Abstract
Seriation methods provide an accurate and efficient means of constructing preliminary multilocus genetic maps. By using both simulated and previously published empirical data, multipoint mapping by seriation was critically evaluated. Analysis of the simulated data sets showed that the seriation methodology could accurately estimate order and interlocus distances. Application to the empirical data demonstrated that seriation could obtain results directly comparable with those of other multipoint mapping methods. Techniques such as seriation can produce preliminary genetic maps that may be used as starting points for more computer-intensive maximum-likelihood multipoint techniques.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buetow K. H., Chakravarti A. Multipoint gene mapping using seriation. I. General methods. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;41(2):180–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. The analysis of X-linkage. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Feb;34(3):229–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1971.tb00237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Antonarakis S. E., Meyers D. A., Levine M. A. c-Ha-ras-1 oncogene lies between beta-globin and insulin loci on human chromosome 11p. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):329–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
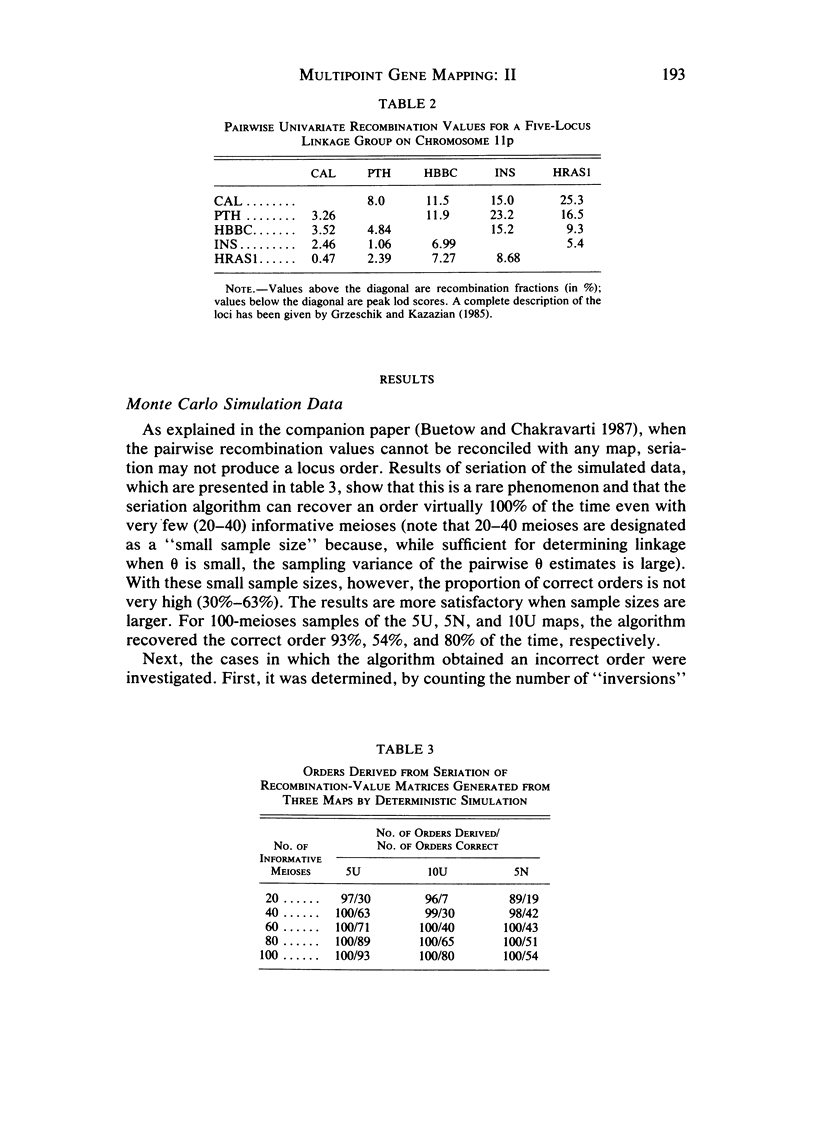
- Grzeschik K. H., Kazazian H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 10, 11, and 12. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):179–205. doi: 10.1159/000132174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Anderson C. E., Neiswanger K., Sparkes R. S., Rimoin D. L. The search for heterogeneity in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM): linkage studies, two-locus models, and genetic heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Nov;35(6):1139–1155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povey S., Morton N. E., Sherman S. L. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 1 and 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):67–106. doi: 10.1159/000132170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Lindsten J., Hultén M., Yee S. A mapping function for man. Hum Hered. 1977;27(2):99–104. doi: 10.1159/000152856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson E. B., King J. Family data on sixteen chromosome 1 loci. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Oct;48(Pt 4):347–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., King J., Robson E. B., Yee S. A revised map of chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;48(Pt 3):243–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedd N. A computer program for constructing a maximum-likelihood map from linkage data and its application to human chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Oct;48(Pt 4):333–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


