Abstract
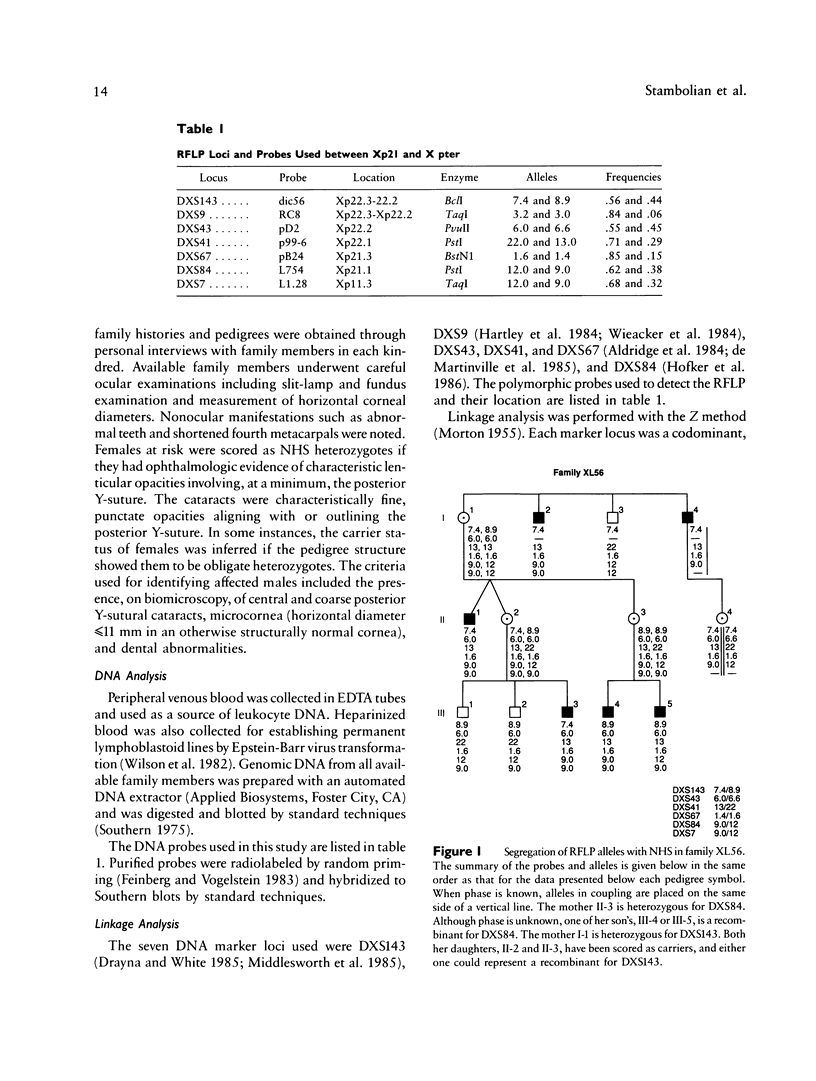
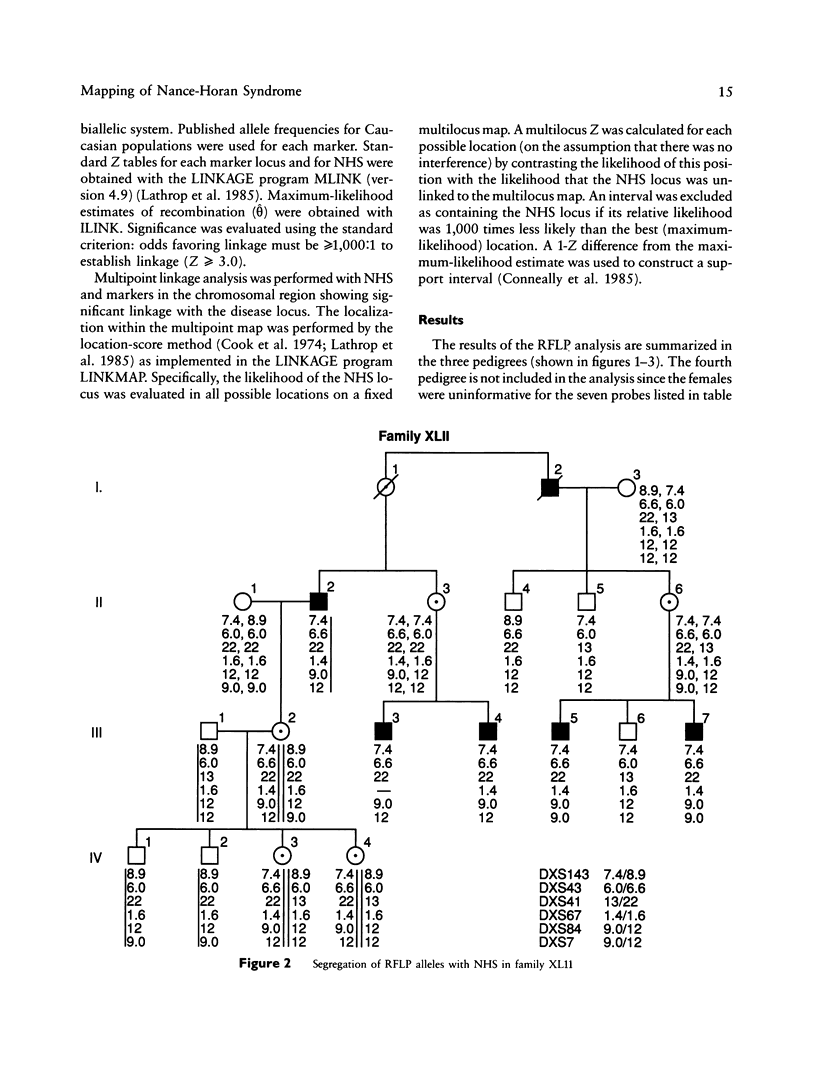
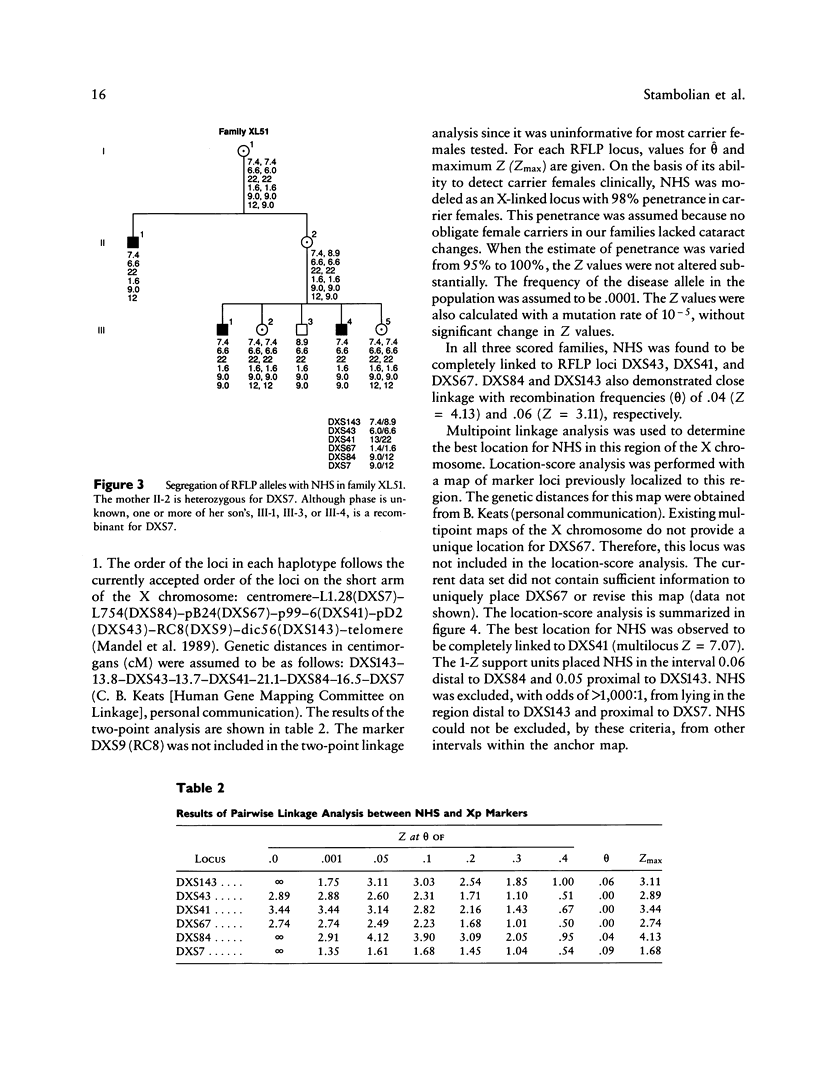
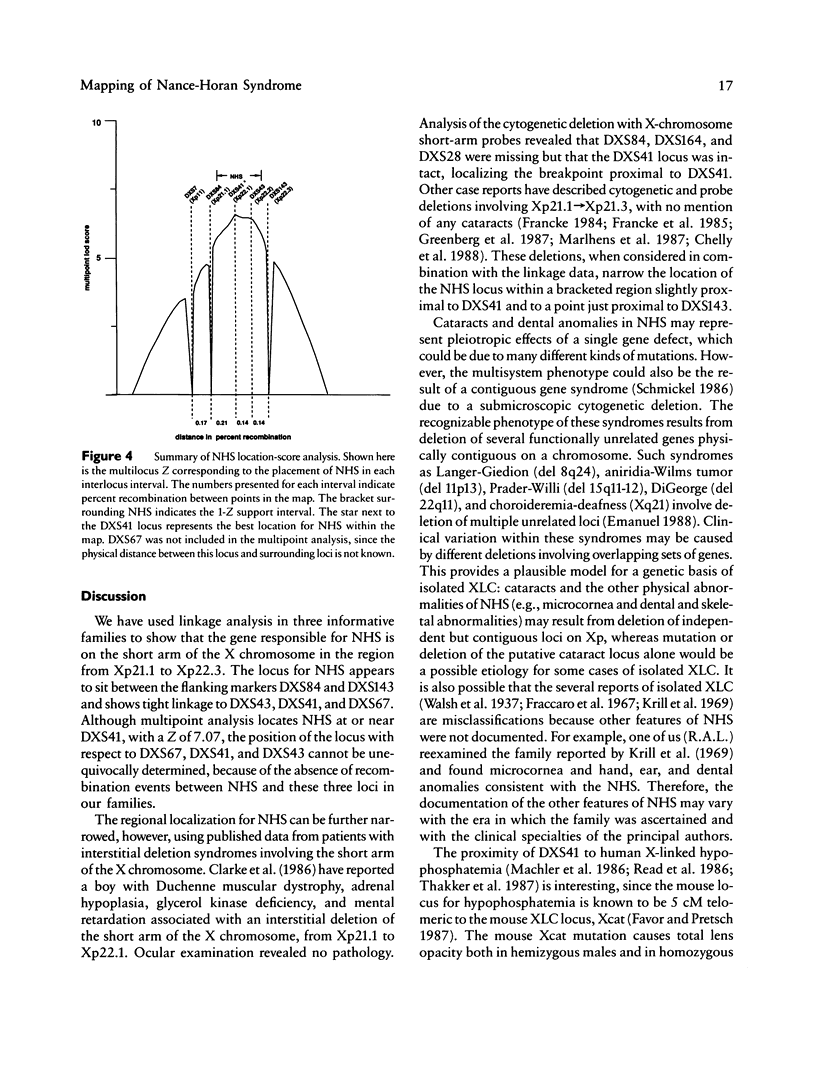
Nance-Horan Syndrome (NHS) or X-linked cataract-dental syndrome (MIM 302350) is a disease of unknown pathogenesis characterized by congenital cataracts and dental anomalies. We performed linkage analysis in three kindreds with NHS by using six RFLP markers between Xp11.3 and Xp22.3. Close linkage was found between NHS and polymorphic loci DXS43 (theta = 0 with lod score 2.89), DXS41 (theta = 0 with lod score 3.44), and DXS67 (theta = 0 with lod score 2.74), defined by probes pD2, p99-6, and pB24, respectively. Recombinations were found with the marker loci DXS84 (theta = .04 with lod score 4.13), DXS143 (theta = .06 with lod score 3.11) and DXS7 (theta = .09 with lod score 1.68). Multipoint linkage analysis determined the NHS locus to be linked completely to DXS41 (lod score = 7.07). Our linkage results, combined with analysis of Xp interstitial deletions, suggest that the NHS locus is located within or close to the Xp22.1-Xp22.2 region.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixler D., Higgins M., Hartsfield J., Jr The Nance-Horan syndrome: a rare X-linked ocular-dental trait with expression in heterozygous females. Clin Genet. 1984 Jul;26(1):30–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle V. J., Edwards J. H., Evans E. P., Jonasson J. A., Lyon M. F., Peters J., Searle A. G., Wedd N. S. Chromosome maps of man and mouse II. Clin Genet. 1984 Jul;26(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Marlhens F., Dutrillaux B., Van Ommen G. J., Lambert M., Haioun B., Boissinot G., Fardeau M., Kaplan J. C. Deletion proximal to DXS68 locus (L1 probe site) in a boy with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, glycerol kinase deficiency, and adrenal hypoplasia. Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;78(3):222–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00291665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A., Roberts S. H., Thomas N. S., Whitfield A., Williams J., Harper P. S. Duchenne muscular dystrophy with adrenal insufficiency and glycerol kinase deficiency: high resolution cytogenetic analysis with molecular, biochemical, and clinical studies. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):501–508. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. J., Robson E. B., Buckton K. E., Jacobs P. A., Polani P. E. Segregation of genetic markers in families with chromosome polymorphisms and structural rearrangements involving chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):261–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel B. S. Molecular cytogenetics: toward dissection of the contiguous gene syndromes. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):575–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraccaro M., Morone G., Manfredini U., Sanger R. X-linked cataract. Ann Hum Genet. 1967 Aug;31(1):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Random X inactivation resulting in mosaic nullisomy of region Xp21.1----p21.3 associated with heterozygosity for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency and for chronic granulomatous disease. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):298–307. doi: 10.1159/000132078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg C. R., Hamerton J. L., Nigli M., Wrogemann K. DNA studies in a family with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and a deletion at Xp21. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;41(2):128–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley D. A., Davies K. E., Drayna D., White R. L., Williamson R. A cytological map of the human X chromosome--evidence for non-random recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5277–5285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Bakker E., Burmeister M., Pearson P. L. Development of additional RFLP probes near the locus for Duchenne muscular dystrophy by cosmid cloning of the DXS84 (754) locus. Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;74(3):270–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00282547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krill A. E., Woodbury G., Bowman J. E. X-chromosomal-linked sutural cataracts. Am J Ophthalmol. 1969 Nov;68(5):867–872. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(69)94582-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Willard H. F., Nussbaum R. L., Romeo G., Puck J. M., Davies K. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):384–437. doi: 10.1159/000132801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlhens F., Chelly J., Kaplan J. C., Lefrancois D., Harpey J. P., Dutrillaux B. Familial deletion of Xp21.2 with glycerol kinase deficiency and congenital adrenal hypoplasia. Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;77(4):379–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00291430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlesworth W., Bertelson C., Kunkel L. M. An RFLP detecting single copy X-chromosome fragment, dic56, from Xp22-Xpter [HGM8 assignment no. DXS 143]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5723–5723. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mächler M., Frey D., Gal A., Orth U., Wienker T. F., Fanconi A., Schmid W. X-linked dominant hypophosphatemia is closely linked to DNA markers DXS41 and DXS43 at Xp22. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):271–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00401243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance W. E., Warburg M., Bixler D., Helveston E. M. Congenital X-linked cataract, dental anomalies and brachymetacarpalia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1974;10(4):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read A. P., Thakker R. V., Davies K. E., Mountford R. C., Brenton D. P., Davies M., Glorieux F., Harris R., Hendy G. N., King A. Mapping of human X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets by multilocus linkage analysis. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00401242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Contiguous gene syndromes: a component of recognizable syndromes. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Read A. P., Davies K. E., Whyte M. P., Weksberg R., Glorieux F., Davies M., Mountford R. C., Harris R., King A. Bridging markers defining the map position of X linked hypophosphataemic rickets. J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;24(12):756–760. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.12.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Cooke H. J., Pearson P. L., Williamson R., Bhattacharya S., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward a complete linkage map of the human X chromosome: regional assignment of 16 cloned single-copy DNA sequences employing a panel of somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Baugher B. W., Mattes P. M., Daddona P. E., Kelley W. N. Human hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Demonstration of structural variants in lymphoblastoid cells derived from patients with a deficiency of the enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):706–715. doi: 10.1172/JCI110499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Kunkel L. M., Bruns G., Morlé F., Koenig M., Mandel J. L., Horwich A., Latt S. A., Gusella J. F., Housman D. Localization of DNA sequences in region Xp21 of the human X chromosome: search for molecular markers close to the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):235–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dorp D. B., Delleman J. W. A family with X-chromosomal recessive congenital cataract, microphthalmia, a peculiar form of the ear and dental anomalies. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1979 May-Jun;16(3):166–171. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19790501-08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


