Abstract
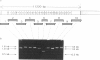
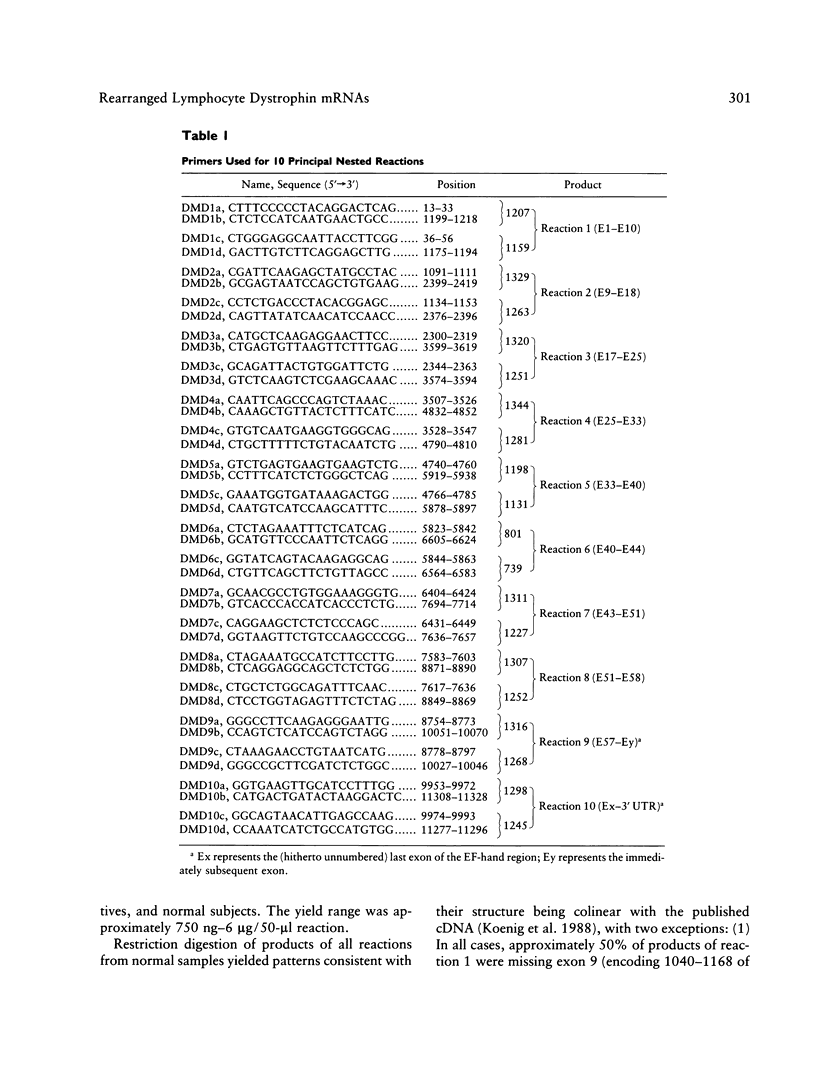
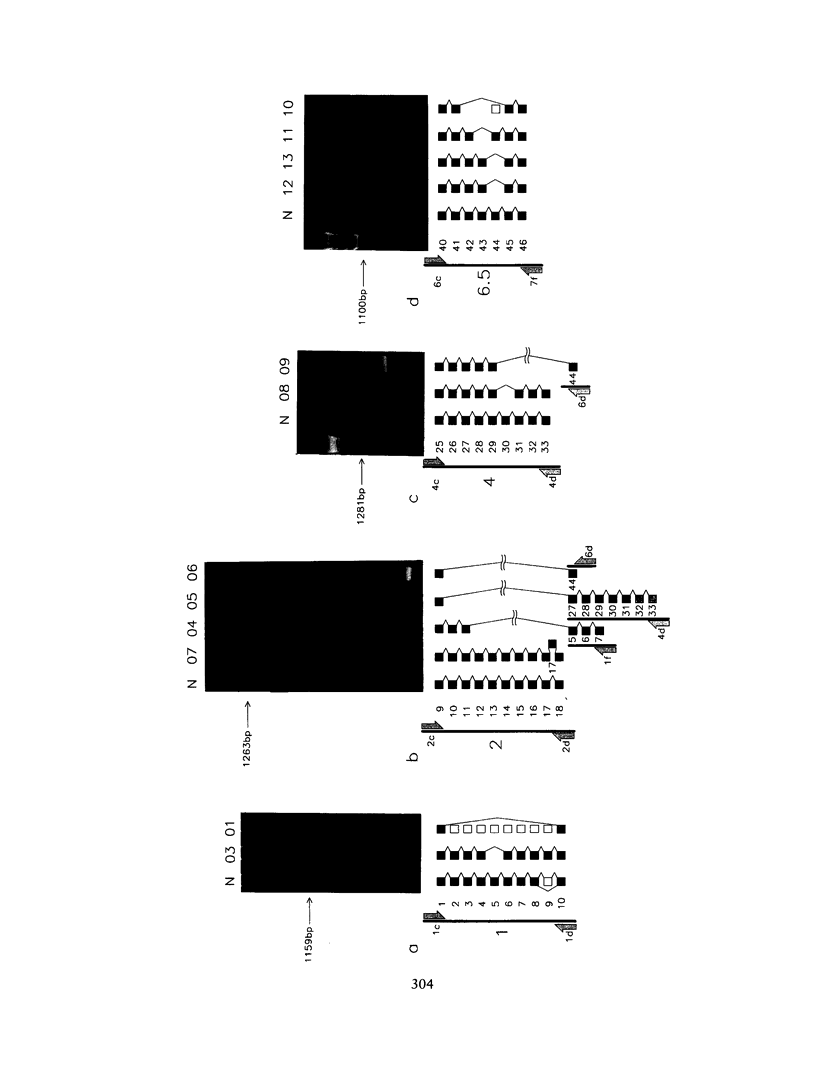
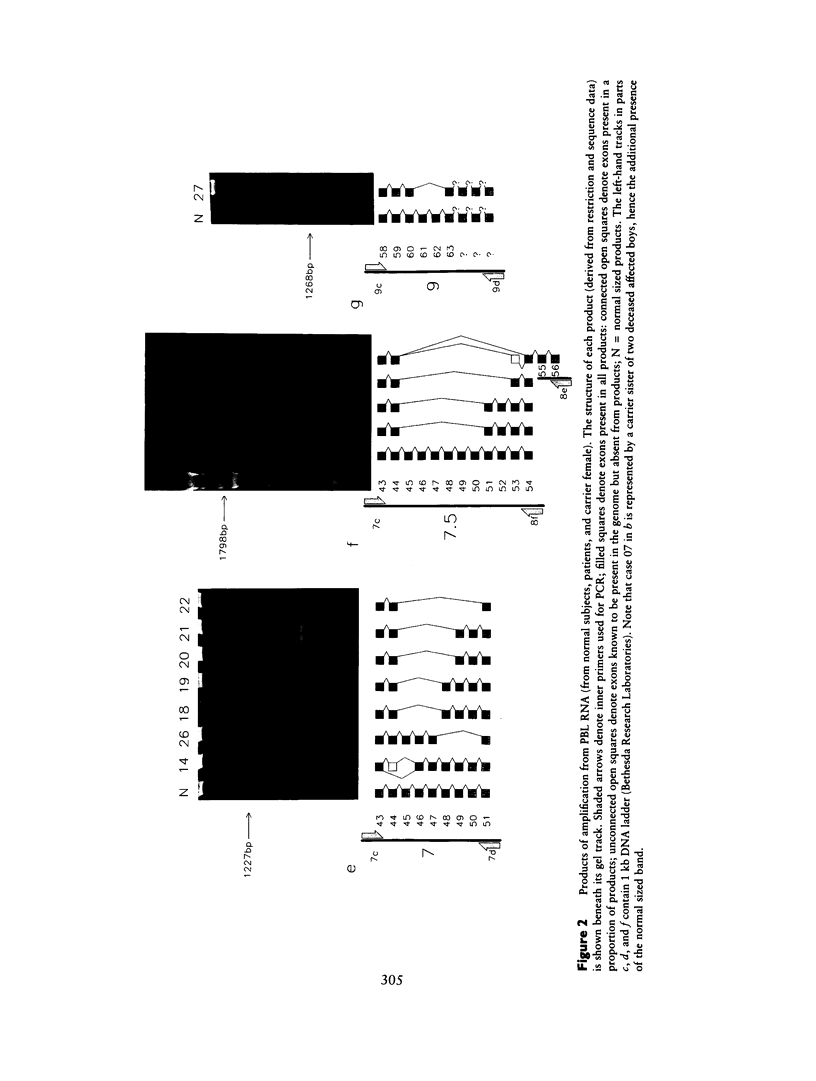
Using 10 overlapping nested sets of primers and using peripheral blood lymphocyte (PBL) total RNA as template, we have developed a system, based on PCR, which allows the rapid production of double-stranded cDNA corresponding to the entire coding sequence of the dystrophin gene. The product can be visualized on native minigels by ethidium staining and directly sequenced after gel purification. We have used this system to analyze the structures of PBL dystrophin mRNA in 26 Duchenne, Becker, or intermediate muscular dystrophy patients who have gross rearrangements of the dystrophin gene. In each case, the effect that the genomic rearrangement has on the structure of the transcript--and, by inference, on the dystrophin protein--has been determined, and the results confirm the frameshift hypothesis. The study also identifies a series of alternatively spliced transcripts which are specific to the rearranged genotypes and which seem therefore to arise following the alteration in the context of the splice signal. The system has been used for unambiguous identification of carrier females. Furthermore, the rapid production of microgram quantities of dystrophin cDNA from a readily accessible tissue makes point-mutation screening a practical proposition.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg L. P., Wieland K., Millar D. S., Schlösser M., Wagner M., Kakkar V. V., Reiss J., Cooper D. N. Detection of a novel point mutation causing haemophilia A by PCR/direct sequencing of ectopically-transcribed factor VIII mRNA. Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;85(6):655–658. doi: 10.1007/BF00193593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Concordet J. P., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A. Illegitimate transcription: transcription of any gene in any cell type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2617–2621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Kaplan J. C., Maire P., Gautron S., Kahn A. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissue. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):858–860. doi: 10.1038/333858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Rodrigues N. R., Campbell R. D. Reactivity of cytosine and thymine in single-base-pair mismatches with hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide and its application to the study of mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4397–4401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz V. The Duchenne dystrophy story: from phenotype to gene and potential treatment. J Child Neurol. 1989 Oct;4(4):240–250. doi: 10.1177/088307388900400402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feener C. A., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M. Alternative splicing of human dystrophin mRNA generates isoforms at the carboxy terminus. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):509–511. doi: 10.1038/338509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Chamberlain J. S., Murphy E. G., Duff C. L., Smith B., Burghes A. H., Thompson M. W., Sutherland J., Oss I., Bodrug S. E. Molecular and phenotypic analysis of patients with deletions within the deletion-rich region of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):507–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. M., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Nilsson I. M., Giannelli F. Molecular pathology of haemophilia B. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S., Hart K., Abbs S., Heckmatt J., Rodillo E., Bobrow M., Dubowitz V. Correlation of clinical and deletion data in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):682–693. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holding C., Monk M. Diagnosis of beta-thalassaemia by DNA amplification in single blastomeres from mouse preimplantation embryos. Lancet. 1989 Sep 2;2(8662):532–535. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90655-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Beggs A. H., Moyer M., Scherpf S., Heindrich K., Bettecken T., Meng G., Müller C. R., Lindlöf M., Kaariainen H. The molecular basis for Duchenne versus Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of severity with type of deletion. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):498–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Kunkel L. M. Detailed analysis of the repeat domain of dystrophin reveals four potential hinge segments that may confer flexibility. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4560–4566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Liechti-Gallati S., Moser H., Kunkel L. M. An explanation for the phenotypic differences between patients bearing partial deletions of the DMD locus. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon A. J., Green P. M., Giannelli F., Bentley D. R. Direct detection of point mutations by mismatch analysis: application to haemophilia B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3347–3358. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor J. A., Green P. M., Montandon A. J., Rizza C. R., Giannelli F. Detection of three novel mutations in two haemophilia A patients by rapid screening of whole essential region of factor VIII gene. Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92450-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. M., Thomas N. S., Kingston H. M., Harper P. S. Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of deletion type with clinical severity. J Med Genet. 1990 Apr;27(4):236–239. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.4.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. G., Bentley D. R., Barby T. F., Manners E., Bobrow M. Direct diagnosis of carriers of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy by amplification of lymphocyte RNA. Lancet. 1990 Dec 22;336(8730):1523–1526. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Access to a messenger RNA sequence or its protein product is not limited by tissue or species specificity. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):331–334. doi: 10.1126/science.2565599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Cox D. R., Lerman L. S., Myers R. M. Attachment of a 40-base-pair G + C-rich sequence (GC-clamp) to genomic DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction results in improved detection of single-base changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R. An improved method for directly sequencing PCR amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1266–1266. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]