Abstract
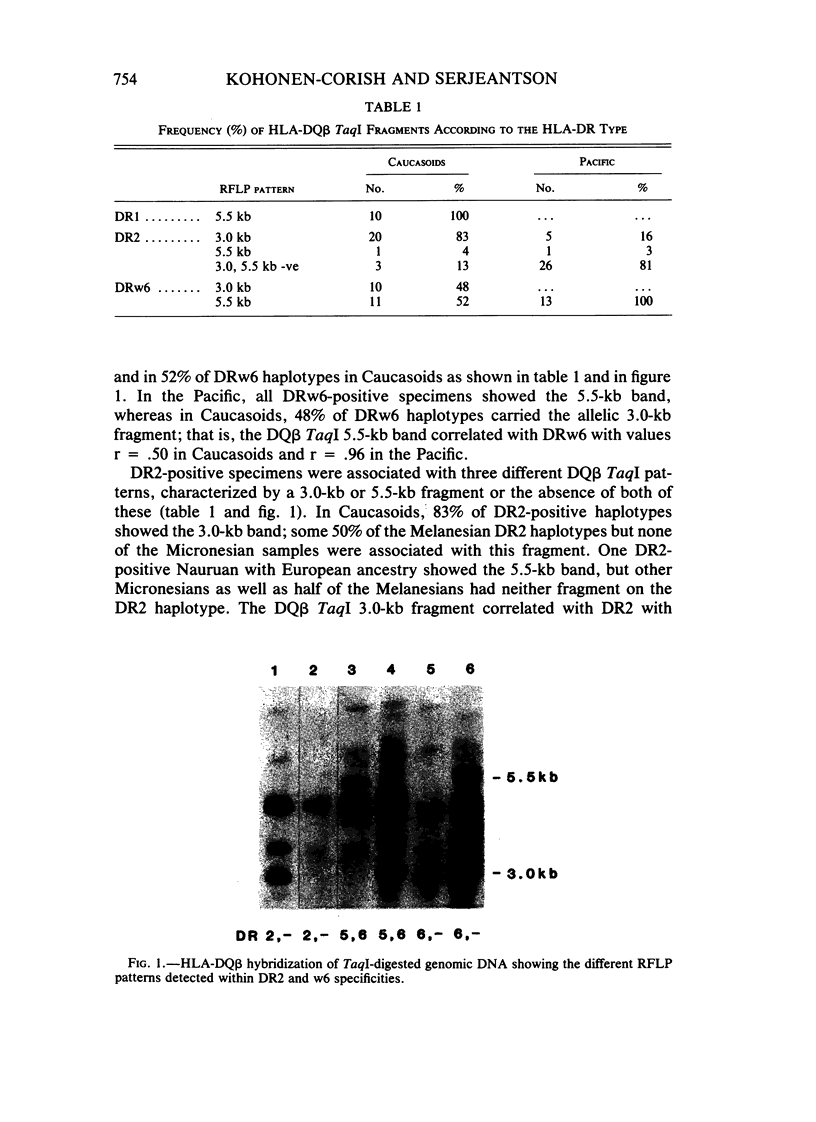
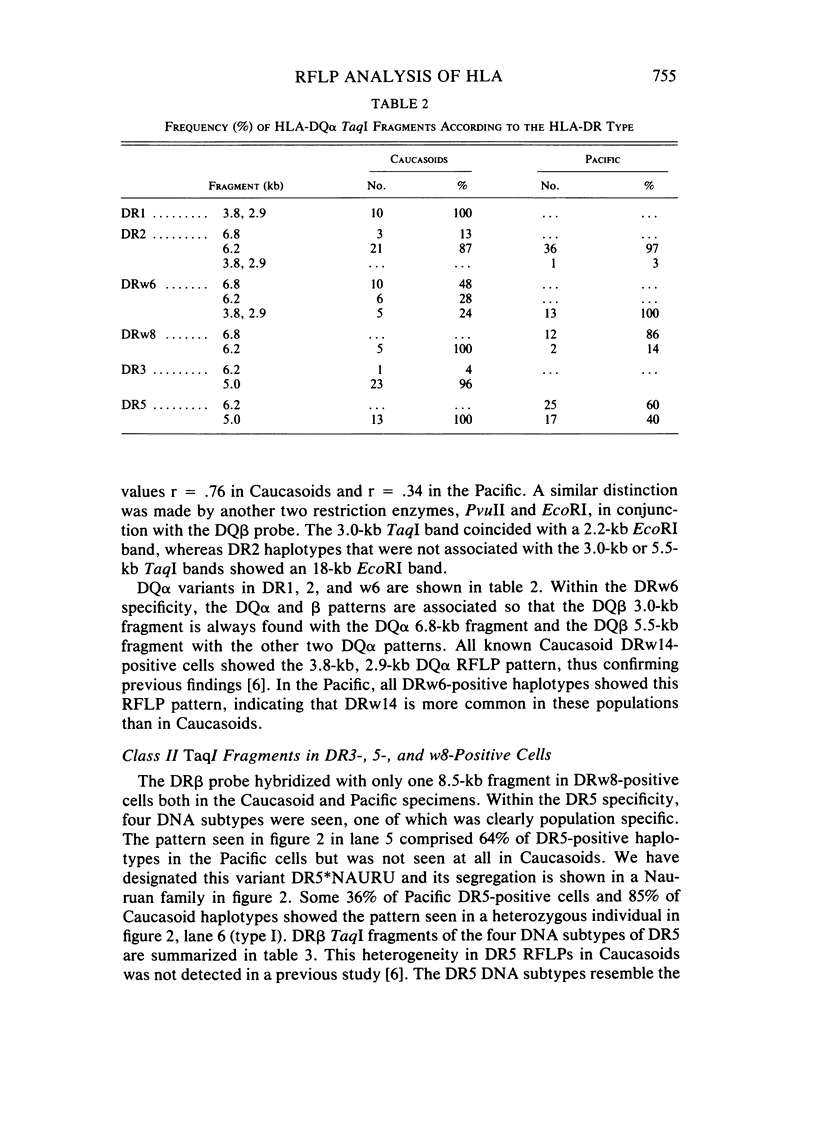
Human genomic DNA samples from Melanesians, Micronesians, and Caucasoids of known HLA-DR type were examined with cDNA probes for HLA-DR alpha, -DR beta, -DQ alpha, and -DQ beta chain genes. DR beta hybridizations with TaqI-digested DNA did not detect any new DR specificities in the Pacific. However, within the DR5 specificity a common DNA subtype was found in Pacific Islanders that was not seen in Caucasoids. Altogether, four DNA subtypes of DR5 are described. With the DQ alpha and DQ beta probes, significantly more variation could be demonstrated between populations. For example, DR2 was associated with a DQ beta TaqI pattern in the Pacific that was very rare in Caucasoids and additional RFLP analysis with other enzymes showed that this pattern is probably associated with the Dw12 subtype of DR2. DRw8-positive samples showed two different DQ alpha TaqI patterns, and these correlated with DQw1 and DQw3 specificities. DR alpha hybridizations with BglII-digested DNA also revealed different linkage relationships of the HLA-class II region genes between Pacific and Caucasoid specimens. The different population linkage disequilibrium relationships have permitted tentative assignment of TaqI fragments to either the DR beta 1 or DR beta 2 genes and are highly suggestive that the DQw1 specificity is encoded by the DQ alpha chain gene. This study shows the value of population comparisons in contributing to knowledge of the genetic organization of the genome.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Lillie J. W., Arnot D., Grossberger D., Kappes D., Strominger J. L. Isotypic and allotypic variation of human class II histocompatibility antigen alpha-chain genes. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):327–333. doi: 10.1038/308327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme J., Andersson M., Andersson G., Möller E., Peterson P. A., Rask L. HLA-DR beta genes vary in number between different DR specificities, whereas the number of DQ beta genes is constant. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2149–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Moriuchi T., Silver J. The heavy chain of human B-cell alloantigen HLA-DS has a variable N-terminal region and a constant immunoglobulin-like region. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):813–815. doi: 10.1038/305813a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Paul P., Le Gall I., Marcadet A., Font M. P., Cohen-Haguenauer O., Sayagh B., Cann H., Lalouel J. M., Dausset J. DNA polymorphism of HLA class I and class II regions. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:87–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane G., Bhatia K., Honeyman M., Doran T., Messel N., Hakos G., Tarlinton D., Amos D. B., Bashir H. HLA studies of Highland and Coastal New Guineans. Hum Immunol. 1985 Apr;12(4):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(85)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feder J., Yen L., Wijsman E., Wang L., Wilkins L., Schroder J., Spurr N., Cann H., Blumenberg M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. A systematic approach for detecting high-frequency restriction fragment length polymorphisms using large genomic probes. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):635–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui K., Festenstein H., de Klein A., Grosveld G., Grosveld F. HLA-DR genotyping by restriction fragment length polymorphism analyses. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(3):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00404482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohonen-Corish M. R., Serjeantson S. W. HLA-DR beta gene DNA polymorphisms revealed by Taq I correlate with HLA-DR specificities. Hum Immunol. 1986 Mar;15(3):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Wake C. T., Strubin M., Gross N., Accolla R. S., Carrel S., Mach B. Isolation of distinct cDNA clones encoding HLA-DR beta chains by use of an expression assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7465–7469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. The regulation of yeast mating-type chromatin structure by SIR: an action at a distance affecting both transcription and transposition. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Lernmark A., Rask L., Peterson P. A., Platz P., Svejgaard A. Detection of HLA-D/DR-related DNA polymorphism in HLA-D homozygous typing cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3758–3761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenning L., Larhammar D., Bill P., Wiman K., Jonsson A. K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Both alpha and beta chains of HLA-DC class II histocompatibility antigens display extensive polymorphism in their amino-terminal domains. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):447–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S. W., Kirk R. L., Ranford P., Beauchamp M. HLA antigens and non-HLA chromosome 6 markers in Micronesians from Nauru. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Jul;22(1):49–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb01165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S. W., Owerbach D., Zimmet P., Nerup J., Thoma K. Genetics of diabetes in Nauru: effects of foreign admixture, HLA antigens and the insulin-gene-linked polymorphism. Diabetologia. 1983 Jul;25(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00251889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S. W., Ryan D. P., Zimmet P., Taylor R., Cross R., Charpin M., Le Gonidec G. HLA antigens in four Pacific populations with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Hum Biol. 1982 Jan-Feb;9(1):69–84. doi: 10.1080/03014468200005501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servenius B., Gustafsson K., Widmark E., Emmoth E., Andersson G., Larhammar D., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Molecular map of the human HLA-SB (HLA-DP) region and sequence of an SB alpha (DP alpha) pseudogene. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3209–3214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Kavathas P., Pollack M. S., Charmot D., Mawas C. Family studies define a new histocompatibility locus, SB, between HLA-DR and GLO. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):745–747. doi: 10.1038/293745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone T., Tsukamoto K., Hirayama K., Nishimura Y., Takenouchi T., Aizawa M., Sasazuki T. Two distinct class II molecules encoded by the genes within HLA-DR subregion of HLA-Dw2 and Dw12 can act as stimulating and restriction molecules. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1288–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman R. S., Lee J., Bodmer W. F., Bodmer J. G., Trowsdale J. Six HLA-D region alpha-chain genes on human chromosome 6: polymorphisms and associations of DC alpha-related sequences with DR types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3461–3465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Hood L. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex in mouse and man. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):727–733. doi: 10.1126/science.6356354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Malissen M., Hood L., Orn A., Maki R. A., Dastoornikoo G. R., Stephan D., Gibb E., Romaniuk R. Tracts of high or low sequence divergence in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2995–3003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D., Das H., Nunberg J. H., Saiki R., Sheng-Dong R., Mullis K. B., Weissman S. M., Erlich H. A. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the human HLA-DR antigen alpha chain by using a synthetic oligonucleotide as a hybridization probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5966–5970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termijtelen A., Boettcher B., Bradley B. A., D'Amaro J., van Leeuwen A., van Rood J. J. DR typing in Australian Aborigines. An indication for a second locus in the HLA--D region defined by serology. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Aug;16(2):140–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi R., Tanigaki N., Centis D., Ferrara G. B., Pressman D. Immunological dissection of human Ia molecules. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1592–1611. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Young J. A., Kelly A. P., Austin P. J., Carson S., Meunier H., So A., Erlich H. A., Spielman R. S., Bodmer J. Structure, sequence and polymorphism in the HLA-D region. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:5–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]