Abstract
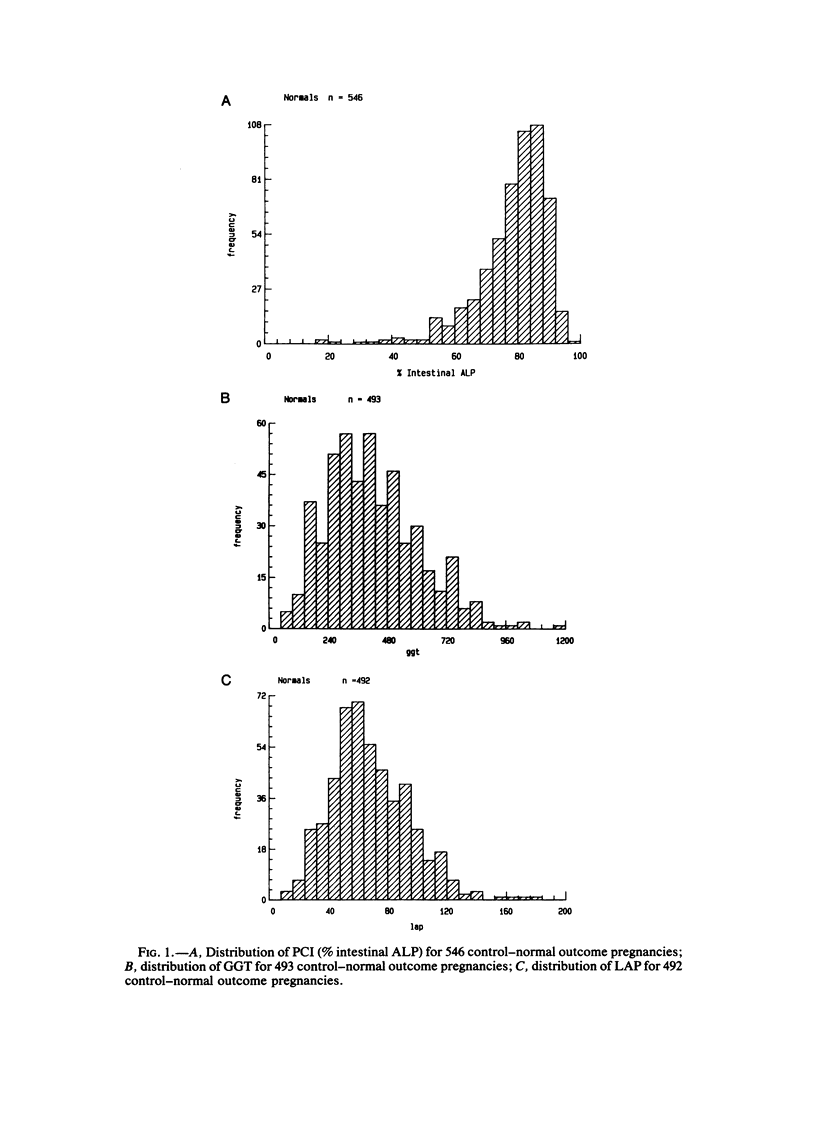
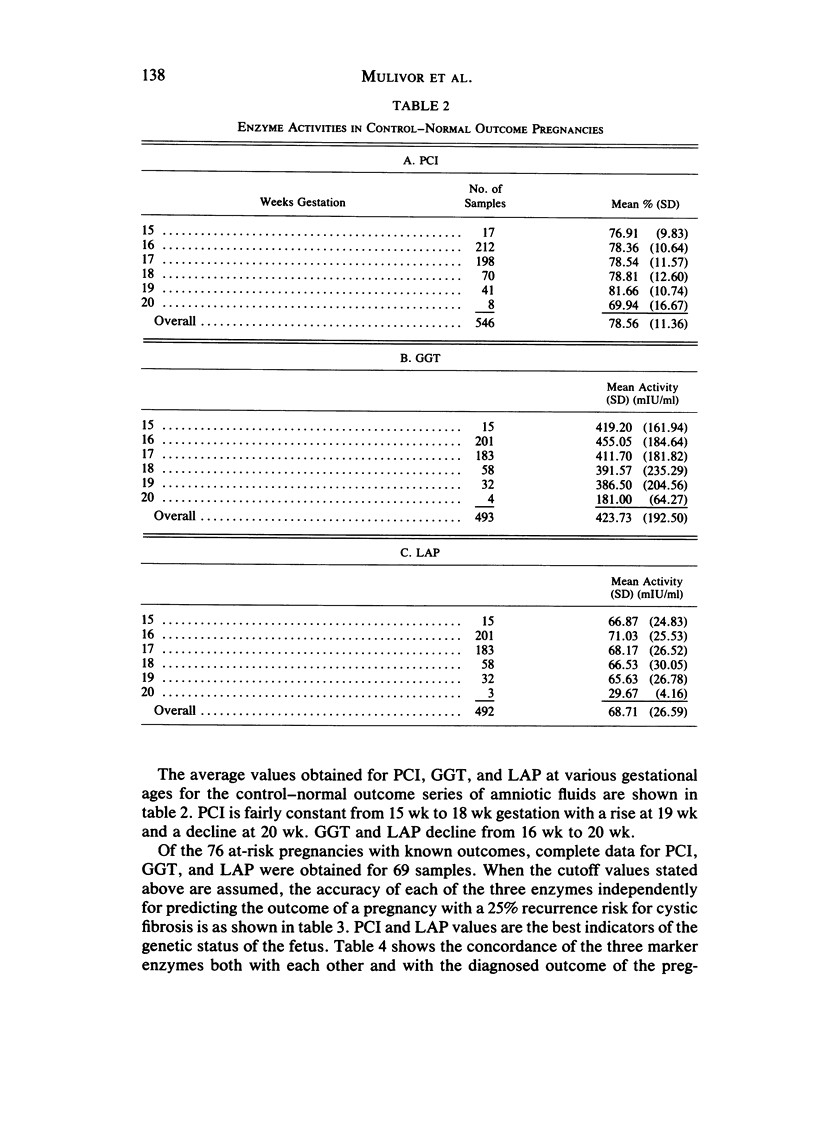
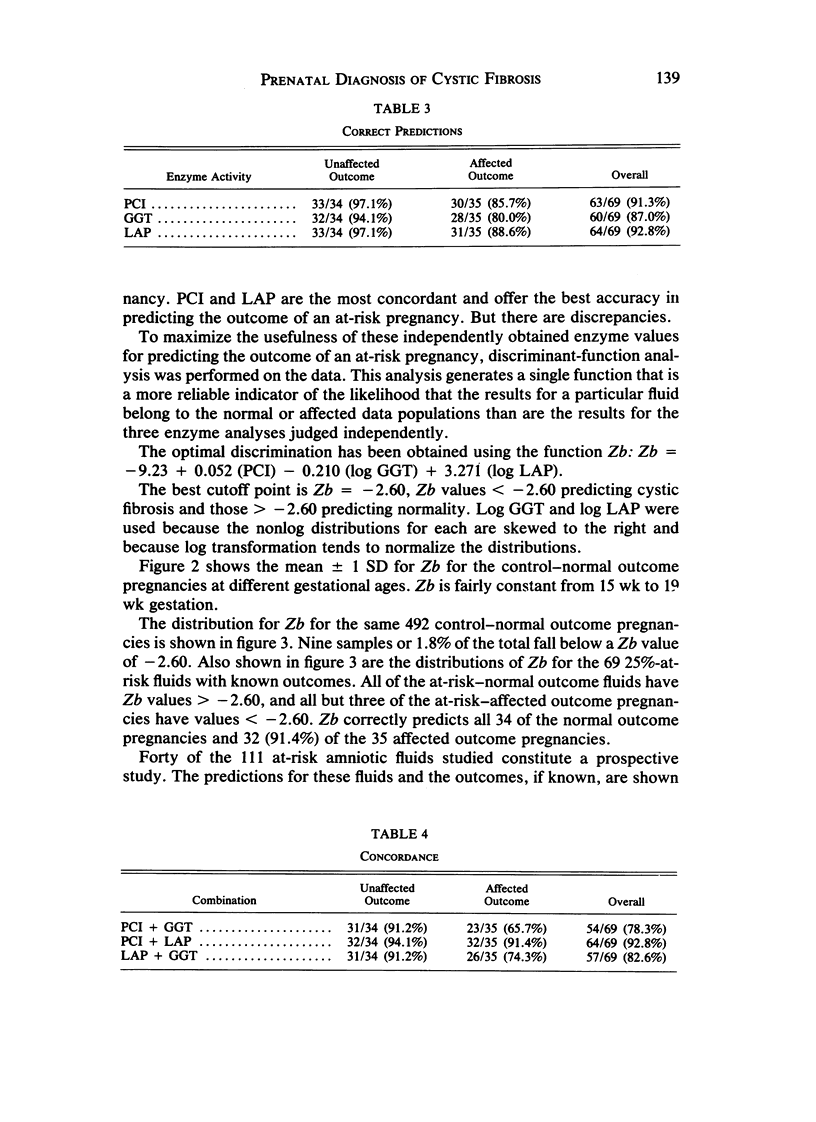
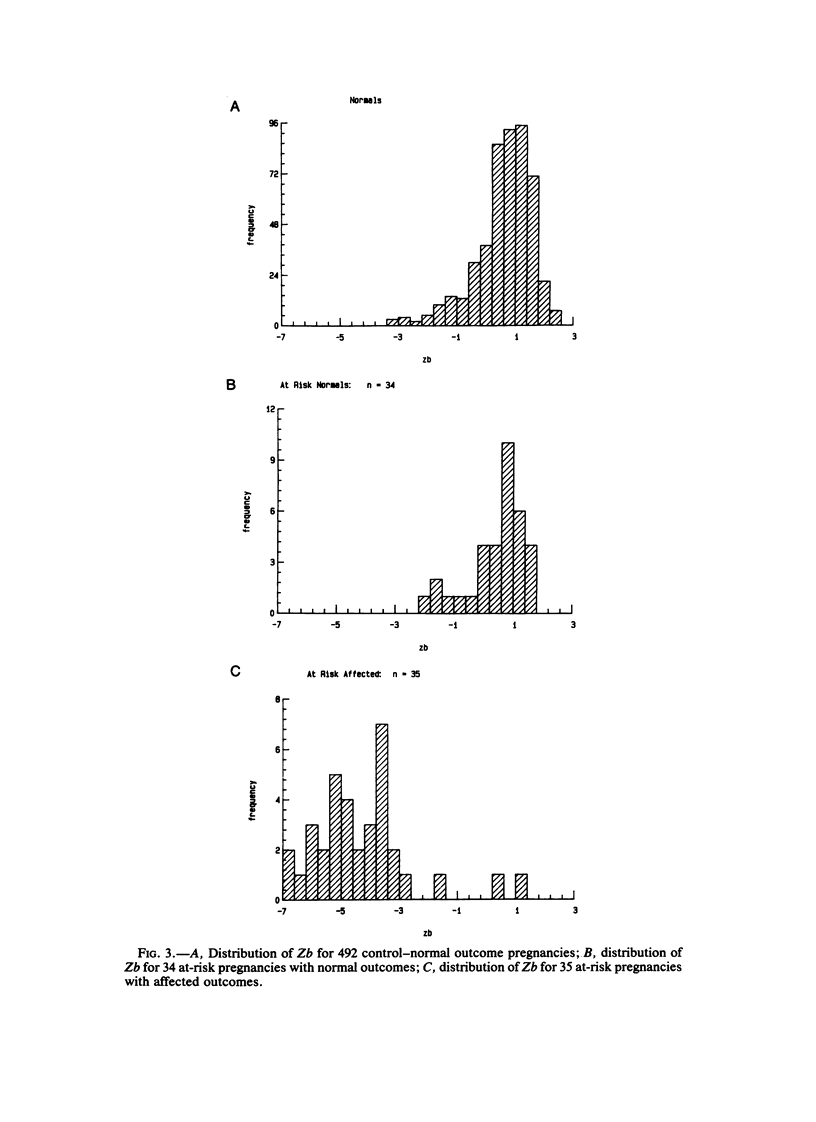
Amniotic-fluid intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity, gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase activity, and leucine-aminopeptidase activity were quantitated to assess their reliability for the prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. The results indicate that for each of these enzymes an arbitrary cutoff point could be chosen that would enable one to correctly predict the outcome for the majority of at-risk pregnancies. However, some false positives and false negatives occurred with each enzyme. To obtain optimal diagnostic discrimination, the three enzyme values obtained for each sample were combined into a single linear discriminant function that proved to be a more accurate indicator of the outcome of the pregnancy. This was especially important for those cases in which the predicted outcome as based on the individual enzyme results was in disagreement. From the cases studied here, it appears that this method can be expected to give a correct prediction in ∼96.5% of all 25%-at-risk pregnancies. False positives can be expected in ∼1.4% of the pregnancies and false negatives in ∼2.2%.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken D. A., Yaqoob M., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Microvillar enzyme analysis in amniotic fluid and the prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Prenat Diagn. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):119–127. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970050205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S., Dann L. G. Peptidases in amniotic fluid: low values in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Mar 26;1(8326 Pt 1):716–717. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Yoseph Y., Rembelski P., Nadler H. L. Correction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase deficiency in amniotic fluid of some cystic fibrosis fetuses by mixing with nondeficient fluids. Pediatr Res. 1984 Dec;18(12):1340–1343. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198412000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boué A., Brock D. J. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1985 Jul 6;2(8445):47–48. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J. Amniotic fluid alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes in early prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Oct 22;2(8356):941–943. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Barron L., Bedgood D., Van Heyningen V. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis using a monoclonal antibody specific for intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Prenat Diagn. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):421–426. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970040605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Bedgood D., Barron L., Hayward C. Prospective prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1985 May 25;1(8439):1175–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92860-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Bedgood D., Hayward C. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis by assay of amniotic fluid microvillar enzymes. Hum Genet. 1984;65(3):248–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00286511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Hayward C., Gosden C., Rodeck C. Immunoreactive trypsin and the prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1984 May;91(5):449–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1984.tb04782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Hayward C. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis by methylumbelliferylguanidinobenzoate protease titration in amniotic fluid. Prenat Diagn. 1983 Jan;3(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbarns N. J., Gosden C., Brock D. J. Microvillar peptidase activity in amniotic fluid: possible use in the prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):329–331. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleijer W. J., Janse H. C., van Diggelen O. P., Niermeijer M. F. Amniotic fluid disaccharidases in the prenatal detection of cystic fibrosis. Prenat Diagn. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):135–143. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970050207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Cohen-Haguenauer O., Van Cong N., Frézal J., Brown V. A., Barker D., Braman J. C., Schumm J. W., Tsui L. C., Buchwald M. A polymorphic DNA marker linked to cystic fibrosis is located on chromosome 7. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):380–382. doi: 10.1038/318380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin P. R., Potier M., LaSalle R., Melançon S. B., Dallaire L. Amniotic-fluid disaccharidases in the prenatal detection of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Sep 10;2(8350):621–622. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90701-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Boccelli D., Harris H. Quantitative analysis of alkaline phosphatases in serum and amniotic fluid: comparison of biochemical and immunologic assays. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Mar;105(3):342–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Hannig V. L., Harris H. Developmental change in human intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3909–3912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Mennuti M. T., Harris H. Origin of the alkaline phosphatases in amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Sep 1;135(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Mennuti M., Zackai E. H., Harris H. Prenatal diagnosis of hypophosphatasia; genetic, biochemical, and clinical studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1978 May;30(3):271–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller F., Aubry M. C., Gasser B., Duchatel F., Boué J., Boué A. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. II. Meconium ileus in affected fetuses. Prenat Diagn. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):109–117. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller F., Berg S., Frot J. F., Boué J., Boué A. Alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme assays for prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1984 Mar 10;1(8376):572–572. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90977-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller F., Frot J. C., Aubry M. C., Boue J., Boue A. Meconium ileus in cystic fibrosis fetuses. Lancet. 1984 Jul 28;2(8396):223–223. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90505-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L., Walsh M. M. Intrauterine detection of cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1980 Nov;66(5):690–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papp Z., Tóth Z., Szabó M., Szeifert G. T. Early prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis by ultrasound. Clin Genet. 1985 Oct;28(4):356–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park R. W., Grand R. J. Gastrointestinal manifestations of cystic fibrosis: a review. Gastroenterology. 1981 Dec;81(6):1143–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenaru L., Vinet M. C. Amniotic fluid protease activity and the prenatal detection of cystic fibrosis. Prenat Diagn. 1983 Apr-Jun;3(2):169–172. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970030218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambler P. J., Wainwright B. J., Watson E., Bates G., Bell G., Williamson R., Farrall M. Isolation of a further anonymous informative DNA sequence from chromosome seven closely linked to cystic fibrosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):1951–1956. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A serine protease activity of human serum albumin towards 4-methylumbelliferyl-guanidinobenzoate (MUGB) and diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DEP): implications for the use of MUGB reactivity in amniotic fluid in prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Sep 15;124(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90389-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Brandt N. J. Disaccharidase deficiency in amniotic fluid from cases of cystic fibrosis. Prenat Diagn. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):145–148. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalev J., Navon R., Urbach D., Mashiach S., Goldman B. Intestinal obstruction and cystic fibrosis: antenatal ultrasound appearance. J Med Genet. 1983 Jun;20(3):229–230. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.3.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó M., Teichmann F., Szeifert G. T., Tóth M., Tóth Z., Török O., Papp Z. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis by trehalase enzyme assay in amniotic fluid. Clin Genet. 1985 Jul;28(1):16–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb01211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Buchwald M., Barker D., Braman J. C., Knowlton R., Schumm J. W., Eiberg H., Mohr J., Kennedy D., Plavsic N. Cystic fibrosis locus defined by a genetically linked polymorphic DNA marker. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1054–1057. doi: 10.1126/science.2997931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright B. J., Scambler P. J., Schmidtke J., Watson E. A., Law H. Y., Farrall M., Cooke H. J., Eiberg H., Williamson R. Localization of cystic fibrosis locus to human chromosome 7cen-q22. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):384–385. doi: 10.1038/318384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Woodward S., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Hoff M., Herbst J., Lalouel J. M., Dean M., Vande Woude G. A closely linked genetic marker for cystic fibrosis. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):382–384. doi: 10.1038/318382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


