Abstract
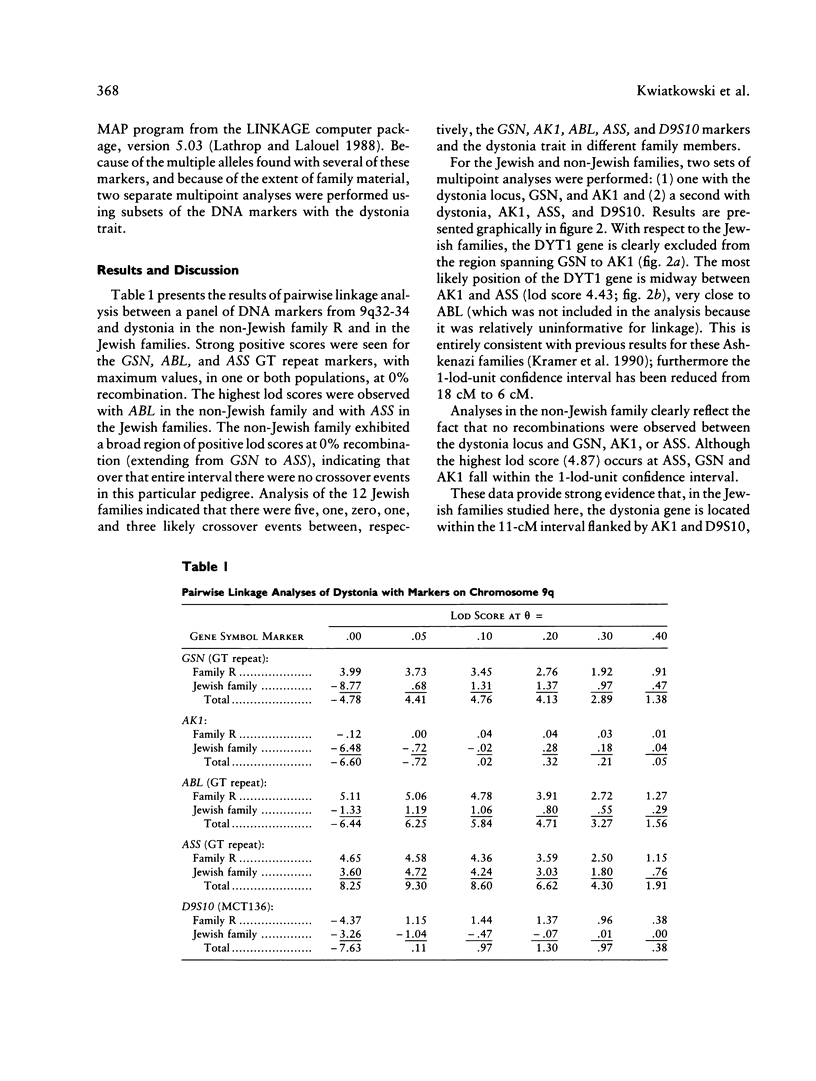
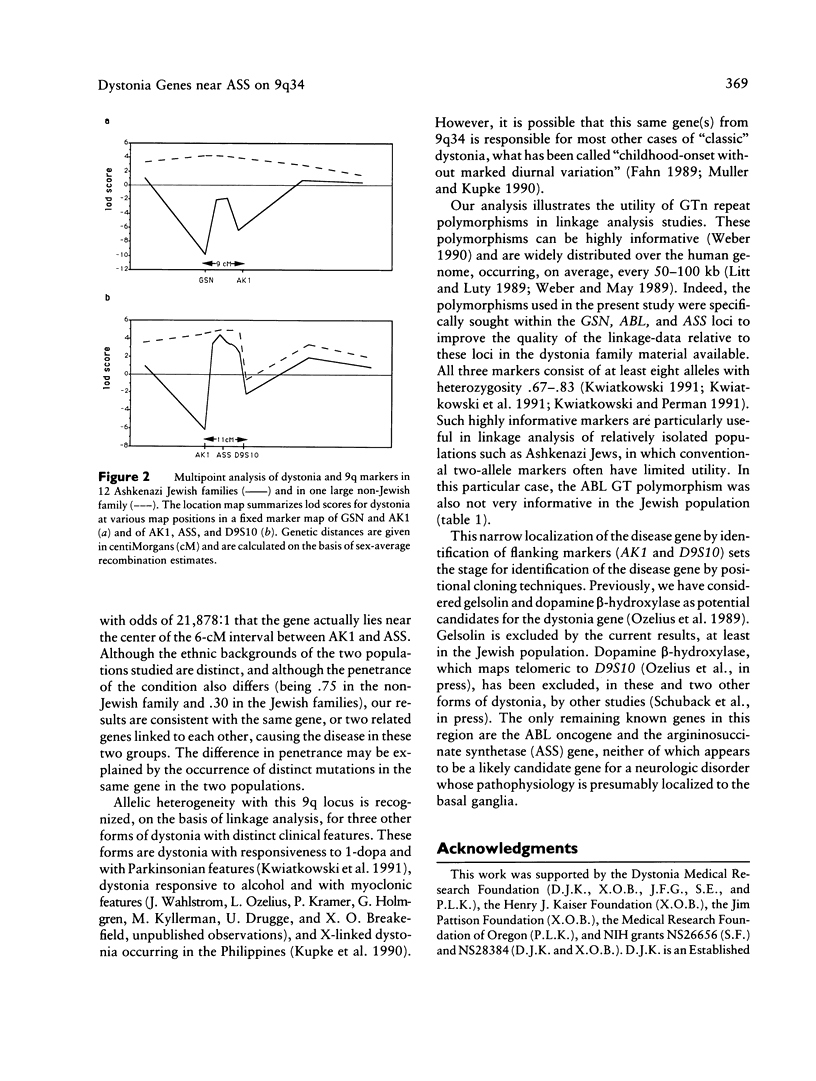
Idiopathic torsion dystonia (ITD) is characterized by sustained, involuntary muscle contractions, frequently causing twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. Most familial forms of ITD display autosomal dominant inheritance with reduced penetrance. Linkage analysis has been previously used to localize a dystonia gene to the 9q32-34 region in a large non-Jewish family and in a group of Ashkenazi Jewish families. Utilizing GT repeat polymorphisms from this region, here we demonstrate that the gene causing dystonia in Ashkenazi Jews can be localized to the 11-cM interval between AK1 and D9S10. Linkage analysis in the non-Jewish family is also consistent with occurrence of the gene in this region, although positive lod scores extend over a greater than 20-cM interval in that family. These results set the stage for positional cloning of the dystonia gene. Currently there are no known candidate genes in this region.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bech-Hansen N. T., Marshall K. J., Kraus S. L. TaqI RFLP in human adenylate kinase-1 (AK1) gene region on chromosome 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):4004–4004. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.4004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressman S. B., de Leon D., Brin M. F., Risch N., Burke R. E., Greene P. E., Shale H., Fahn S. Idiopathic dystonia among Ashkenazi Jews: evidence for autosomal dominant inheritance. Ann Neurol. 1989 Nov;26(5):612–620. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressman S. B., de Leon D., Brin M. F., Risch N., Shale H., Burke R. E., Greene P. E., Fahn S. Inheritance of idiopathic torsion dystonia among Ashkenazi Jews. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:45–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge R. The torsion dystonias: literature review and genetic and clinical studies. Neurology. 1970 Nov;20(11):1–78. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.11_part_2.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahn S. Concept and classification of dystonia. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giménez-Roldán S., Delgado G., Marín M., Villanueva J. A., Mateo D. Hereditary torsion dystonia in gypsies. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines J. L., Ozelius L. J., McFarlane H., Menon A., Tzall S., Martiniuk F., Hirschhorn R., Gusella J. F. A genetic linkage map of chromosome 17. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90218-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. L., Ozelius L., Brin M. F., Fahn S., Kidd K. K., Gusella J., Breakefield X. O. Molecular genetics of an autosomal dominant form of torsion dystonia. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:57–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. L., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Risch N., Bressman S. B., Brin M. F., Schuback D. E., Burke R. E., Kwiatkowski D. J., Shale H. Dystonia gene in Ashkenazi Jewish population is located on chromosome 9q32-34. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):114–120. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Lee L. V., Viterbo G. H., Arancillo J., Donlon T., Müller U. X-linked recessive torsion dystonia in the Philippines. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jun;36(2):237–242. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320360219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the ABL locus (9q34). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):967–967. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Nygaard T. G., Schuback D. E., Perman S., Trugman J. M., Bressman S. B., Burke R. E., Brin M. F., Ozelius L., Breakefield X. O. Identification of a highly polymorphic microsatellite VNTR within the argininosuccinate synthetase locus: exclusion of the dystonia gene on 9q32-34 as the cause of dopa-responsive dystonia in a large kindred. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):121–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Ozelius L., Schuback D., Gusella J., Breakefield X. O. The gelsolin (GSN) cDNA clone, from 9q32-34, identifies BclI and StuI RFLPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4425–4425. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Perman S. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the GSN locus (9q32-34). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):967–967. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Westbrook C. A., Bruns G. A., Morton C. C. Localization of gelsolin proximal to ABL on chromosome 9. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Apr;42(4):565–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barlow A., Daly M. J., Lincoln S. E., Newberg L. A., Newburg L. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Efficient computations in multilocus linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;42(3):498–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop M., Nakamura Y., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Woodward S., Lalouel J. M., White R. A mapped set of genetic markers for human chromosome 9. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. V., Pascasio F. M., Fuentes F. D., Viterbo G. H. Torsion dystonia in Panay, Philippines. Adv Neurol. 1976;14:137–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):397–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Kupke K. G. The genetics of primary torsion dystonia. Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;84(2):107–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00208922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup H., Lathrop M., Lu S. Y., Daiger S. P., Beaudet A. L., O'Brien W. E. Multilocus linkage analysis with the human argininosuccinate synthetase gene. Genomics. 1989 Oct;5(3):442–444. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A computer program for linkage analysis of general human pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):528–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L., Kramer P. L., Moskowitz C. B., Kwiatkowski D. J., Brin M. F., Bressman S. B., Schuback D. E., Falk C. T., Risch N., de Leon D. Human gene for torsion dystonia located on chromosome 9q32-q34. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1427–1434. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. J., Bressman S. B., deLeon D., Brin M. F., Burke R. E., Greene P. E., Shale H., Claus E. B., Cupples L. A., Fahn S. Segregation analysis of idiopathic torsion dystonia in Ashkenazi Jews suggests autosomal dominant inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):533–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa M., Hosaka A., Miyagawa F., Nomura Y., Imai H. Hereditary progressive dystonia with marked diurnal fluctuation. Adv Neurol. 1976;14:215–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L. Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):524–530. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90195-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman W., Dyken P. Dystonia musculorum deformans. Clinical, genetic and pathoanatomical studies. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir. 1967 Mar-Apr;70(2):77–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilber N., Korczyn A. D., Kahana E., Fried K., Alter M. Inheritance of idiopathic torsion dystonia among Jews. J Med Genet. 1984 Feb;21(1):13–20. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuffardi O., Caiulo A., Maraschio P., Tupler R., Bianchi E., Amisano P., Beluffi G., Moratti R., Liguri G. Regional assignment of the loci for adenylate kinase to 9q32 and for alpha 1-acid glycoprotein to 9q31-q32. A locus for Goltz syndrome in region 9q32-qter? Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):17–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00288264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Yebenes J. G., Moskowitz C., Fahn S., Saint-Hilaire M. H. Long-term treatment with levodopa in a family with autosomal dominant torsion dystonia. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:101–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


