Abstract
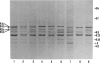
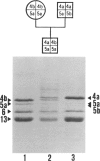
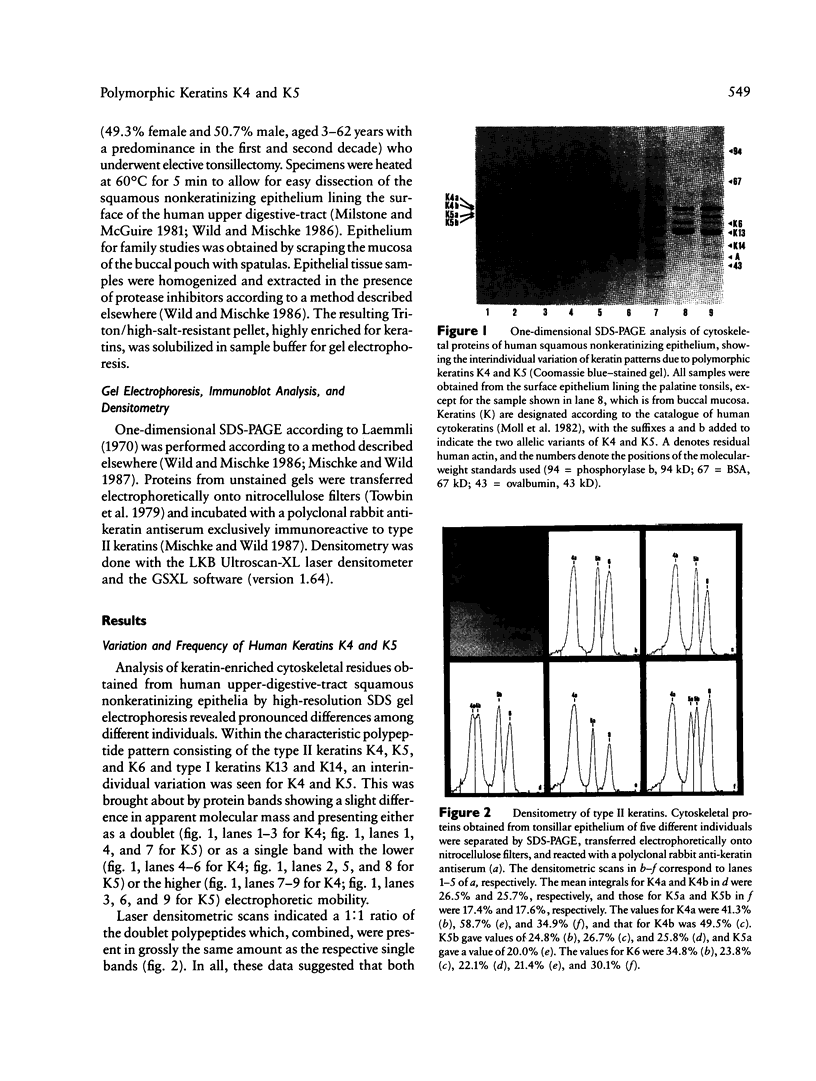
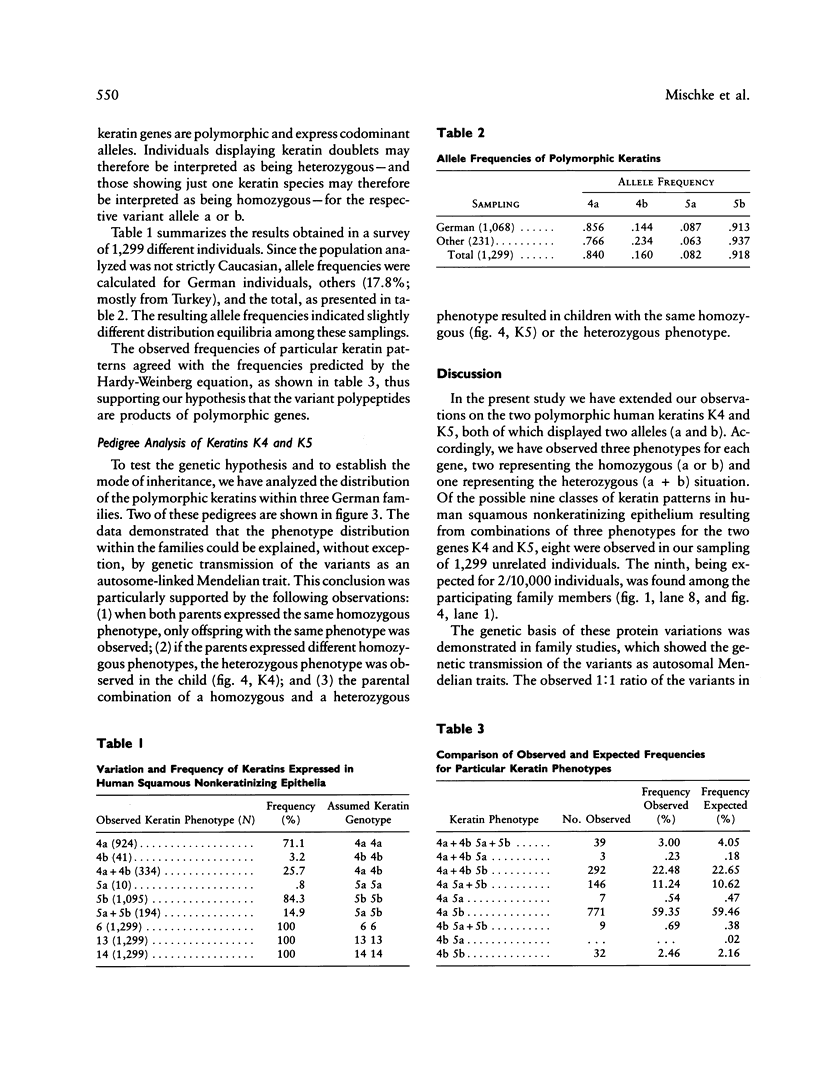
Two electrophoretic variants for each of the human keratins K4 and K5 that are expressed in squamous nonkeratinizing epithelia lining the upper digestive tract could be distinguished on SDS-PAGE. Based on a sampling size of 1,299 unrelated individuals, calculation of allele frequencies showed the alleles to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The genetic basis of this variation was confirmed by both quantitative gene dosage dependence and the transmission of the variants as Mendelian traits in two families. Thus the human keratin genes K4 and K5 are polymorphic, and each presents with two codominant alleles (a and b).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenberg M. Concerted gene duplications in the two keratin gene families. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(3):203–211. doi: 10.1007/BF02100075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of human brain proteins. IV. Disorders of glial proliferation and a polymorphism of glial fibrillary acidic protein--GFAP Duarte. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 2):805–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner R., Sun T. T., Aebi U. The role of keratin subfamilies and keratin pairs in the formation of human epidermal intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1767–1777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W. Nuclear lamins and cytoplasmic intermediate filament proteins: a growing multigene family. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. Keratins as biochemical markers of epithelial differentiation. Trends Genet. 1988 Oct;4(10):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Pair formation and promiscuity of cytokeratins: formation in vitro of heterotypic complexes and intermediate-sized filaments by homologous and heterologous recombinations of purified polypeptides. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1826–1841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessin S. R., Huebner K., Isobe M., Croce C. M., Steinert P. M. Chromosomal mapping of human keratin genes: evidence of non-linkage. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Dec;91(6):572–578. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12477087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstone L. M., McGuire J. Different polypeptides form the intermediate filaments in bovine hoof and esophageal epithelium and in aortic endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):312–316. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischke D., Wild G. Polymorphic keratins in human epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Feb;88(2):191–197. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Guin W. M., Galvin S., Schermer A., Sun T. T. Patterns of keratin expression define distinct pathways of epithelial development and differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1987;22:97–125. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., Bowden P. E., DiPaolo J. A. Two type II keratin genes are localized on human chromosome 12. Hum Genet. 1989 May;82(2):109–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00284039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano V., Bosco P., Rocchi M., Costa G., Leube R. E., Franke W. W., Romeo G. Chromosomal assignments of human type I and type II cytokeratin genes to different chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(3):148–151. doi: 10.1159/000132612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., RayChaudhury A., Shows T. B., Le Beau M. M., Fuchs E. A group of type I keratin genes on human chromosome 17: characterization and expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):722–736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Geisler N. Intermediate filaments: structural conservation and divergence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild G. A., Mischke D. Variation and frequency of cytokeratin polypeptide patterns in human squamous non-keratinizing epithelium. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jan;162(1):114–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90430-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M. B. Genetically determined protein polymorphism in the rabbit nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3641–3645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]