Abstract
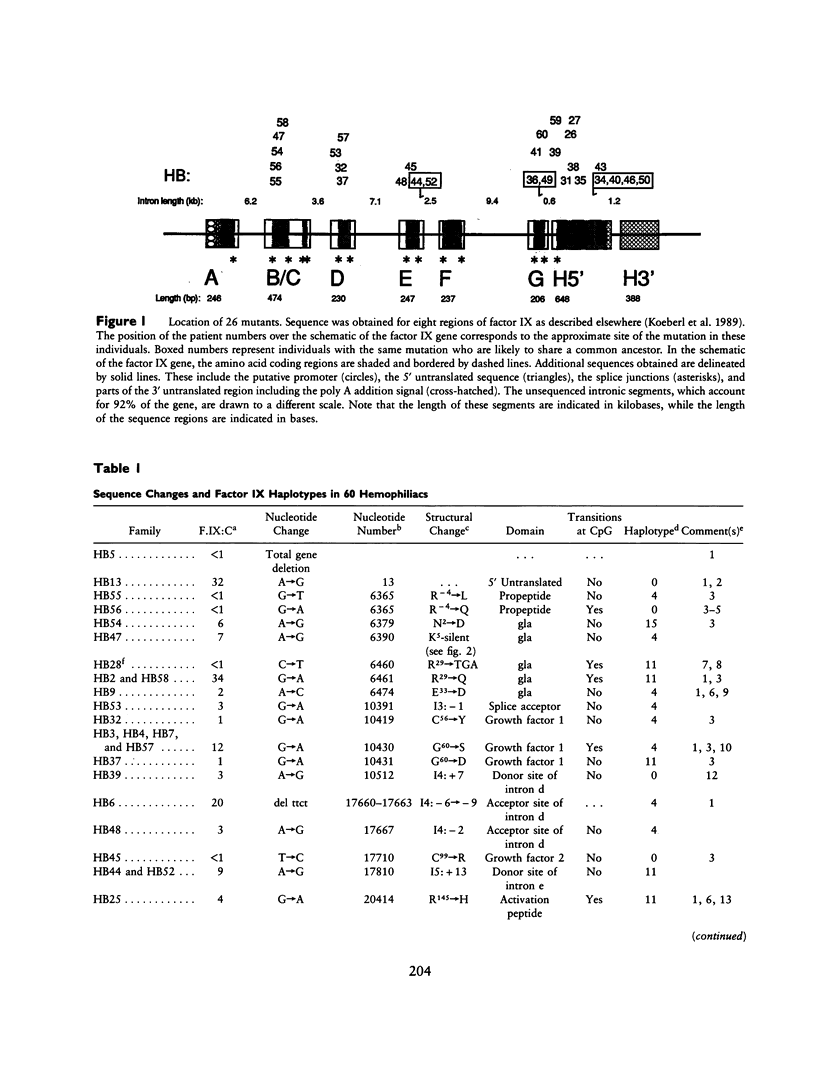
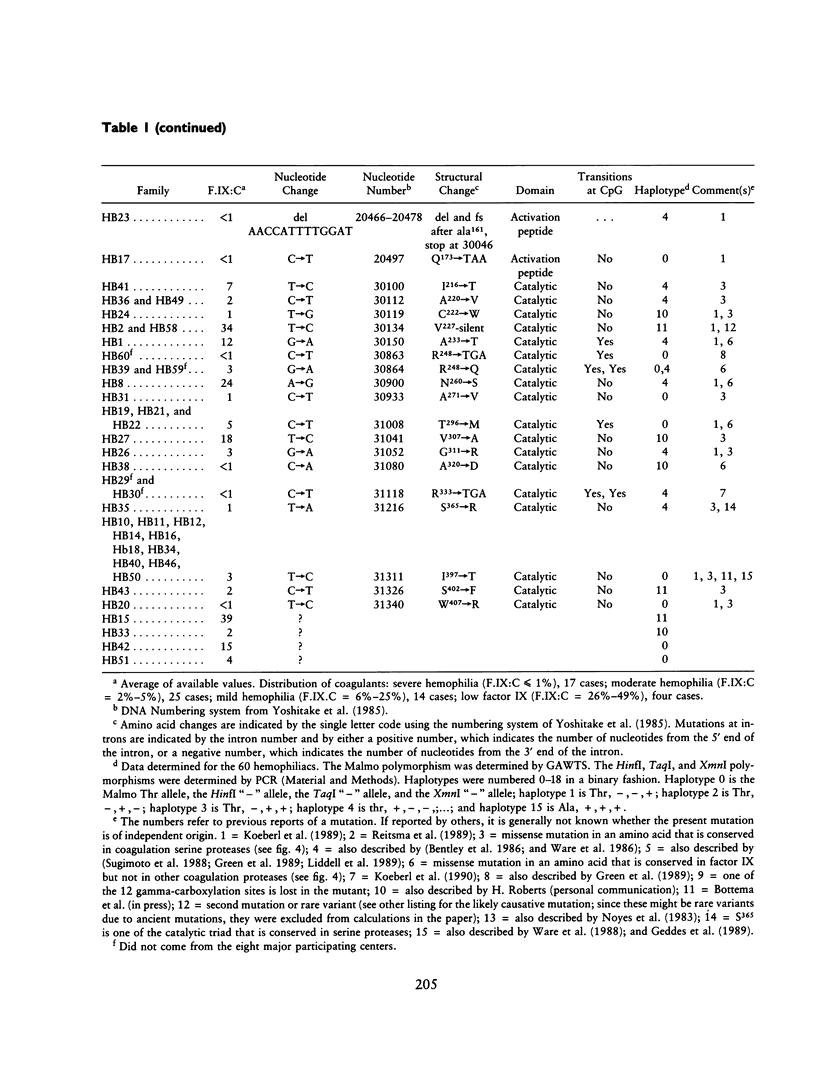
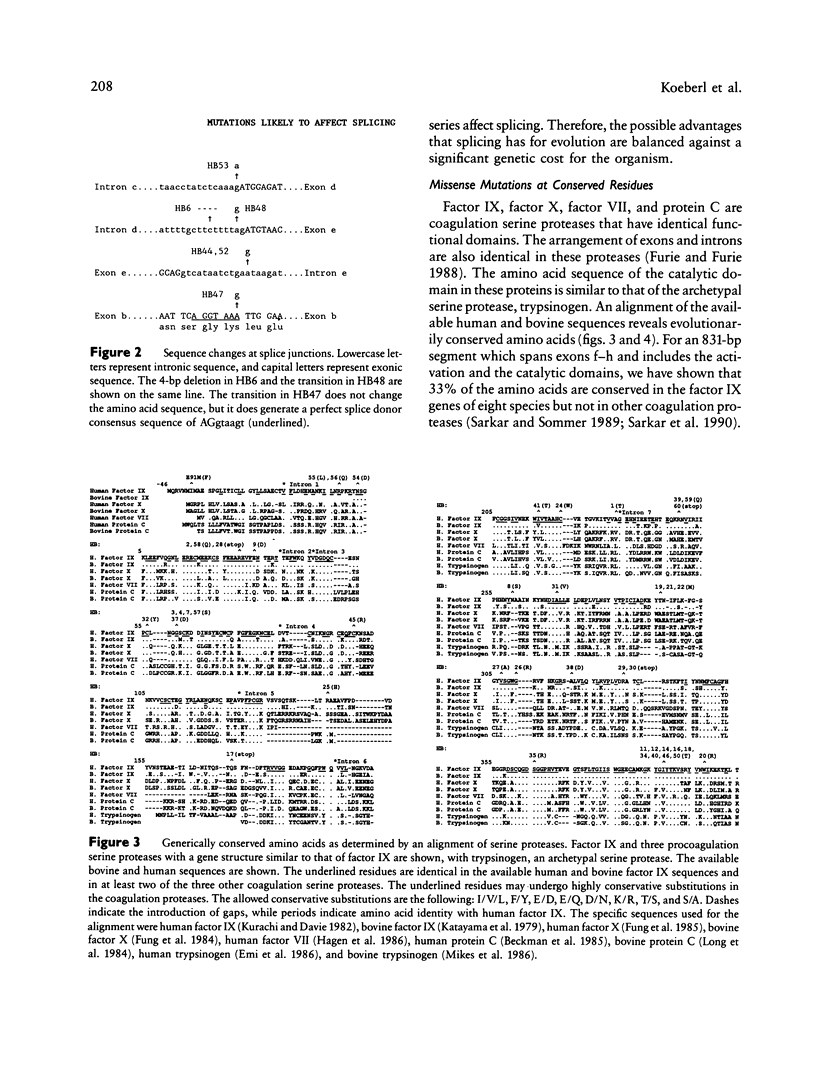
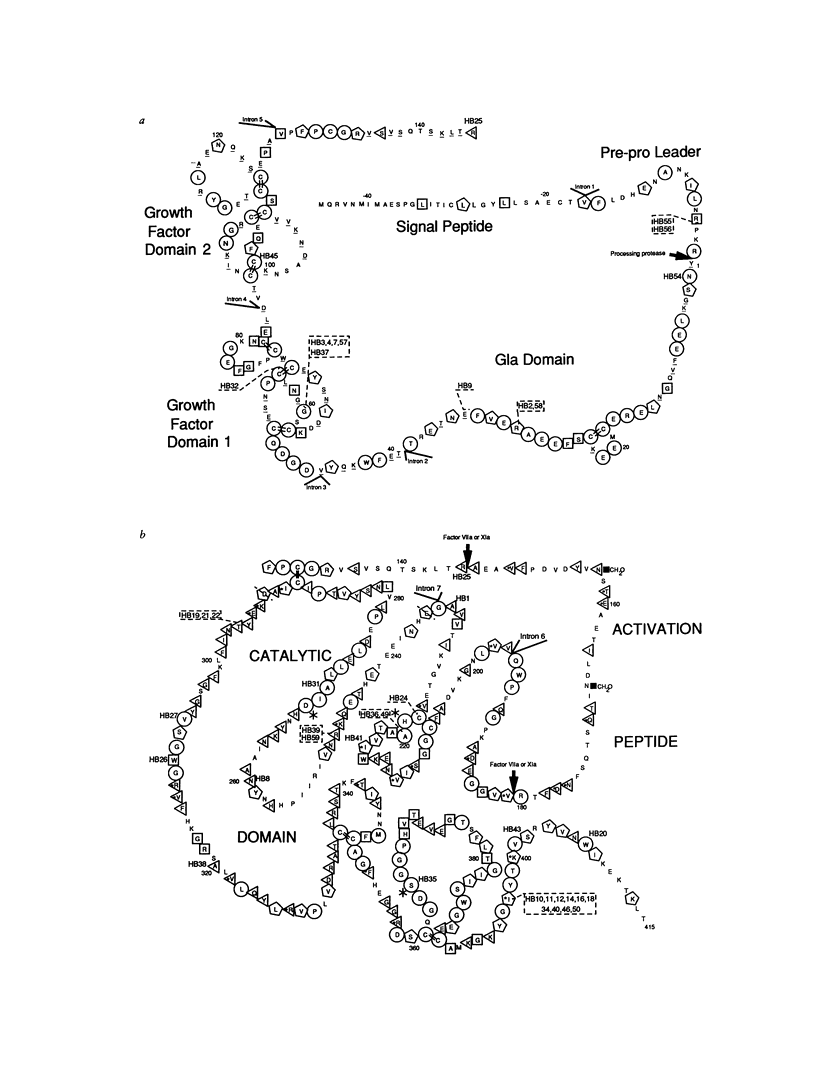
Spontaneous mutation provides the substrate for evolution on one hand and for genetic susceptibility to disease on the other hand. X-linked diseases such as hemophilia B offer an opportunity to examine recent germ-line mutations in humans. By utilizing the direct sequencing method of genomic amplification with transcript sequencing, eight regions (2.46 kb) of likely functional significance in the factor IX gene have been sequenced in a total of 60 consecutive, unrelated hemophiliacs. The high frequency of patient ascertainment from three regions in the midwestern United States and Canada suggests that the sample is representative of hemophiliacs of northern European descent. Twenty-six of the delineated mutations are reported herein, and the group of 60 is analyzed as a whole. From the pattern of mutations causing disease and from a knowledge of evolutionarily conserved amino acids, it is possible to reconstruct the underlying pattern of mutation and to calculate the mutation rates per base pair per generation for transitions (27 x 10(-10)), transversions (4.1 x 10(-10), and deletions (0.9 x 10(-10)) for a total mutation rate of 32 x 10(-10). The proportion of transitions at non-CpG nucleotides is elevated sevenfold over that expected if one base substitution were as likely as another. At the dinucleotide CpG, transitions are elevated 24-fold relative to transitions at other sites. The pattern of spontaneous mutations in factor IX resembles that observed in Escherichia coli when the data are corrected for ascertainment bias. The aggregate data hint that most mutations may be due to endogenous processes. The following additional conclusions emerge from the data: (1) Although in recent decades reproductive fitness in individuals with mild and moderate hemophilia has been approximately normal, the large number of different mutations found strongly suggest that these levels of disease substantially compromised reproduction in previous centuries. (2) Mutations which putatively affect splicing account for at least 13% of independent mutations, indicating that the division of the gene into eight exons presents a significant genetic cost for the organism. In one individual a "silent" mutation at lysine 5 is likely to cause hemophilia by generating a perfect splice donor consensus sequence in exon b. (3) All the missense mutations occurred at evolutionarily conserved amino acids. As additional data are generated on the pattern of mutations caused by specific mutagens, it will be possible to utilize the pattern of spontaneous mutation to estimate the maximal contribution of that mutagen during the past century.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Giannelli F., Gould K., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The gene structure of human anti-haemophilic factor IX. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Orkin S. H. DNA polymorphism and molecular pathology of the human globin gene clusters. Hum Genet. 1985;69(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00295521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr The molecular basis of hemophilia A in man. Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attree O., Vidaud D., Vidaud M., Amselem S., Lavergne J. M., Goossens M. Mutations in the catalytic domain of human coagulation factor IX: rapid characterization by direct genomic sequencing of DNA fragments displaying an altered melting behavior. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrai I., Cann H. M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Barbujani G., De Nicola P. Segregation analysis of hemophilia A and B. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):680–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. J., Schmidt R. J., Santerre R. F., Plutzky J., Crabtree G. R., Long G. L. The structure and evolution of a 461 amino acid human protein C precursor and its messenger RNA, based upon the DNA sequence of cloned human liver cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5233–5247. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. K., Rees D. J., Rizza C., Brownlee G. G. Defective propeptide processing of blood clotting factor IX caused by mutation of arginine to glutamine at position -4. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Grzeschik K. H., Jaye M., De La Salle H., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Regional localization on the human X chromosome and polymorphism of the coagulation factor IX gene (hemophilia B locus). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R., Neel J. V. Description and validation of a method for simultaneous estimation of effective population size and mutation rate from human population data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9407–9411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Youssoufian H. The CpG dinucleotide and human genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):151–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00278187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. P., Watzke H. H., Ware J. L., Stafford D. W., High K. A. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding canine factor IX. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster M. E., Lewis J. H., Shapiro S. S., Gill F., Kajani M., Prager D., Djerassi I., Rice S., Lusch C., Keller A. The Pennsylvania hemophilia program 1973-1978. Am J Hematol. 1980;9(3):277–286. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830090306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Campbell R. M., MacGillivray R. T. Blood coagulation factor X mRNA encodes a single polypeptide chain containing a prepro leader sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4481–4492. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Hay C. W., MacGillivray R. T. Characterization of an almost full-length cDNA coding for human blood coagulation factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3591–3595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes V. A., Le Bonniec B. F., Louie G. V., Brayer G. D., Thompson A. R., MacGillivray R. T. A moderate form of hemophilia B is caused by a novel mutation in the protease domain of factor IXVancouver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4689–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Boyd Y., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Gene deletions in patients with haemophilia B and anti-factor IX antibodies. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):181–182. doi: 10.1038/303181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Nguyen P. N., McBride L. J., Koepf S. M., Caskey C. T. Identification of mutations leading to the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome by automated direct DNA sequencing of in vitro amplified cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. M., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Nilsson I. M., Giannelli F. Molecular pathology of haemophilia B. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson S., Proper J. A., Bowie E. J., Sommer S. S. Parameters affecting the yield of DNA from human blood. Anal Biochem. 1987 Sep;165(2):294–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Gray C. L., O'Hara P., Grant F. J., Saari G. C., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kurachi K. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Kawabata S., Nishimura H., Takeya H., Sueyoshi T., Miyata T., Iwanaga S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Ikenaka T. A new trisaccharide sugar chain linked to a serine residue in bovine blood coagulation factors VII and IX. J Biochem. 1988 Dec;104(6):867–868. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. N., Kasper C. K., Roberts H. R., Stafford D. W., High K. A. Molecular defect in factor IXHilo, a hemophilia Bm variant: Arg----Gln at the carboxyterminal cleavage site of the activation peptide. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):718–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M., Gallinaro H. The 5' splice site: phylogenetic evolution and variable geometry of association with U1RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2159–2180. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K., Ericsson L. H., Enfield D. L., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W., Titani K. Comparison of amino acid sequence of bovine coagulation Factor IX (Christmas Factor) with that of other vitamin K-dependent plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeberl D. D., Bottema C. D., Buerstedde J. M., Sommer S. S. Functionally important regions of the factor IX gene have a low rate of polymorphism and a high rate of mutation in the dinucleotide CpG. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):448–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeberl D. D., Bottema C. D., Sarkar G., Ketterling R. P., Chen S. H., Sommer S. S. Recurrent nonsense mutations at arginine residues cause severe hemophilia B in unrelated hemophiliacs. Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;84(5):387–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00195805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson S. A. Life expectancy of Swedish haemophiliacs, 1831-1980. Br J Haematol. 1985 Apr;59(4):593–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson S. A., Nilsson I. M., Blombäck M. Current status of Swedish hemophiliacs. I. A demographic survey. Acta Med Scand. 1982;212(4):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1982.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddell M. B., Lillicrap D. P., Peake I. R., Bloom A. L. Defective propeptide processing and abnormal activation underlie the molecular pathology of factor IX Troed-y-Rhiw. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jun;72(2):208–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Belagaje R. M., MacGillivray R. T. Cloning and sequencing of liver cDNA coding for bovine protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5653–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L. Dystrophin. The gene and its product. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):584–586. doi: 10.1038/339584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masys D. R., Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I. Activation of human factor VII by activated factors IX and X. Blood. 1982 Nov;60(5):1143–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw R. A., Davis L. M., Noyes C. M., Lundblad R. L., Roberts H. R., Graham J. B., Stafford D. W. Evidence for a prevalent dimorphism in the activation peptide of human coagulation factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2847–2851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikes O., Holeysovský V., Tomásek V., Sorm F. Covalent structure of bovine trypsinogen. The position of the remaining amides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 12;24(3):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon A. J., Green P. M., Giannelli F., Bentley D. R. Direct detection of point mutations by mismatch analysis: application to haemophilia B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3347–3358. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: pathogenetic aspects and genetic prevention. Hum Genet. 1984;66(1):17–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00275183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V., Satoh C., Goriki K., Fujita M., Takahashi N., Asakawa J., Hazama R. The rate with which spontaneous mutation alters the electrophoretic mobility of polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):389–393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes C. M., Griffith M. J., Roberts H. R., Lundblad R. L. Identification of the molecular defect in factor IX Chapel Hill: substitution of histidine for arginine at position 145. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4200–4202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poort S. R., Briët E., Bertina R. M., Reitsma P. H. A Dutch family with moderately severe hemophilia B (factor IXHeerde) has a missense mutation identical to that of factor IX London 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3614–3614. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Mandalaki T., Kasper C. K., Bertina R. M., Briët E. Two novel point mutations correlate with an altered developmental expression of blood coagulation factor IX (hemophilia B Leyden phenotype). Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):743–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Yoshioka A., Yamamoto K., Niinomi K., Fujimura Y., Fukui H., Miyata T., Iwanaga S. Blood clotting factor IX Kashihara: amino acid substitution of valine-182 by phenylalanine. J Biochem. 1989 May;105(5):756–759. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Koeberl D. D., Sommer S. S. Direct sequencing of the activation peptide and the catalytic domain of the factor IX gene in six species. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Access to a messenger RNA sequence or its protein product is not limited by tissue or species specificity. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):331–334. doi: 10.1126/science.2565599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Danforth B. N., Glickman B. W. Mechanisms of spontaneous mutagenesis: an analysis of the spectrum of spontaneous mutation in the Escherichia coli lacI gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90509-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Dunn R. L. Spectra of spontaneous mutations in Escherichia coli strains defective in mismatch correction: the nature of in vivo DNA replication errors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6220–6224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Cohen J. E. The size distributions of proteins, mRNA, and nuclear RNA. J Mol Evol. 1980 Mar;15(1):37–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01732582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer S. G., Pendurthi U. R., Kasper C. K., Bajaj S. P. Molecular defect in factor IXBm Lake Elsinore. Substitution of Ala390 by Val in the catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10545–10548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoflet E. S., Koeberl D. D., Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Genomic amplification with transcript sequencing. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.3340835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Miyata T., Kawabata S., Yoshioka A., Fukui H., Takahashi H., Iwanaga S. Blood clotting factor IX Niigata: substitution of alanine-390 by valine in the catalytic domain. J Biochem. 1988 Dec;104(6):878–880. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang T. C., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Giannelli F. A factor IX mutation, verified by direct genomic sequencing, causes haemophilia B by a novel mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3009–3015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Kopun M. Higher frequencies of transitions among point mutations. J Mol Evol. 1977 Apr 29;9(2):159–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01732746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Rathenberg R. Spontaneous mutation in man. Adv Hum Genet. 1975;5:223–318. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9068-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliamy T. J., D'Urso M., Battistuzzi G., Estrada M., Foulkes N. S., Martini G., Calabro V., Poggi V., Giordano R., Town M. Diverse point mutations in the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene cause enzyme deficiency and mild or severe hemolytic anemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5171–5175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Davis L., Frazier D., Bajaj S. P., Stafford D. W. Genetic defect responsible for the dysfunctional protein: factor IXLong Beach. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):820–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Diuguid D. L., Liebman H. A., Rabiet M. J., Kasper C. K., Furie B. C., Furie B., Stafford D. W. Factor IX San Dimas. Substitution of glutamine for Arg-4 in the propeptide leads to incomplete gamma-carboxylation and altered phospholipid binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11401–11406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Jr, Martin R. G., Ames B. N. Classification of aminotransferase (C gene) mutants in the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):335–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R., Anson D. S., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Carrier detection in haemophilia B using two further intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8861–8872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Dowling C. E., Saiki R. K., Higuchi R. G., Erlich H. A., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of beta-thalassaemia mutations using direct genomic sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):384–386. doi: 10.1038/330384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake S., Schach B. G., Foster D. C., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3736–3750. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Phillips D. G., Aronis S., Tsiftis G., Brown V. A., Antonarakis S. E. Recurrent mutations in haemophilia A give evidence for CpG mutation hotspots. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):380–382. doi: 10.1038/324380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


