Abstract
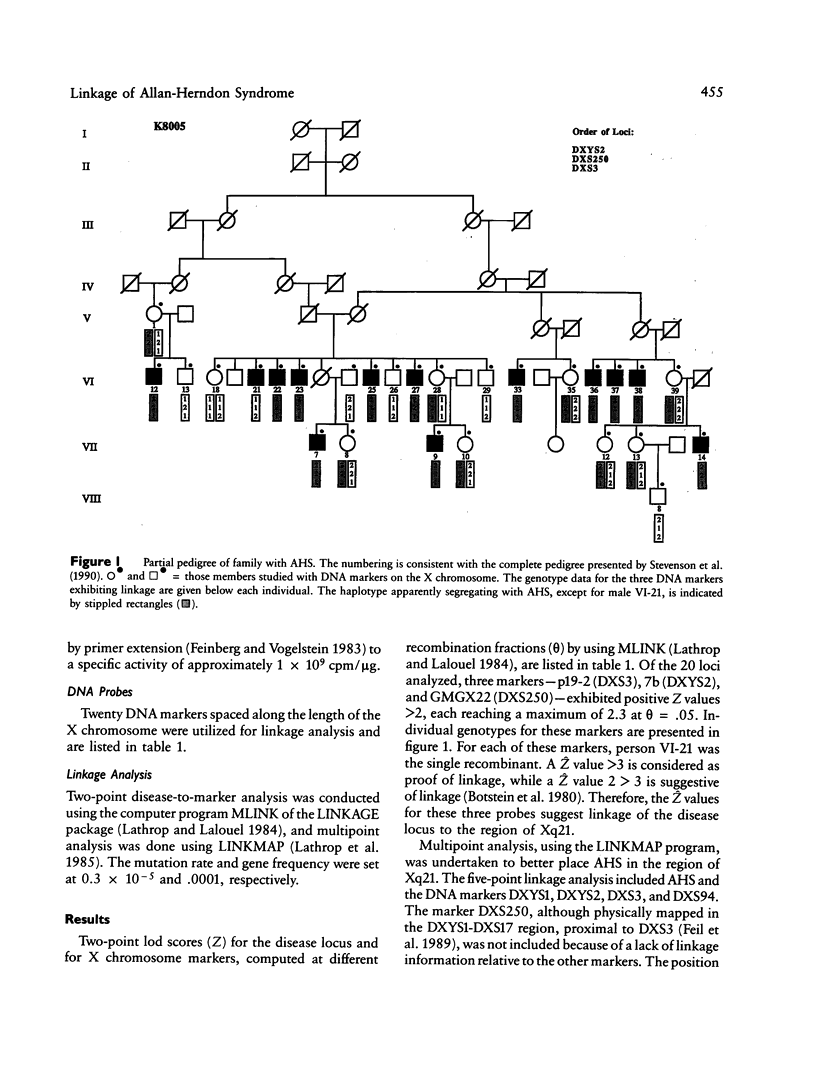
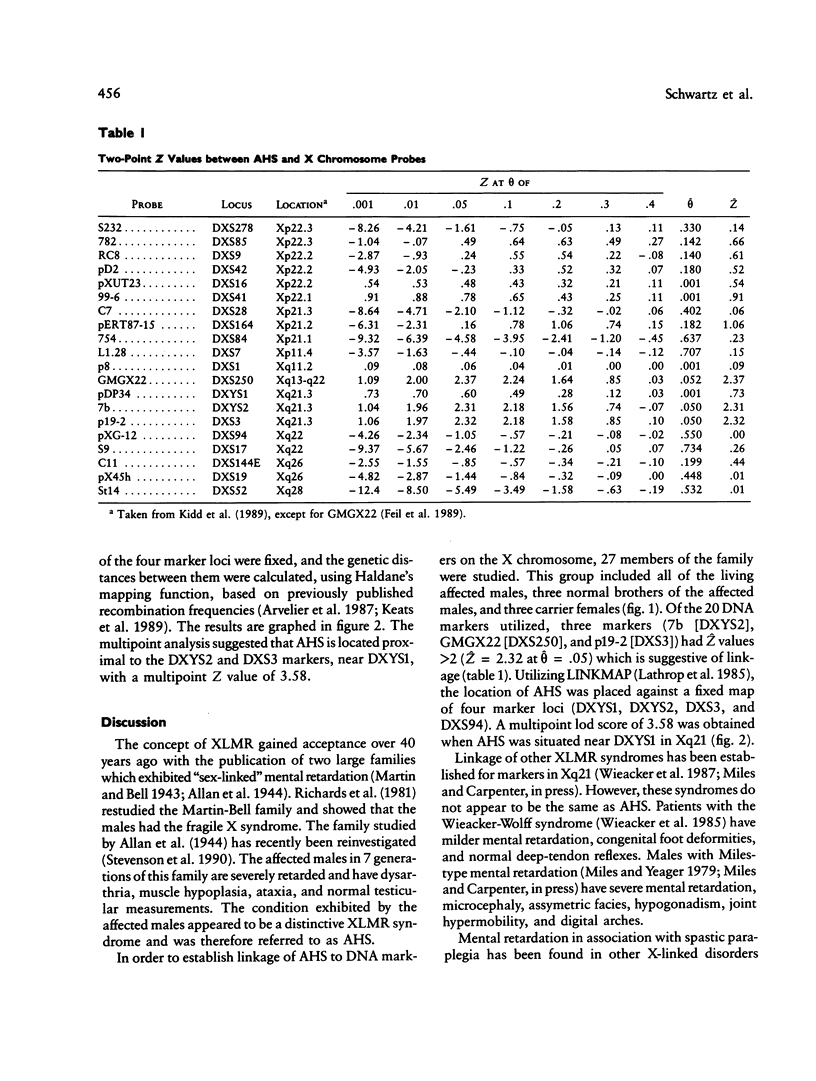
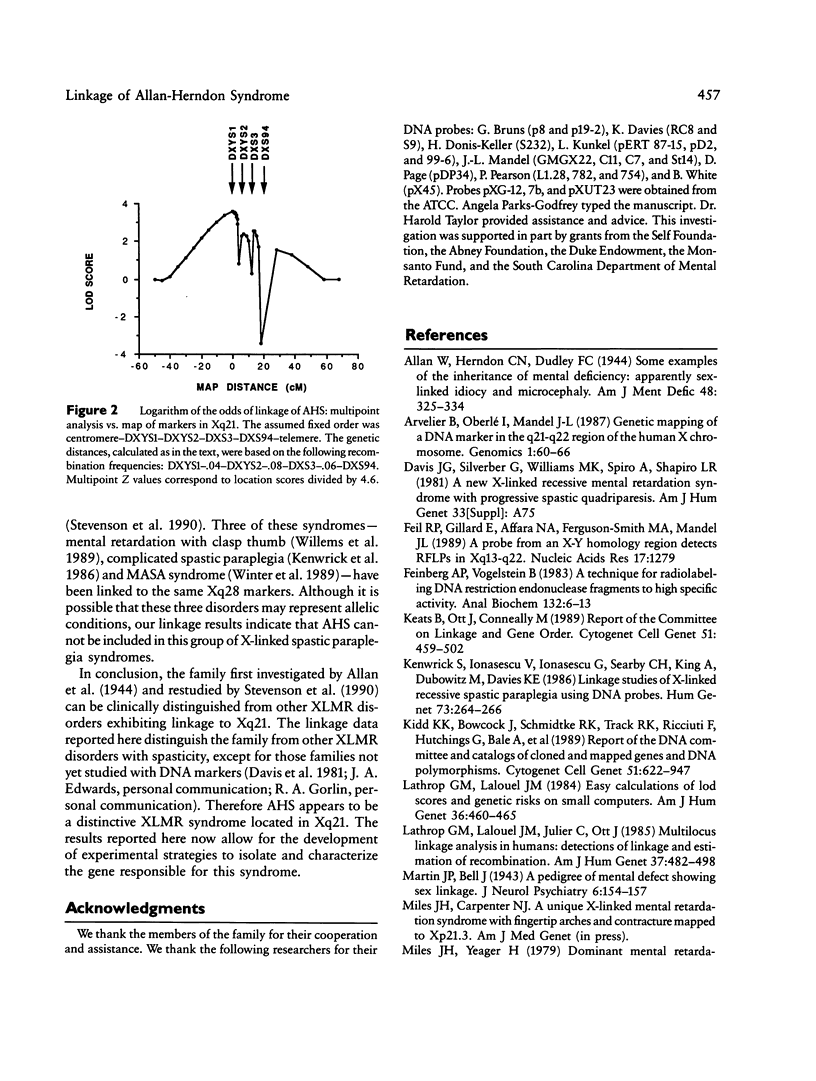
The original family with the Allan-Herndon type of X-linked mental retardation has been investigated for linkage by using DNA probes spanning the length of the X chromosome. Available for study, over 3 generations, were 13 affected males, three obligate carriers, and three normal sons of the obligate carriers. Initial disease-to-marker analysis suggested linkage to three markers (DXYS2 [7b], DXS250 [GMGX22], and DXS3 [p19-2]) located in Xq21. All three exhibited the same maximum lod score of 2.3 at a maximum theta of .05. Multipoint analysis using LINKMAP and a set of four DNA markers (DXYS1-DXYS2-DXS3-DXS94) gave a multipoint lod score of 3.58 for a location of the Allan-Herndon syndrome near locus DXYS1 (pDP34). Therefore, our data indicate that the gene for the Allan-Herndon syndrome is likely located in Xq21.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arveiler B., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. Genetic mapping of nine DNA markers in the q11----q22 region of the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):60–66. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil R. P., Gillard E., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Mandel J. L. A probe from an X-Y homology region detects RFLPs in Xq13-q22. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1279–1279. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu G., Searby C., King A., Dubowitz M., Davies K. E. Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00401241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards B. W., Sylvester P. E., Brooker C. Fragile X-linked mental retardation: the Martin-Bell syndrome. J Ment Defic Res. 1981 Dec;25(Pt 4):253–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1981.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. E., McNally E., Leinwand L., Skolnick M. H. A polymorphic human myosin heavy chain locus is linked to an anonymous single copy locus (D17S1) at 17p13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(1-2):117–120. doi: 10.1159/000132307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson R. E., Goodman H. O., Schwartz C. E., Simensen R. J., McLean W. T., Jr, Herndon C. N. Allan-Herndon syndrome. I. Clinical studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Sep;47(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wolff G., Wienker T. F. Close linkage of the Wieacker-Wolff syndrome to the DNA segment DXYS1 in proximal Xq. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):245–253. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wolff G., Wienker T. F., Sauer M. A new X-linked syndrome with muscle atrophy, congenital contractures, and oculomotor apraxia. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Apr;20(4):597–606. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Davies K. E., Bell M. V., Huson S. M., Patterson M. N. MASA syndrome: further clinical delineation and chromosomal localisation. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00273999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


