Abstract
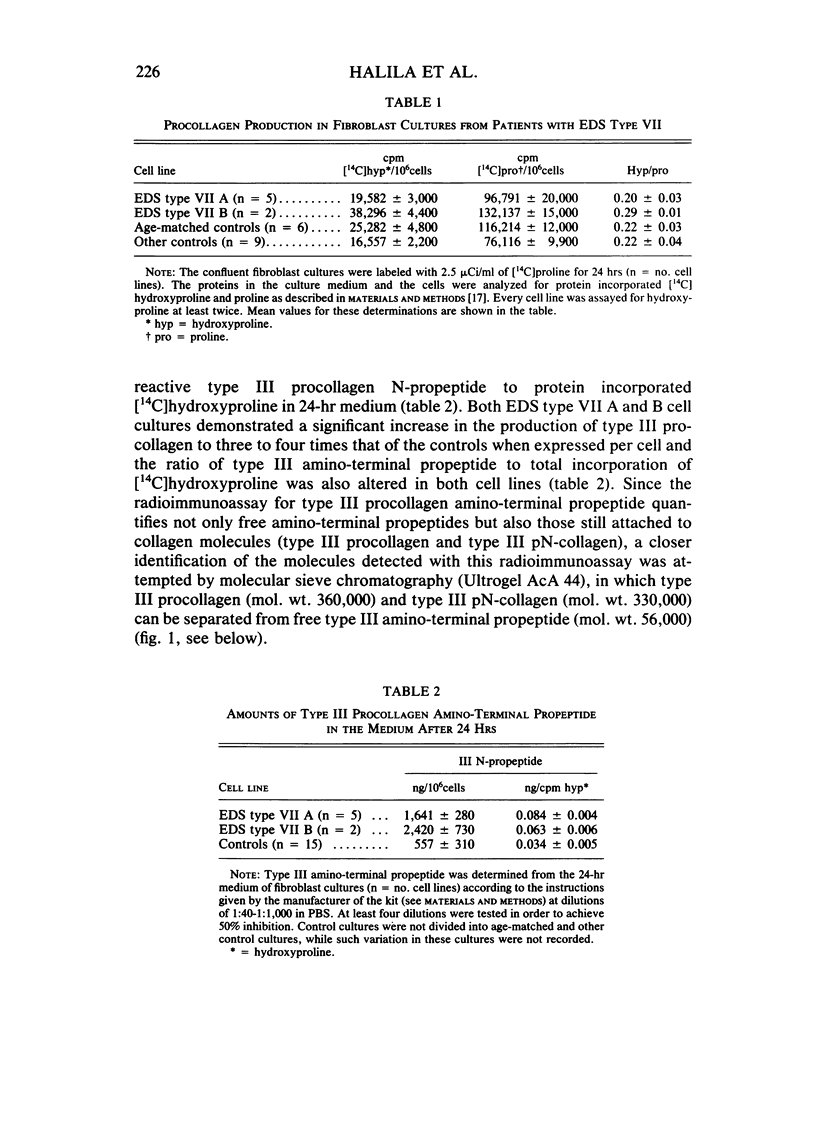
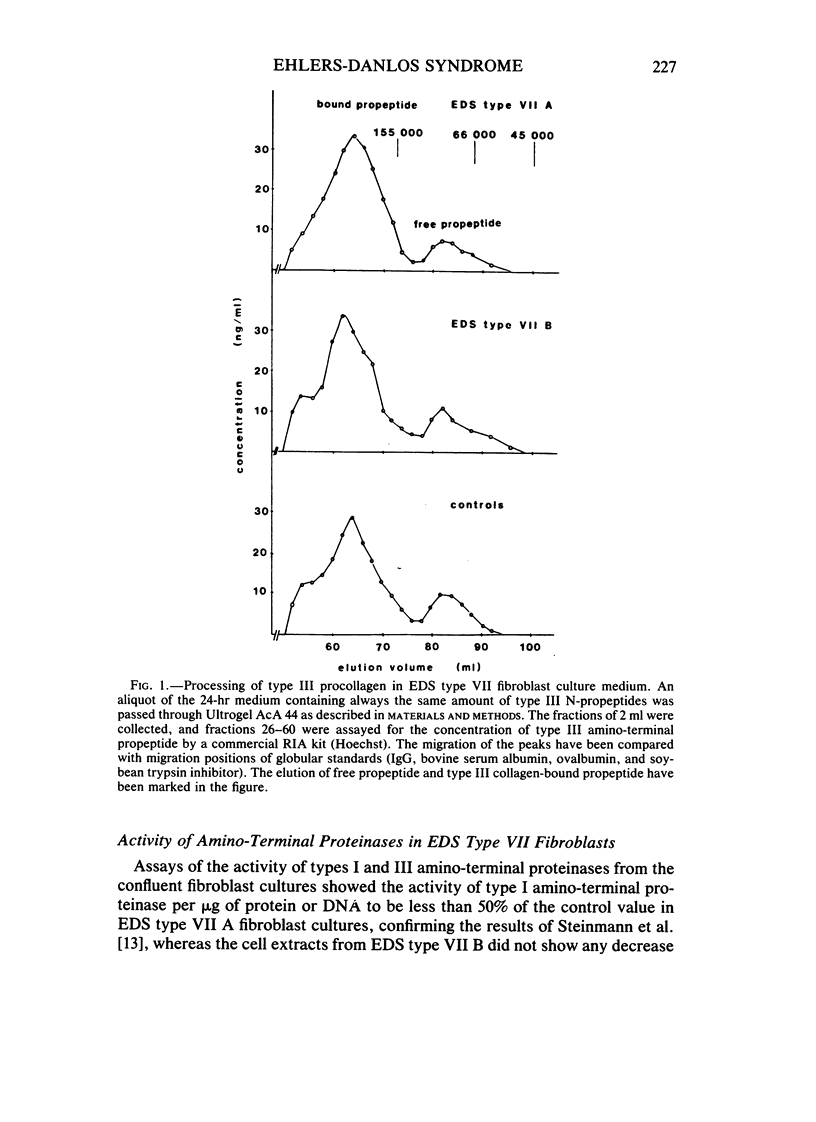
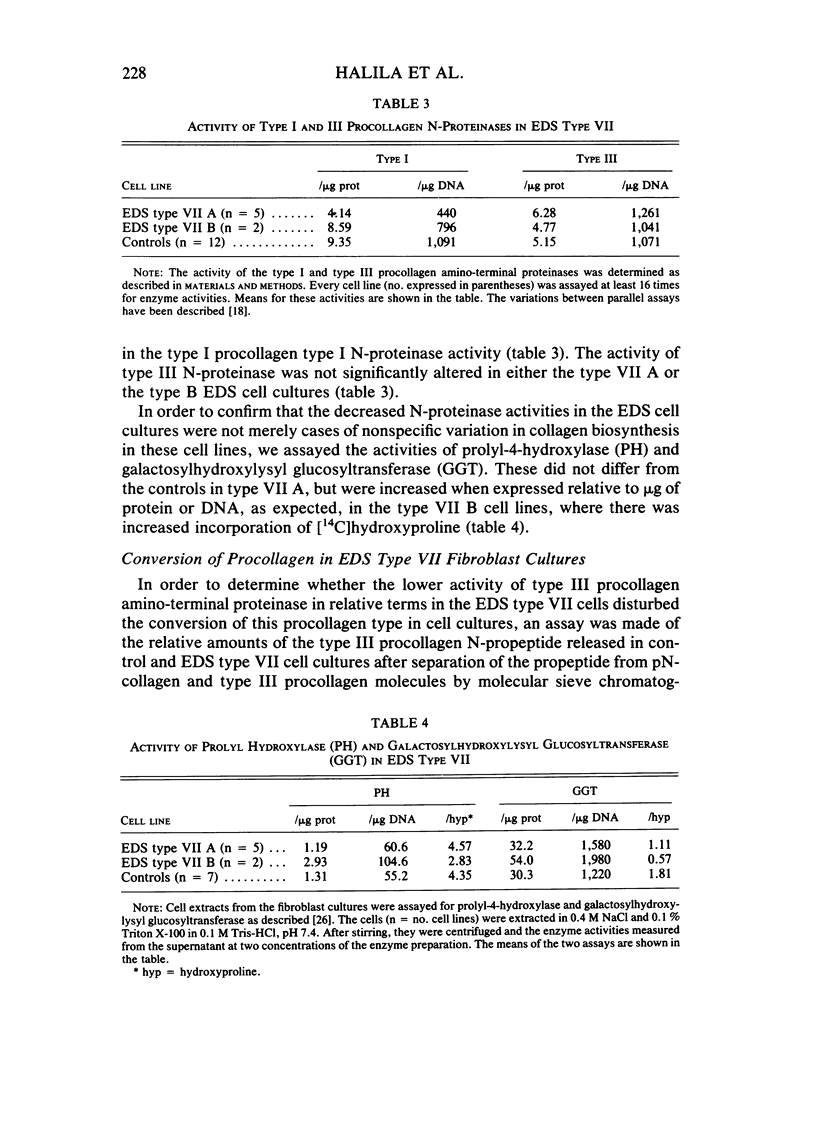
The processing of types I and III procollagen was studied in skin fibroblast cultures from type VII A and B of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome [EDS] and age-matched controls. Synthesis of collagenous proteins was significantly increased in EDS type VII B, and the activities of prolyl-4-hydroxylase and galactosylhydroxylysyl glucosyltransferase were slightly increased in these cell lines, reflecting increased biosynthesis of collagen. The synthesis of collagenous proteins was close to normal in EDS type VII A cells. The synthesis of type III procollagen per cell was increased, as also was the ratio of immunoreactive type III procollagen to total collagen production. The activity of type I procollagen amino-terminal proteinase was decreased in skin fibroblasts of type VII A and normal in those of type VII B relative to cell protein or DNA. Type III amino-terminal proteinase activity was of a level found in normal cells when expressed relative to the protein or DNA, and the release of type III amino-terminal propeptides was nevertheless not disturbed in these EDS type VII cell cultures. The results show that only the conversion of type I procollagen is defective in EDS type VII, and no general defect in procollagen processing can be found in EDS type VII as has been suggested in the case of dermatosparaxis, a connective tissue disorder in animals caused by disturbed procollagen conversion.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. R. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by fluorescent Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Timpl R., Fessler J. H. Assembly and processing of procollagen type III in chick embryo blood vessels. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2531–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjolstad M., Helle O. A hereditary dysplasia of collagen tissues in sheep. J Pathol. 1974 Mar;112(3):183–188. doi: 10.1002/path.1711120309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Olsen B. R., Timpl R., Perlish J. S., Lovelace O. Collagen fibril formation during embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3354–3358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Timpl R., Tuderman L., Raisher L., Wiestner M., Perlish J. S., Graves P. N. Ultrastructural identification of extension aminopropeptides of type I and III collagens in human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7360–7364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halila R. A sensitive and rapid method for assaying the activity of type III procollagen amino-terminal proteinase. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;145(1):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halila R., Peltonen L. Neutral protease cleaving the N-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen: partial purification and characterization of the enzyme from smooth muscle cells of bovine aorta. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1251–1256. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook K. A., Byers P. H., Counts D. F., Hegreberg G. A. Dermatosparaxis in a Himalayan cat: II. Ultrastructural studies of dermal collagen. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Feb;74(2):100–104. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12520000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., Kohn L. D., Byers P. H., McKusick V. A. Defect in conversion of procollagen to collagen in a form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):298–300. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara M., Hayashi K., Berger J., Tanzawa K., Njieha F. K., Trelstad R. L., Prockop D. J. Formation of collagen fibrils by enzymic cleavage of precursors of type I collagen in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9891–9898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I. Heritable diseases of collagen. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):376–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde H., Vargas L., Hahn E., Kalbfleisch H., Bruguera M., Timpl R. Radioimmunoassay for type III procollagen peptide and its application to human liver disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;9(6):451–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai H., Lapiere C. M. Characterization of oligosaccharide units of p-N-collagen type III from dermatosparactic bovine skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 5;758(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Tuderman L., Peltonen L., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A., Prockop D. J. Evidence for a structural mutation of procollagen type I in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8887–8893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuderman L., Kivirikko K. I., Prockop D. J. Partial purification and characterization of a neutral protease which cleaves the N-terminal propeptides from procollagen. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):2948–2954. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestner M., Krieg T., Hörlein D., Glanville R. W., Fietzek P., Müller P. K. Inhibiting effect of procollagen peptides on collagen biosynthesis in fibroblast cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7016–7023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestner M., Rohde H., Helle O., Krieg T., Timpl R., Müller P. K. Low rate of procollagen conversion in dermatosparactic sheep fibroblasts is paralleled by increased synthesis of type I and type III collagens. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):513–516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


