Abstract
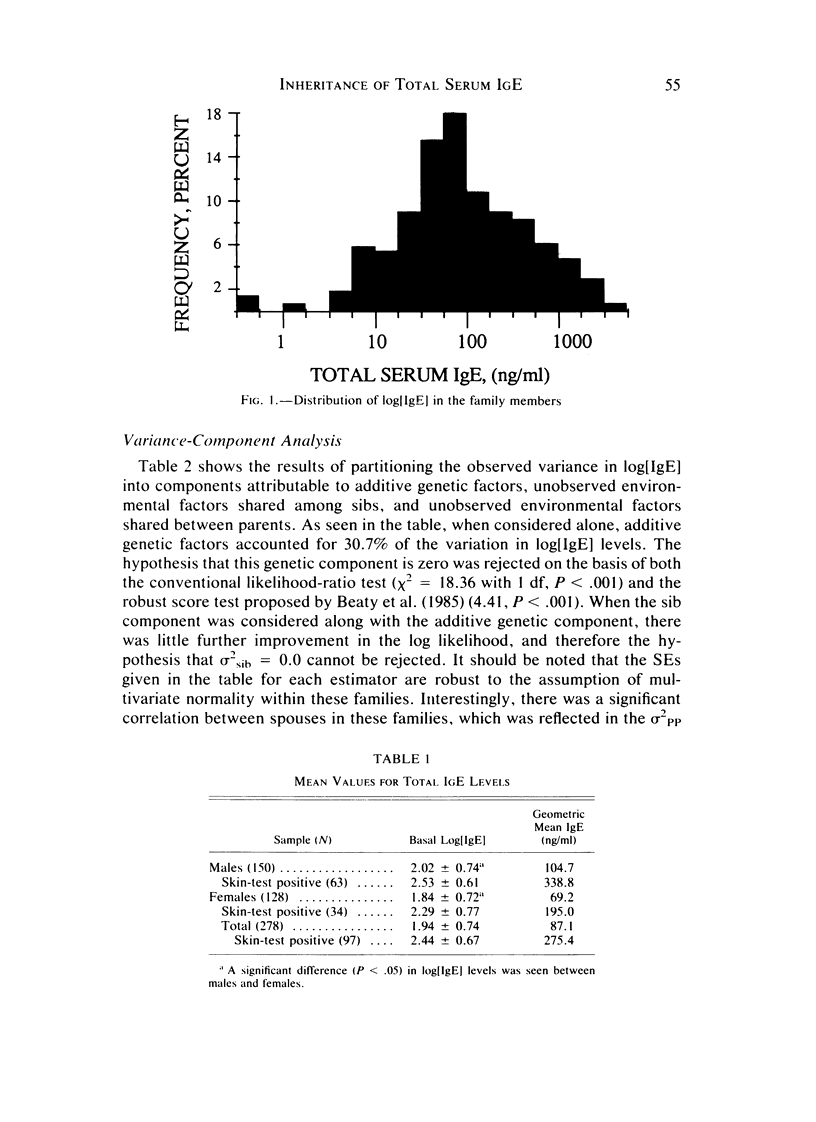
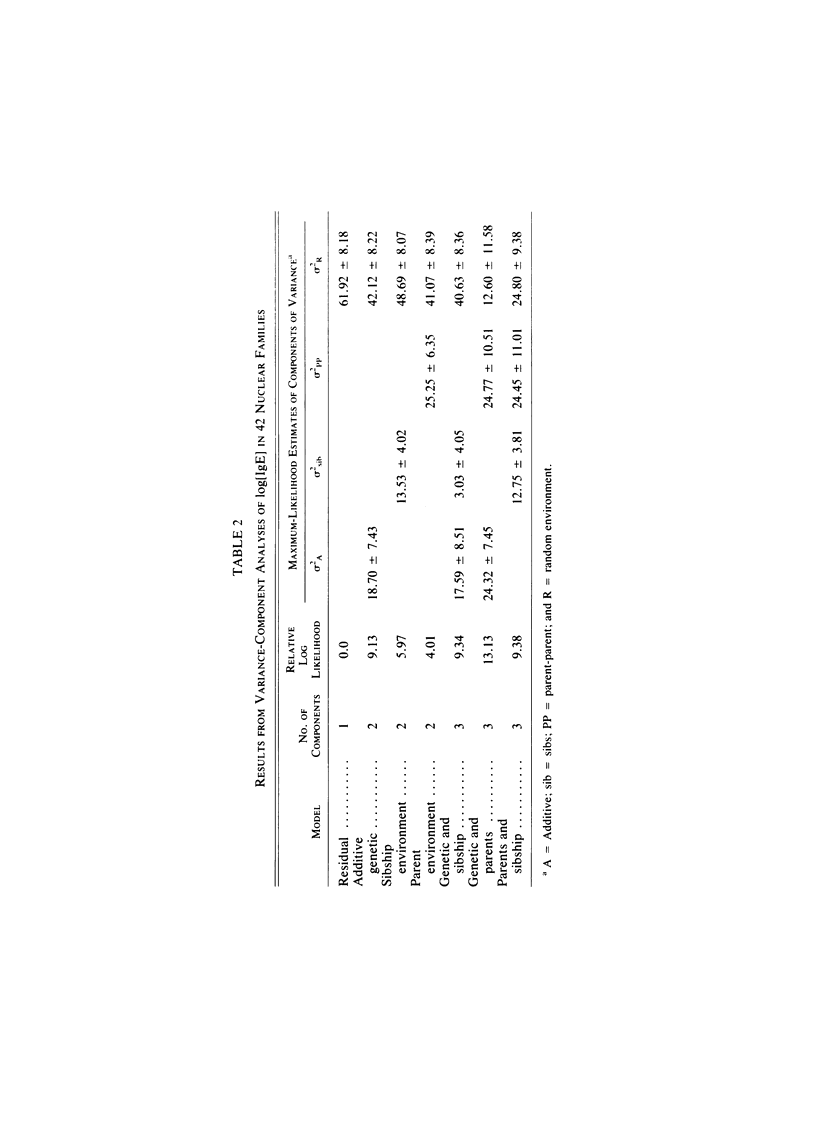
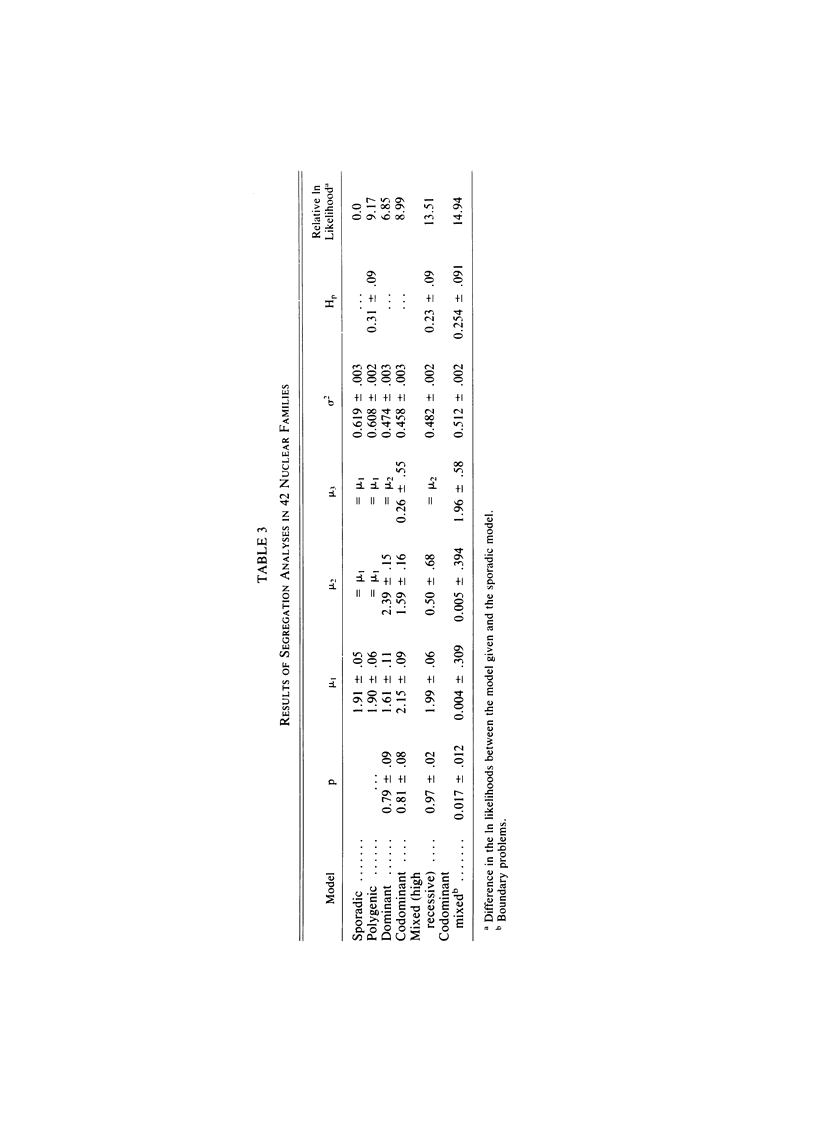
Since allergic individuals with atopic allergy tend to have higher total serum IgE levels than do nonallergic subjects, family studies of total serum IgE levels are necessary in delineating the genetic and environmental factors involved in the expression of allergic disease. However, previous studies do not agree as to the genetic basis of total IgE production. To try to resolve this conflict, a total of 278 individuals from 42 nuclear families ascertained for large family size (at least four children) were studied. The families were not selected for the presence of allergic disease. Segregation analysis showed that the mixed model of recessive inheritance of high levels was most appropriate for these data--with approximately 36% of the total phenotypic variation in log[IgE] attributable to genetic factors, equally divided between a Mendelian component and a more general polygenic component. Thus, these data suggest some role for Mendelian control of basal IgE levels, but there is significant familial aggregation in IgE levels over and above that due to a Mendelian factor.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbee R. A., Halonen M., Lebowitz M., Burrows B. Distribution of IgE in a community population sample: correlations with age, sex, and allergen skin test reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Aug;68(2):106–111. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty T. H., Self S. G., Liang K. Y., Connolly M. A., Chase G. A., Kwiterovich P. O. Use of robust variance components models to analyse triglyceride data in families. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Oct;49(Pt 4):315–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal M. N., Amos D. B., Noreen H. Genetic mapping of Ir locus in man: linkage to second locus of HL-A. Science. 1974 Jun 21;184(4143):1301–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4143.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal M. N., Namboodiri K., Mendell N., Gleich G., Elston R. C., Yunis E. Genetic transmission of serum IgE Levels. Am J Med Genet. 1981;10(3):219–228. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borecki I. B., Rao D. C., Lalouel J. M., McGue M., Gerrard J. W. Demonstration of a common major gene with pleiotropic effects on immunoglobulin E levels and allergy. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(4):327–338. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidhoff L. R., Marsh D. G., Meyers D. A., Hussain R. The structuring of an allergy index based on IgE-mediated skin sensitivity to common environmental allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Sep;72(3):274–287. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidhoff L. R., Meyers D. A., Bias W. B., Chase G. A., Hussain R., Marsh D. G. A genetic-epidemiologic study of human immune responsiveness to allergens in an industrial population: I. Epidemiology of reported allergy and skin-test positivity. Am J Med Genet. 1981;9(4):323–340. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320090409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidhoff L. R., Meyers D. A., Marsh D. G. A genetic-epidemiologic study of human immune responsiveness to allergens in an industrial population. III. Environmental influences on skin sensitivity and total serum IgE in a stratified random sample. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;79(2):188–195. doi: 10.1159/000233969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. W., Horne S., Vickers P., MacKenzie J. W., Goluboff N., Garson J. Z., Maningas C. S. Serum IgE levels in parents and children. J Pediatr. 1974 Nov;85(5):660–663. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. W., Rao D. C., Morton N. E. A genetic study of immunoglobulin E. Am J Hum Genet. 1978 Jan;30(1):46–58. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J. A mixed-model likelihood approximation on large pedigrees. Comput Biomed Res. 1982 Jun;15(3):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(82)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Meyers D. A., Marsh D. G. Inheritance of immunoglobulin E: genetic model fitting. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Jan;14(1):61–66. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Westlake J., Spence M. A. Extensions to pedigree analysis. III. Variance components by the scoring method. Ann Hum Genet. 1976 May;39(4):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1976.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Bias W. B., Ishizaka K. Genetic control of basal serum immunoglobulin E level and its effect on specific reaginic sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3588–3592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Meyers D. A., Bias W. B. The epidemiology and genetics of atopic allergy. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 24;305(26):1551–1559. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112243052603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. A., Bias W. B., Marsh D. G. A genetic study of total IgE levels in the Amish. Hum Hered. 1982;32(1):15–23. doi: 10.1159/000153262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. A., Freidhoff L. R., Marsh D. G. Predicting skin test sensitivity and total serum IgE levels in family members. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Apr;77(4):608–615. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. A., Hasstedt S. J., Marsh D. G., Skolnick M., King M. C., Bias W. B., Amos D. B. The inheritance of immunoglobulin E: genetic linkage analysis. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Dec;16(4):575–581. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. A., Marsh D. G. Report on a National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases-sponsored workshop on the genetics of total immunoglobulin E levels in humans. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Mar;67(3):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg R. R., Adkinson N. F., Jr Measurement of absolute amounts of antigen-specific human IgE by a radioallergosorbent test (RAST) elution technique. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1577–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren C. P., Holford-Strevens V., Wong C., Manfreda J. The relationship between smoking and total immunoglobulin E levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Apr;69(4):370–375. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Kojima S., Ovary Z. Suppression of IgE antibody production in SJL mice. I. Nonspecific suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):833–845. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


