. Nature. 1963 Feb 9;197:576–577. doi: 10.1038/197576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBLETT E. R. Haptoglobin types in American Negroes. Nature. 1959 Jan 17;183(4655):192–193. doi: 10.1038/183192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBLETT E. R., STEINBERG A. G. The inheritance of serum haptoglobin types in American Negroes: evidence for a third allele Hp-2m. Am J Hum Genet. 1960 Jun;12:160–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS H., LAWLER S. D., ROBSON E. B., SMITHIES O. The occurrence of two unusual serum protein phenotypes in a single pedigree. Ann Hum Genet. 1960 Apr;24:63–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1959.tb01715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V., Bowden D. K., Flint J., Whitehouse D. B., Hopkinson D. A., Oppenheimer S. J., Serjeantson S. W., Clegg J. B. A population genetic survey of the haptoglobin polymorphism in Melanesians by DNA analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;38(3):382–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javid J. Human haptoglobins. Curr Top Hematol. 1978;1:151–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke R. P. Typing and subtyping of haptoglobin from native serum using disc gel electrophoresis in alkaline buffer: application to routine screening. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;141(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., McEvoy S. M., Harris H. F., Huisman T. H., Smithies O. Polymorphisms in the human haptoglobin gene cluster: chromosomes with multiple haptoglobin-related (Hpr) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7395–7399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Yang F., Barnett D. R., Bowman B. H., Smithies O. Duplication within the haptoglobin Hp2 gene. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):131–135. doi: 10.1038/309131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene promoter: interleukin-6-responsive elements interact with a DNA-binding protein induced by interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER W. C., BEARN A. G. Control gene mutation as a possible explanation of certain haptoglobin phenotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1963 Jun;15:159–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Harpel B., Mory Y., Schwartz E., Surrey S. Construction of human gene libraries from small amounts of peripheral blood: analysis of beta-like globin genes. Hemoglobin. 1982;6(1):27–36. doi: 10.3109/03630268208996930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raugei G., Bensi G., Colantuoni V., Romano V., Santoro C., Costanzo F., Cortese R. Sequence of human haptoglobin cDNA: evidence that the alpha and beta subunits are coded by the same mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5811–5819. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTTON H. E., KARP G. W., Jr VARIATIONS IN HETEROZYGOUS EXPRESSION AT THE HAPTOGLOBIN LOCUS. Am J Hum Genet. 1964 Dec;16:419–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Effect of manganese ions on the incorporation of dideoxynucleotides by bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase and Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4076–4080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Brune J. L., Baldwin W. D., Barnett D. R., Bowman B. H. Identification and characterization of human haptoglobin cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5875–5879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vander Straten A., Herzog A., Jacobs P., Cabezón T., Bollen A. Molecular cloning of human haptoglobin cDNA: evidence for a single mRNA coding for alpha 2 and beta chains. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):1003–1007. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]