Abstract
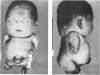
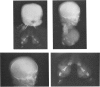
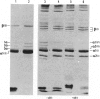
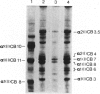
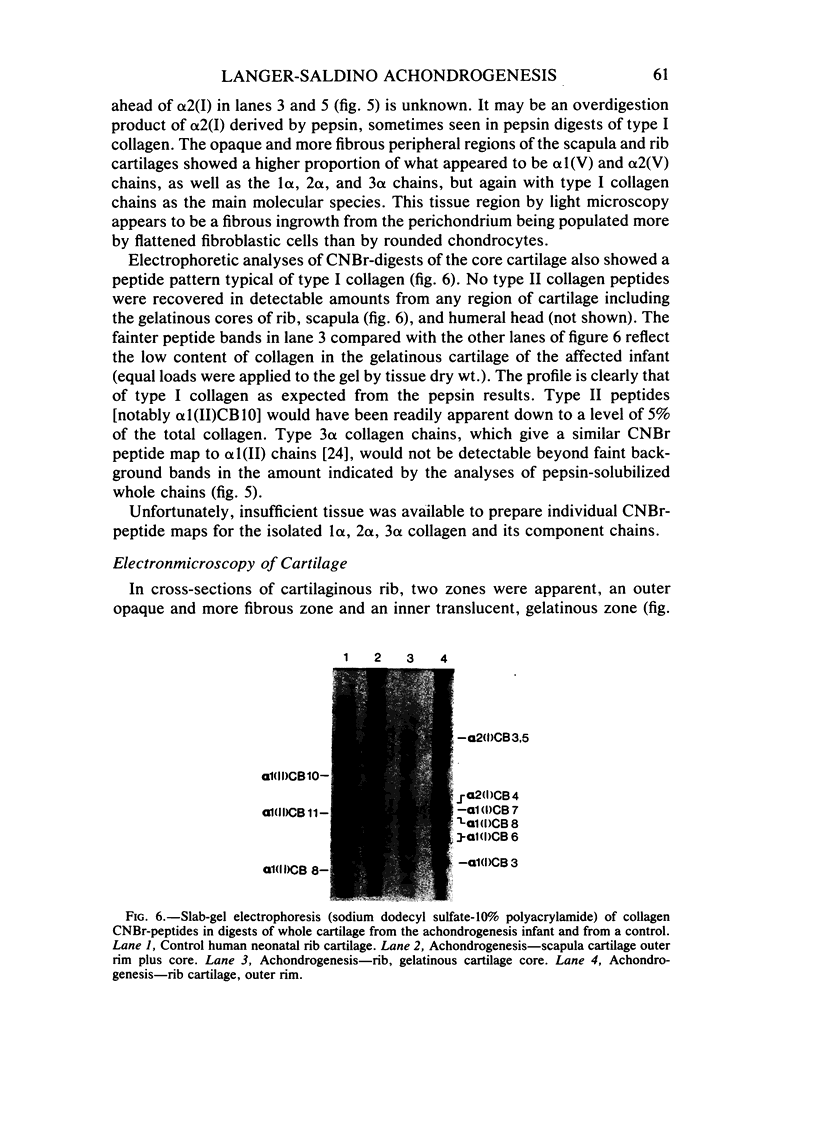
A lethal short-limbed dwarfism was diagnosed at autopsy as the Langer-Saldino variant of achondrogenesis by radiological, histological, and gross pathological criteria. Cartilage was obtained for biochemical and ultrastructural analyses from the ends of long bones, from ribs and from a scapula of the newborn infant. At all sites, it had an abnormal gelatinous texture and translucent appearance. Biochemical analyses of the cartilages to identify pepsin-solubilized collagen alpha-chains and collagen-specific CNBr-peptides failed to detect type II collagen at any site where it would normally be the main constituent. Instead, type I was the predominant collagen present. However, three cartilage-specific minor collagen chains identified as 1 alpha, 2 alpha, and 3 alpha chains by their electrophoretic mobility were present at about 10% of the total collagen. Cartilage-specific proteoglycans also appeared to be abundant in the tissue judging by its high hexosamine content and high ratio of galactosamine to glucosamine. The findings indicate that a chondrocyte phenotype had differentiated but without the expression of type II collagen. In addition to the skeletal abnormalities, the severe pulmonary hypoplasia was also felt to be directly related to the underlying pathology in collagen expression. The term chondrogenesis imperfecta rather than achondrogenesis should be considered a more accurate description of this and related conditions.
Full text
PDF


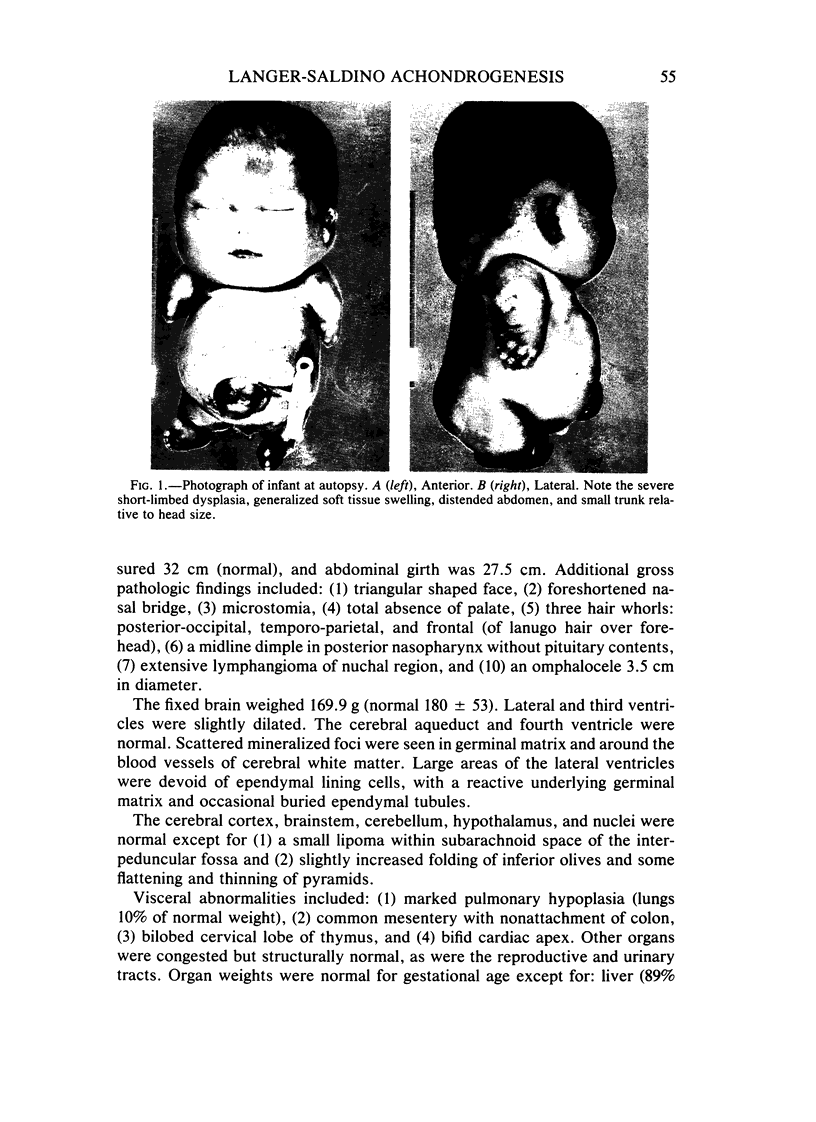
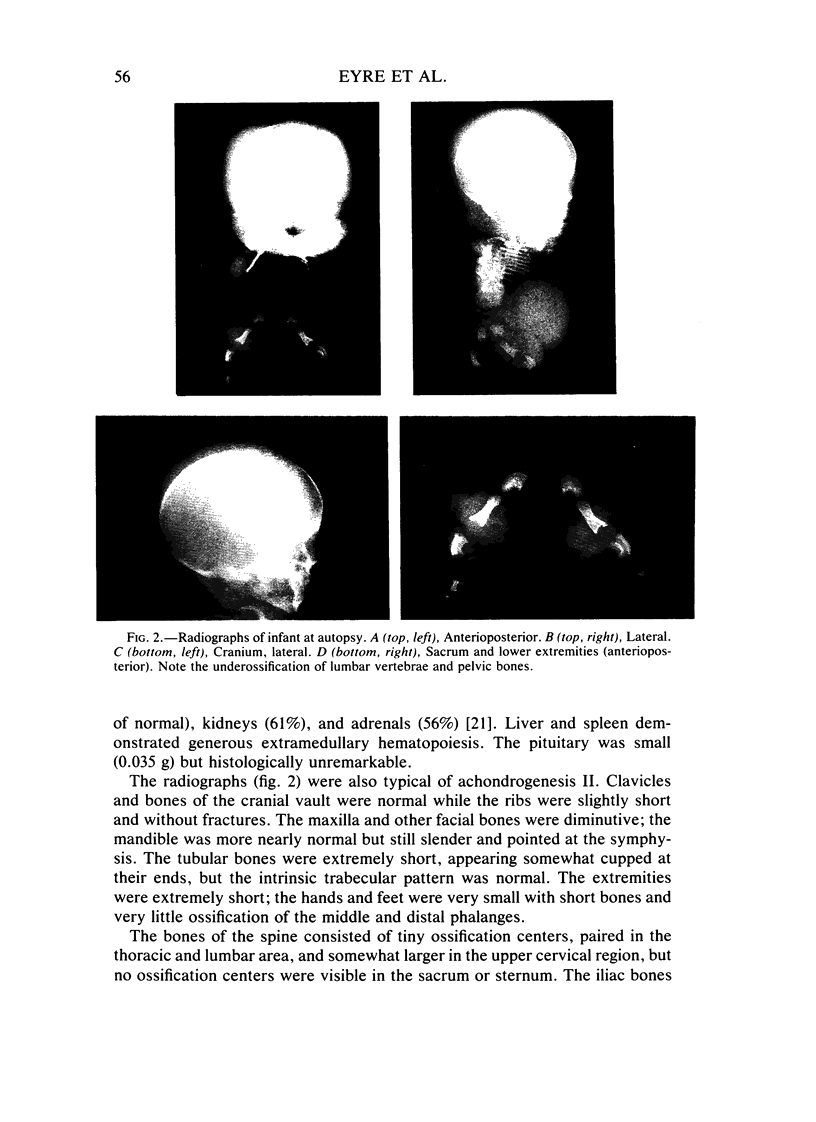


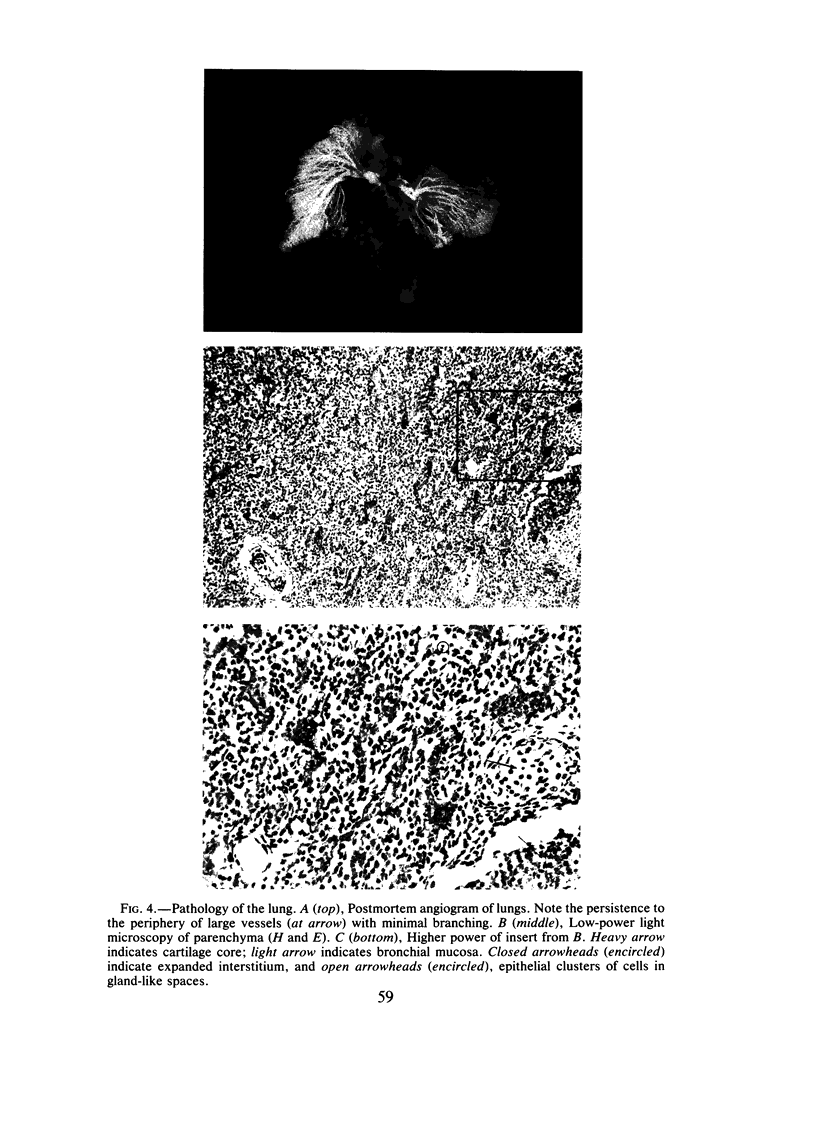
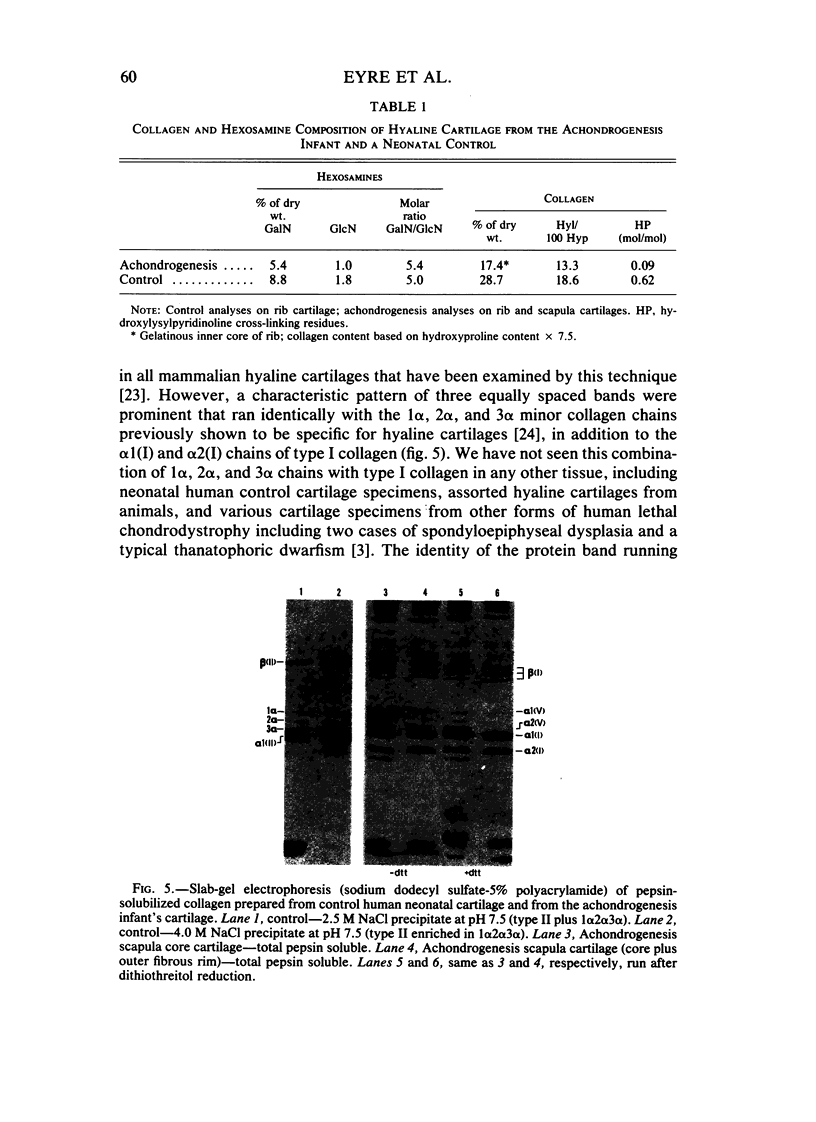






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgeson R. E., Hollister D. W. Collagen heterogeneity in human cartilage: identification of several new collagen chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):1124–1131. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Koob T. J., Van Ness K. P. Quantitation of hydroxypyridinium crosslinks in collagen by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Muir H. The distribution of different molecular species of collagen in fibrous, elastic and hyaline cartilages of the pig. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):595–602. doi: 10.1042/bj1510595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Wu J. J. Collagen of fibrocartilage: a distinctive molecular phenotype in bovine meniscus. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 25;158(2):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80592-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Wu J. J., Woolley D. E. All three chains of 1 alpha 2 alpha 3 alpha collagen from hyaline cartilage resist human collagenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):724–729. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91454-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton W. A. Histochemistry, a valuable tool in connective tissue research. Coll Relat Res. 1984 May;4(3):231–237. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata K., Barrach H. J., Brown K. S., Pennypacker J. P. Absence of proteoglycan core protein in cartilage from the cmd/cmd (cartilage matrix deficiency) mouse. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6961–6968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn K., von der Mark K. The influence of proteoglycans on the macromolecular structure of collagen. Suppl Thromb Haemost. 1978;63:123–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer L. O., Jr, Spranger J. W., Greinacher I., Herdman R. C. Thanatophoric dwarfism. A condition confused with achondroplasia in the neonate, with brief comments on achondrogenesis and homozygous achondroplasia. Radiology. 1969 Feb;92(2):285–passim. doi: 10.1148/92.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown P. J., Goetinck P. F. A comparison of the proteoglycans synthesized in Meckel's and sternal cartilage from normal and nanomelic chick embryos. Dev Biol. 1979 Aug;71(2):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. D., Rabinovitch M., Goldstein J. D., Reid L. M. The structural basis of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1981 Jun;98(6):962–967. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I. Heritable diseases of collagen. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):376–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUELCE-SALGADO A. A NEW TYPE OF DWARFISM WITH VARIOUS BONE APLASIAS AND HYPOPLASIAS OF THE EXTREMITIES. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1964;14:63–66. doi: 10.1159/000151832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoin D. L., Hollister D. W., Lachman R. S., Kaufman R. L., McAlister W. H., Rosenthal R. E., Hughes G. N. Histologic studies in the chondrodystrophies. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1974;10(12):274–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEGEMANN H. Mikrobestimmung von Hydroxyprolin mit Chloramin-T und p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyd. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1958;311(1-3):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldino R. M. Lethal short-limbed dwarfism: achondrogenesis and thanatophoric dwarfism. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1971 May;112(1):185–197. doi: 10.2214/ajr.112.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldino R. M. Radiographic diagnosis of neonatal short-limbed dwarfism. Med Radiogr Photogr. 1973;49(3):61–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangiorgi F. O., Benson-Chanda V., de Wet W. J., Sobel M. E., Ramirez F. Analysis of cDNA and genomic clones coding for the pro alpha 1 chain of calf type II collagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2815–2826. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangiorgi F. O., Benson-Chanda V., de Wet W. J., Sobel M. E., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F. Isolation and partial characterization of the entire human pro alpha 1(II) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2207–2225. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Linsenmayer T. F. Immunohistochemical localization of short chain cartilage collagen (type X) in avian tissues. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):598–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro F. Ultrastructural observations on osteosarcoma tissue: a study of 10 cases. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1983 Mar-Apr;4(2-3):151–161. doi: 10.3109/01913128309140786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Upholt W. B. Copy number of the chicken type II procollagen gene. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jan;5(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Hiorns L. R., Spurr N., Kurkinen M., Barlow D., Hogan B. L., Dalgleish R. Chromosomal assignments of the genes coding for human types II, III, and IV collagen: a dispersed gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3330–3334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart Houston C., Awen C. F., Kent H. P. Fatal neonatal dwarfism. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1972 Mar;23(1):45–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthakos U. F., Rejent M. M. Achondrogenesis: case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):658–663. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Brough A. J., Garewal G. S., Bernstein J. Two types of heritable lethal achondrogenesis. J Pediatr. 1974 Dec;85(6):796–801. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Mayne R., Ninomiya Y., Seidah N. G., Chretien M., Olsen B. R. The structure of type IX collagen. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]