Abstract
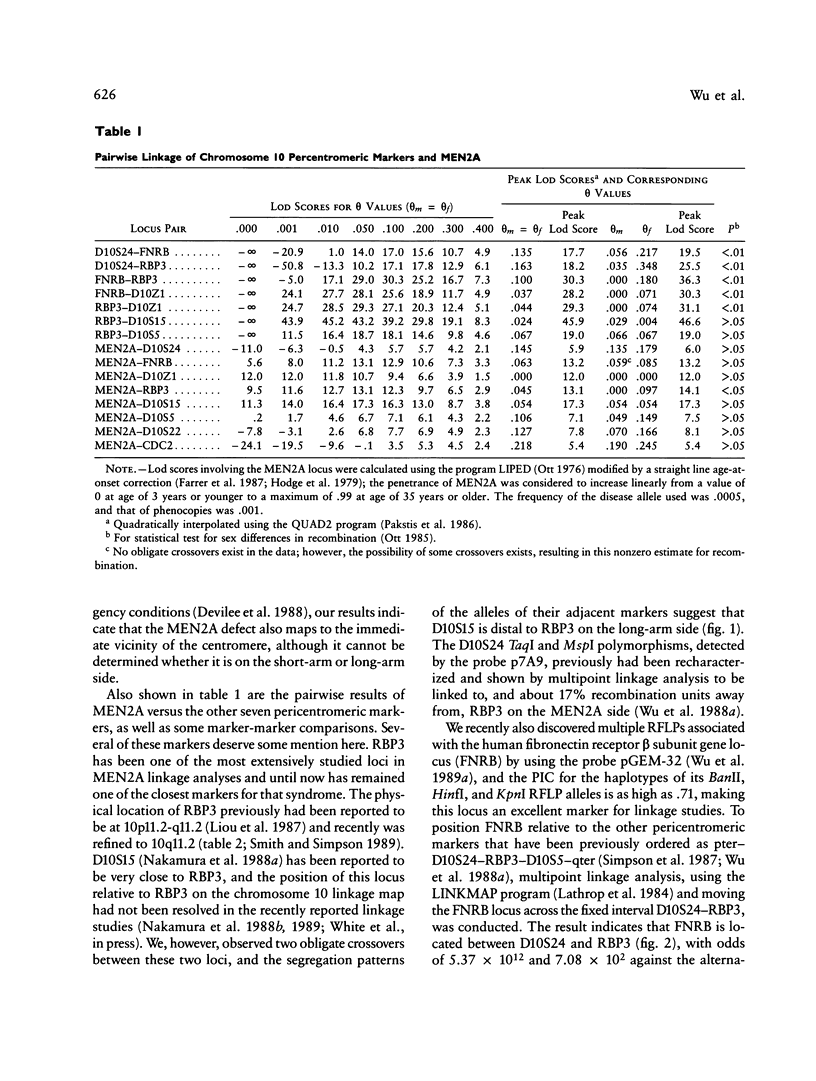
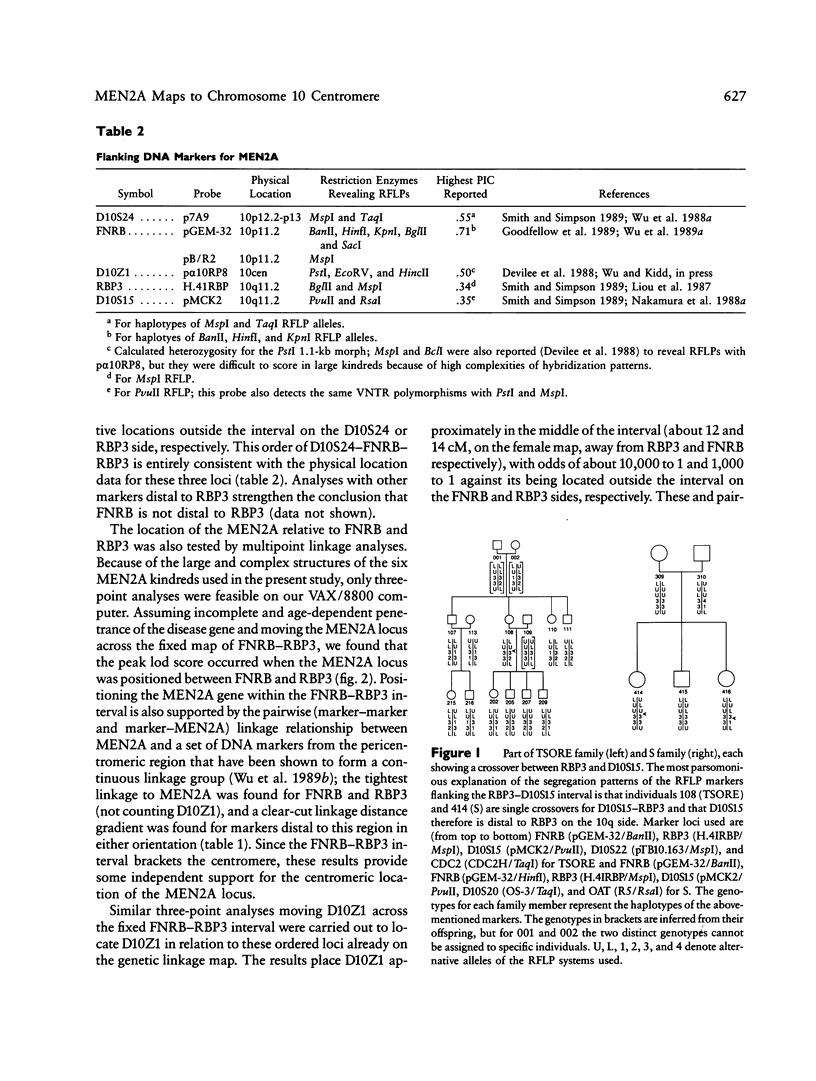
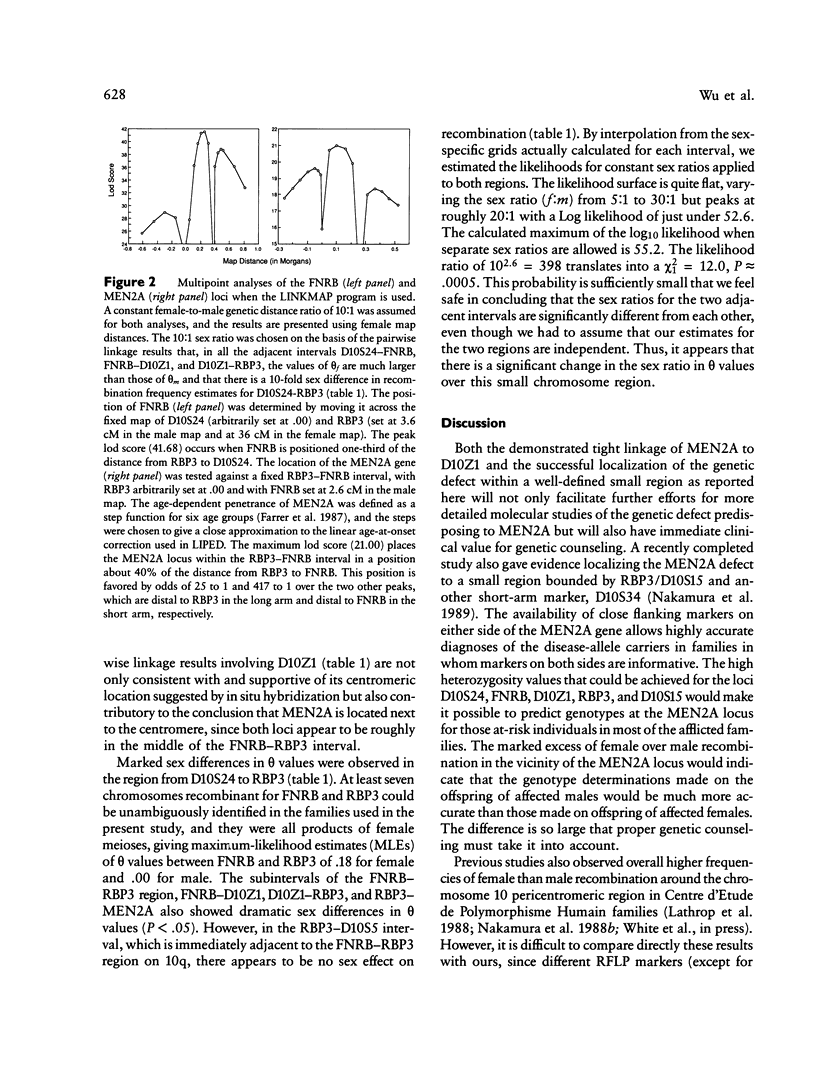
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN2A) is a rare cancer syndrome that is inherited in an apparently autosomal dominant fashion. Previous linkage studies had assigned the MEN2A locus to chromosome 10 in the pericentromeric region. We recently have described several new easily scorable RFLPs for the chromosome 10–specific alpha satellite DNA (the D10Z1) locus that is known, on the basis of previous in situ hybridization experiments, to lie at the centromere. We report here tight linkage between MEN2A and D10Z1, as demonstrated by a maximum lod score of 12.02 at the recombination frequency of zero (1-lod-unit support interval 0–4 cM), indicating that the genetic defect in MEN2A lies in the immediate vicinity of the centromere. By means of a set of ordered polymorphic DNA markers from the pericentromeric region, multipoint as well as pairwise linkage analyses place the MEN2A locus at the middle of a small region (∼11 cM) bracketing the centromere with FNRB (at 10p11.2) and RBP3 (at 10q11.2) on either side, providing further support for the centromeric location of the MEN2A locus. Marked sex difference in recombination frequencies exists in this pericentromeric region: significantly (P < .01) more female than male crossovers were observed across all of the adjacent intervals D10S24–FNRB, FNRB–D10Z1, and D10Z1–RBP3. However, a sex difference was not seen in the 7-cM interval from RBP3 to D10S5, suggesting that large variation in the sex difference in recombination can occur over small chromosomal regions. Proper clinical application of these DNA markers in genetic counseling to determine the genotypes at the disease locus for those at-risk members in informative afflicted families must therefore take into account the implications imposed by the large and highly significant sex effect on recombination in the MEN2A region.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudet A. L., Feldman G. L., Fernbach S. D., Buffone G. J., O'Brien W. E. Linkage disequilibrium, cystic fibrosis, and genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):319–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Kievits T., Waye J. S., Pearson P. L., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA: isolation and mapping of a polymorphic alphoid repeat from human chromosome 10. Genomics. 1988 Jul;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D. F., Ponder M. A., Cummings T., Gagel R. F., Hansen H. H., Reichlin S., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Telenius-Berg M., Ponder B. A. The clinical and screening age-at-onset distribution for the MEN-2 syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;44(2):208–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Bonne-Tamir B., Frydman M., Magazanik A., Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Predicting genotypes at loci for autosomal recessive disorders using linked genetic markers: application to Wilson's disease. Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;79(2):109–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00280547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Goodfellow P. J., White B. N., Holden J. J., Kidd J. R., Simpson N. E., Kidd K. K. Linkage analysis of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN-2A) and three DNA markers on chromosome 20: evidence against synteny. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Aug;27(2):327–334. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagel R. F., Jackson C. E., Block M. A., Feldman Z. T., Reichlin S., Hamilton B. P., Tashjian A. H., Jr Age-related probability of development of hereditary medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Pediatr. 1982 Dec;101(6):941–946. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagel R. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Cummings T., Papathanasopoulos N., Kaplan M. M., DeLellis R. A., Wolfe H. J., Reichlin S. The clinical outcome of prospective screening for multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2a. An 18-year experience. N Engl J Med. 1988 Feb 25;318(8):478–484. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198802253180804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Nevanlinna H. A., Gorman P., Sheer D., Lam G., Goodfellow P. N. Assignment of the gene encoding the beta-subunit of the human fibronectin receptor (beta-FNR) to chromosome 10p11.2. Ann Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;53(Pt 1):15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1989.tb01118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop M., Nakamura Y., Cartwright P., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Jones C., Tateishi H., Bragg T., Lalouel J. M., White R. A primary genetic map of markers of human chromosome 10. Genomics. 1988 Feb;2(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew C. G., Chin K. S., Easton D. F., Thorpe K., Carter C., Liou G. I., Fong S. L., Bridges C. D., Haak H., Kruseman A. C. A linked genetic marker for multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A on chromosome 10. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):527–528. doi: 10.1038/328527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Carlson M., Krapcho K., Gill J., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pMCK2 on chromosome 10 [D10S15]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):374–374. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., Bragg T., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Jones C., Lalouel J. M., White R. An extended genetic linkage map of markers for human chromosome 10. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):389–392. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90133-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Mathew C. G., Sobol H., Easton D. F., Telenius H., Bragg T., Chin K., Clark J., Jones C., Lenoir G. M. Linked markers flanking the gene for multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A computer program for linkage analysis of general human pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):528–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakstis A. J., Kidd J. R., Castiglione C., Sparkes R. S., Kidd K. K. Close linkage of MT2P1 with GC on chromosome 4. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(3):189–190. doi: 10.1159/000132226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson N. E., Kidd K. K., Goodfellow P. J., McDermid H., Myers S., Kidd J. R., Jackson C. E., Duncan A. M., Farrer L. A., Brasch K. Assignment of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A to chromosome 10 by linkage. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):528–530. doi: 10.1038/328528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Simpson N. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 9 and 10. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):202–225. doi: 10.1159/000132792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol H., Salvetti A., Bonnardel C., Lenoir G. M. Screening multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A families using DNA markers. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):62–62. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells S. A., Jr, Baylin S. B., Linehan W. M., Farrell R. E., Cox E. B., Cooper C. W. Provocative agents and the diagnosis of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Ann Surg. 1978 Aug;188(2):139–141. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197808000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Giuffra L. A., Goodfellow P. J., Myers S., Carson N. L., Anderson L., Hoyle L. S., Simpson N. E., Kidd K. K. The beta subunit locus of the human fibronectin receptor: DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism and linkage mapping studies. Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;83(4):383–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00291386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Cavenee W. K., Miki T., Kidd K. K. A polymorphic DNA marker on chromosome 10 linked to RBP3 on the MEN2A side. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(4):246–247. doi: 10.1159/000132639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Takai S., Miki T., Motomura K., Okazaki M., Nishisho I., Tateishi H., Miyauchi A., Honjo T., Pakstis A. J. Close linkage of MEN2A with RBP3 locus in Japanese kindreds. Hum Genet. 1989 Jun;82(3):287–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00291173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


