Abstract
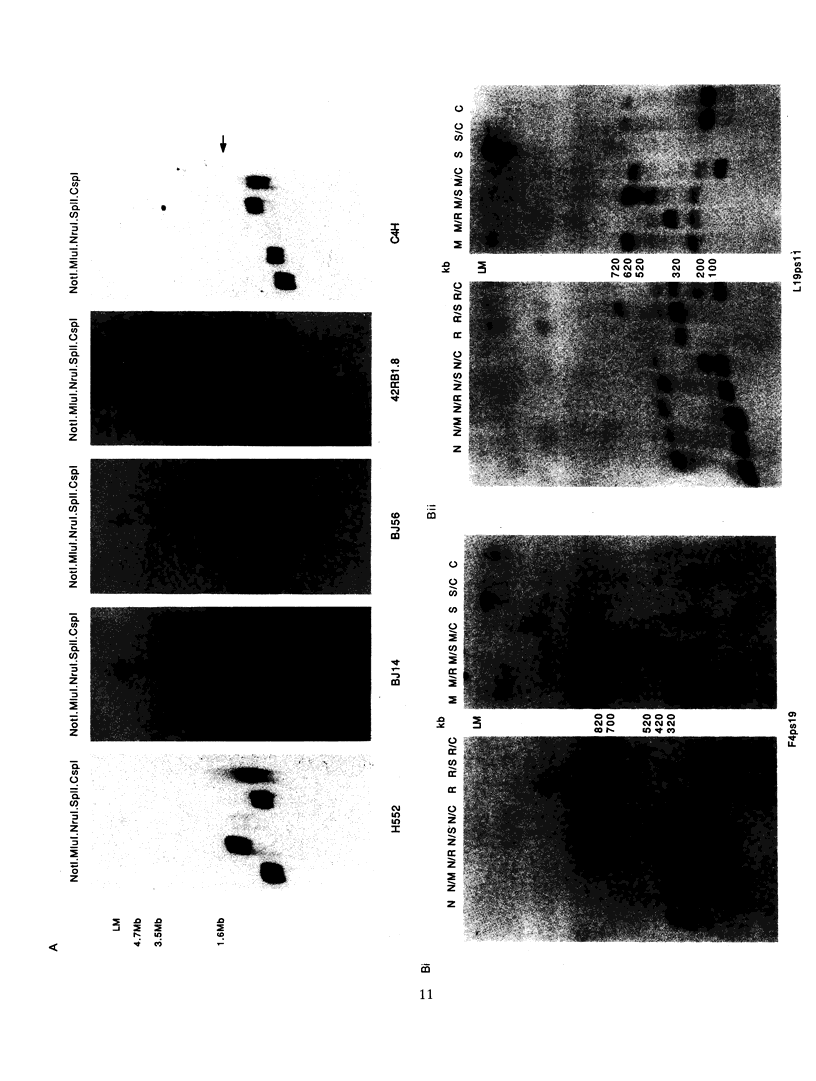
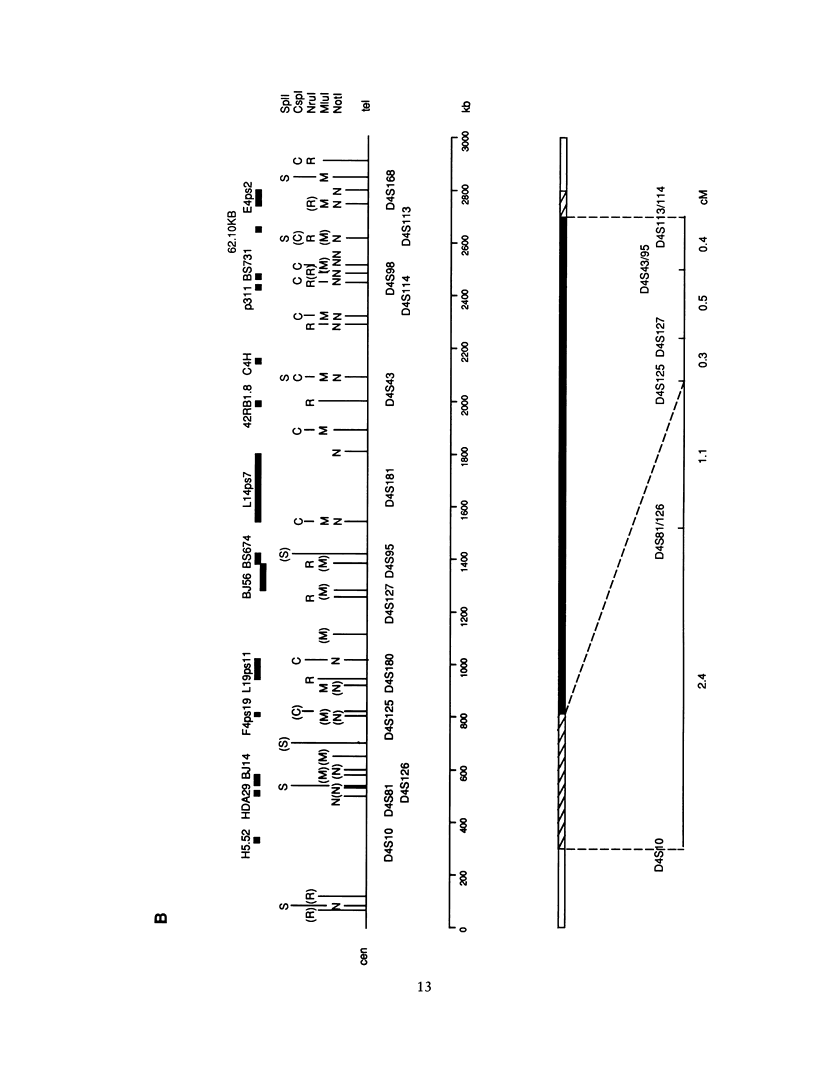
The Huntington disease (HD) gene has been mapped 4 cM distal to D4S10 within the telomeric chromosome band, 4p16.3. The published physical map of this region extends from D4S10 to the telomere but contains two gaps of unknown size. Recombination events have been used to position the HD mutation with respect to genetic markers within this region, and one such event places the gene proximal to D4S168, excluding the distal gap as a possible location for the defect. One previously published recombination event appeared to have excluded the proximal gap. We have reassessed this event and have moved the proximal boundary for the HD candidate region centromeric to the gap within a "hot spot" for recombination between D4S10 and D4S125. We have closed the proximal gap and report here the complete physical map spanning the HD candidate region from D4S10 to D4S168, the maximum size of which can now be placed accurately at 2.5 Mb.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allitto B. A., MacDonald M. E., Bucan M., Richards J., Romano D., Whaley W. L., Falcone B., Ianazzi J., Wexler N. S., Wasmuth J. J. Increased recombination adjacent to the Huntington disease-linked D4S10 marker. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates G. P., MacDonald M. E., Baxendale S., Sedlacek Z., Youngman S., Romano D., Whaley W. L., Allitto B. A., Poustka A., Gusella J. F. A yeast artificial chromosome telomere clone spanning a possible location of the Huntington disease gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):762–775. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bućan M., Zimmer M., Whaley W. L., Poustka A., Youngman S., Allitto B. A., Ormondroyd E., Smith B., Pohl T. M., MacDonald M. Physical maps of 4p16.3, the area expected to contain the Huntington disease mutation. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90442-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Haines J. L., Tanzi R. E., Wexler N. S., Penchaszadeh G. K., Harper P. S., Folstein S. E., Cassiman J. J., Myers R. H., Young A. B. Huntington disease: no evidence for locus heterogeneity. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivill X., Farrall M., Scambler P. J., Bell G. M., Hawley K. M., Lench N. J., Bates G. P., Kruyer H. C., Frederick P. A., Stanier P. A candidate for the cystic fibrosis locus isolated by selection for methylation-free islands. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):840–845. doi: 10.1038/326840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Horisberger M., Kraus J., Tantravahi U., Korenberg J., Rao V., Reddy S., Patterson D. Analysis of human chromosome 21: correlation of physical and cytogenetic maps; gene and CpG island distributions. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Bucan M., MacDonald M. E., Zimmer M., Haines J. L., Cheng S. V., Pohl T. M., Meyers R. H., Whaley W. L., Allitto B. A. A DNA segment encoding two genes very tightly linked to Huntington's disease. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.2890209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Bonner T. I., Faryniarz A. G., Hobbs W. J., MacDonald M. E., Cheng S. V., Folstein S. E., Conneally P. M. Localization of the Huntington's disease gene to a small segment of chromosome 4 flanked by D4S10 and the telomere. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Anderson M. A., Gilliam T. C., Tranejaerg L., Carpenter N. J., Magenis E., Hayden M. R., Healey S. T., Bonner T. I., Gusella J. F. A somatic cell hybrid panel for localizing DNA segments near the Huntington's disease gene. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Cheng S. V., Zimmer M., Haines J. L., Poustka A., Allitto B., Smith B., Whaley W. L., Romano D. M., Jagadeesh J. Clustering of multiallele DNA markers near the Huntington's disease gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):1013–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI114222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Haines J. L., Zimmer M., Cheng S. V., Youngman S., Whaley W. L., Wexler N., Bucan M., Allitto B. A., Smith B. Recombination events suggest potential sites for the Huntington's disease gene. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. B., Gusella J. F. Huntington's disease. Pathogenesis and management. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 13;315(20):1267–1276. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611133152006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Culver M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pYNZ32) on chromosome 4p [D4S125]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4186–4186. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl T. M., Zimmer M., MacDonald M. E., Smith B., Bucan M., Poustka A., Volinia S., Searle S., Zehetner G., Wasmuth J. J. Construction of a NotI linking library and isolation of new markers close to the Huntington's disease gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9185–9198. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C., Casher D., Bull L., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. A cloned DNA segment from the telomeric region of human chromosome 4p is not detectably rearranged in Huntington disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7309–7313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Gilliam T. C., Cole J. L., Drumm M. L., Wasmuth J. J., Gusella J. F., Collins F. S. Chromosome jumping from D4S10 (G8) toward the Huntington disease gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6437–6441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins C., Theilmann J., Youngman S., Haines J., Altherr M. J., Harper P. S., Payne C., Junker A., Wasmuth J., Hayden M. R. Evidence from family studies that the gene causing Huntington disease is telomeric to D4S95 and D4S90. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):422–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skraastad M. I., Bakker E., de Lange L. F., Vegter-van der Vlis M., Klein-Breteler E. G., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Mapping of recombinants near the Huntington disease locus by using G8 (D4S10) and newly isolated markers in the D4S10 region. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):560–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Skarecky D., Bengtsson U., Magenis R. E., Carpenter N., Wasmuth J. J. Isolation of DNA markers in the direction of the Huntington disease gene from the G8 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):335–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Lazarou L. P., Youngman S., Quarrell O. W., Wasmuth J. J., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Linkage disequilibrium in Huntington's disease: an improved localisation for the gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):673–675. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann J., Kanani S., Shiang R., Robbins C., Quarrell O., Huggins M., Hedrick A., Weber B., Collins C., Wasmuth J. J. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley W. L., Michiels F., MacDonald M. E., Romano D., Zimmer M., Smith B., Leavitt J., Bucan M., Haines J. L., Gilliam T. C. Mapping of D4S98/S114/S113 confines the Huntington's defect to a reduced physical region at the telomere of chromosome 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11769–11780. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman S., Sarfarazi M., Bucan M., MacDonald M., Smith B., Zimmer M., Gilliam C., Frischauf A. M., Wasmuth J. J., Gusella J. F. A new DNA marker (D4S90) is located terminally on the short arm of chromosome 4, close to the Huntington disease gene. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):802–809. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]