Abstract
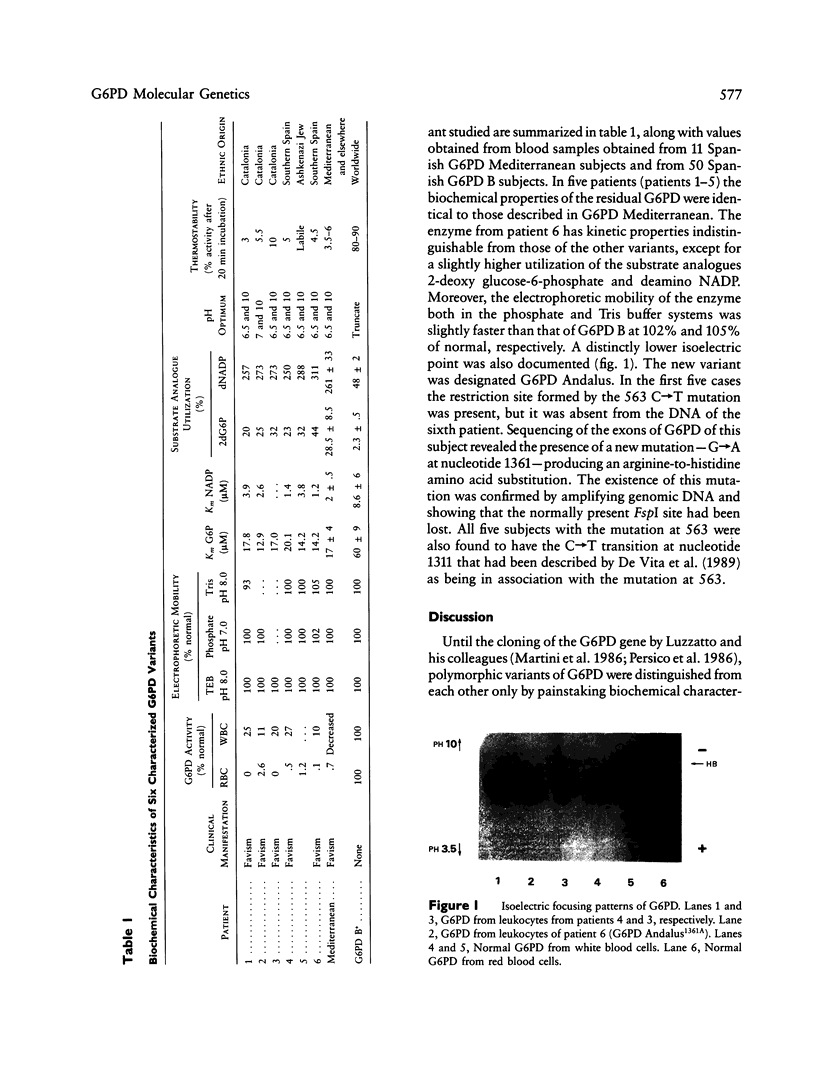
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD; E.C.1.1.1.49) deficiency is the most common human enzymopathy; more than 300 different biochemical variants of the enzyme have been described. In many parts of the world the Mediterranean type of G6PD deficiency is prevalent. However, G6PD Mediterranean has come to be regarded as a generic term applied to similar G6PD mutations thought, however, to represent a somewhat heterogeneous group. A C----T mutation at nucleotide 563 of G6PD Mediterranean has been identified by Vulliamy et al., and the same mutation has been found by De Vita et al. in G6PD Mediterranean, G6PD Sassari, and G6PD Cagliari. The latter subjects had an additional mutation, at nucleotide 1311, that did not produce a coding change. We have examined genomic DNA of five patients--four of Spanish origin and one of Jewish origin--having enzymatically documented G6PD Mediterranean. All had both the mutation at nucleotide 563 and that at nucleotide 1311. A sixth sample, resembling G6PD Mediterranean kinetically but with a slightly rapid electrophoretic mobility, was designated G6PD Andalus and was found to have a different mutation, a G----A transition at nucleotide 1361, producing an arginine-to-histidine substitution. These studies suggest that G6PD Mediterranean is, after all, relatively homogeneous.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset P., Beuzard Y., Garel M. C., Rosa J. Isoelectric focusing of human hemoglobin: its application to screening, to the characterization of 70 variants, and to the study of modified fractions of normal hemoglobins. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):971–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W., Vives-Corrons J. L., Prchal J. T. Molecular heterogeneity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase A-. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2550–2555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Lisker R., Kuhl W. Molecular biology of G 6 PD variants. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1990;49(2-3):S236–S241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Yoshida A. Genetic variation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a catalog and future prospects. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988 Sep;67(5):311–334. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198809000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vita G., Alcalay M., Sampietro M., Cappelini M. D., Fiorelli G., Toniolo D. Two point mutations are responsible for G6PD polymorphism in Sardinia. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;44(2):233–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks V. F., Nepo A. G., Beutler E., Dickson E. R., Honig G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variants: reexamination of G6PD Chicago and Cornell and a new variant (G6PD Pea Ridge) resembling G6PD Chicago. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):216–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirono A., Beutler E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant A(-). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3951–3954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirono A., Kuhl W., Gelbart T., Forman L., Fairbanks V. F., Beutler E. Identification of the binding domain for NADP+ of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by sequence analysis of mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10015–10017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRKMAN H. N., DOXIADIS S. A., VALAES T., TASSOPOULOS N., BRINSON A. G. DIVERSE CHARACTERISTICS OF GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE FROM GREEK CHILDREN. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:212–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Polymorphism of DNA sequence adjacent to human beta-globin structural gene: relationship to sickle mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5631–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Testa U. Human erythrocyte glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase: structure and function in normal and mutant subjects. Curr Top Hematol. 1978;1:1–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G., Toniolo D., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., Dono R., Viglietto G., Paonessa G., D'Urso M., Persico M. G. Structural analysis of the X-linked gene encoding human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1849–1855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa S. H., Nakashima K., Ono J., Fujii H., Suzuki E. Three glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase variants found in Japan. Hum Genet. 1977 May 10;36(3):327–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00446284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panich V., Na-Nakorn S. G-6-PD variants in Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai. 1980 Oct;63(10):537–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Viglietto G., Martini G., Toniolo D., Paonessa G., Moscatelli C., Dono R., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., D'Urso M. Isolation of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) cDNA clones: primary structure of the protein and unusual 5' non-coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2511–2522. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattazzi M. C. Isolation and purification of human erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from small amounts of blood. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May;181(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos G., Voigtlander V., Kotsakis P., Akrivakis A. Genetic diversity of the "Mediterranean" glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1253–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI106603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vives Corrons J. L., Pujades A. Heterogeneity of "Mediterranean type" glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in Spain and description of two new variants associated with favism. Hum Genet. 1982;60(3):216–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00303006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliamy T. J., D'Urso M., Battistuzzi G., Estrada M., Foulkes N. S., Martini G., Calabro V., Poggi V., Giordano R., Town M. Diverse point mutations in the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene cause enzyme deficiency and mild or severe hemolytic anemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5171–5175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]