Abstract
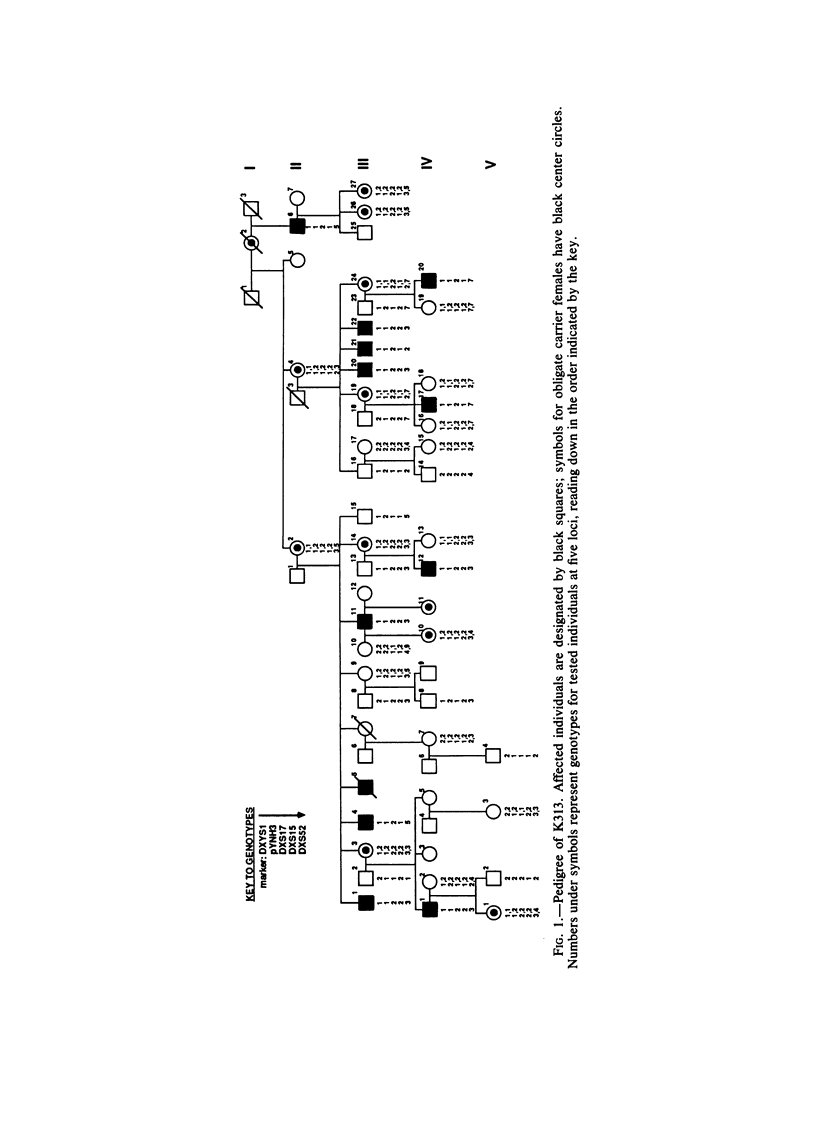
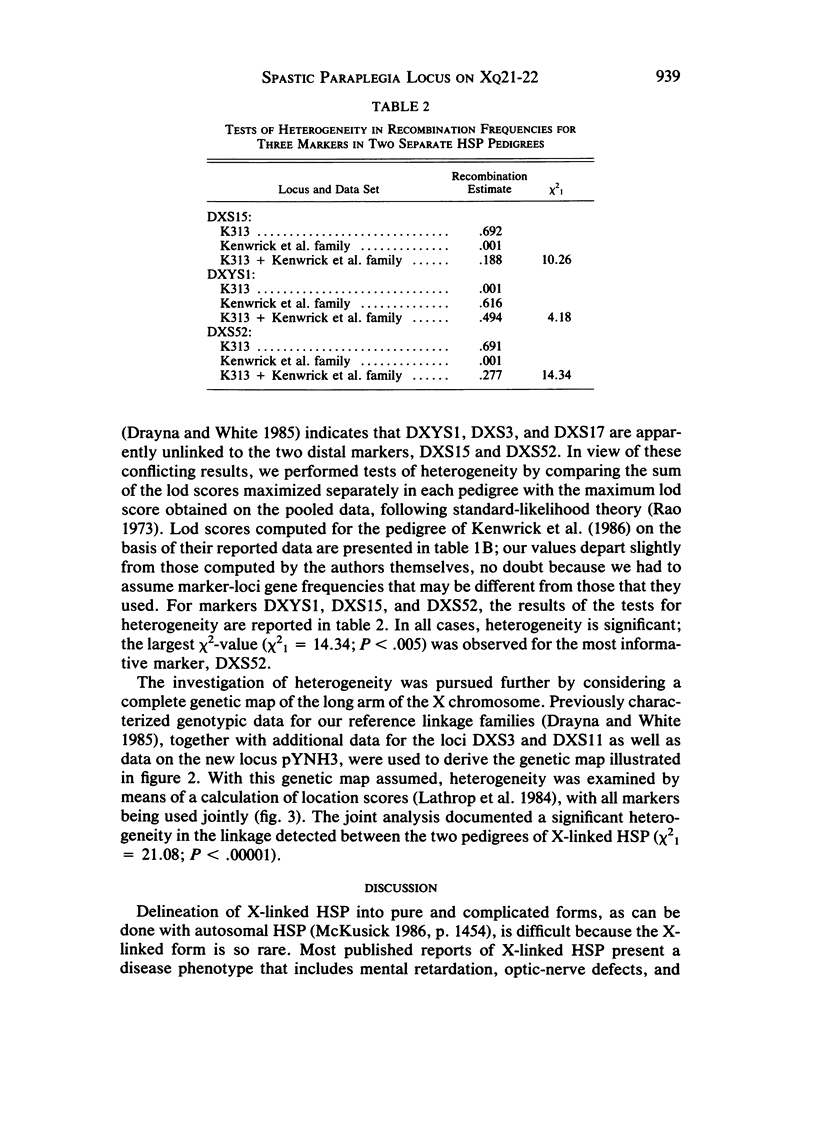
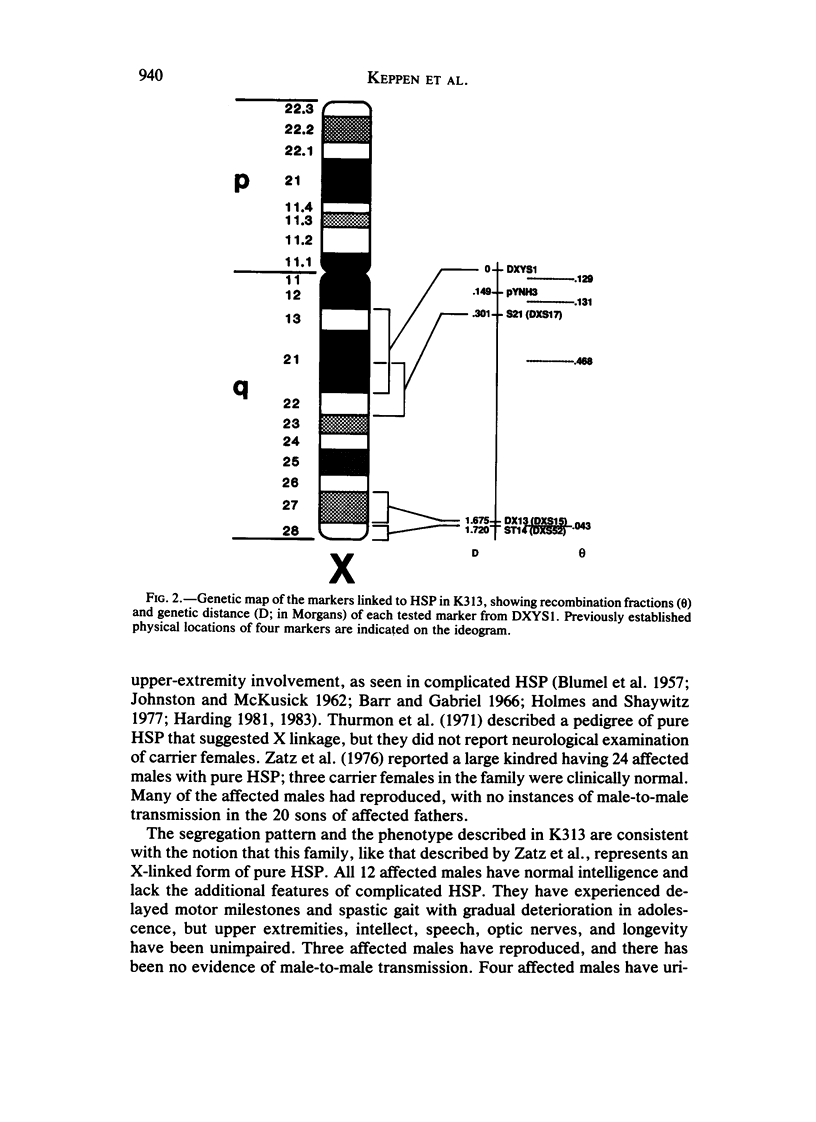
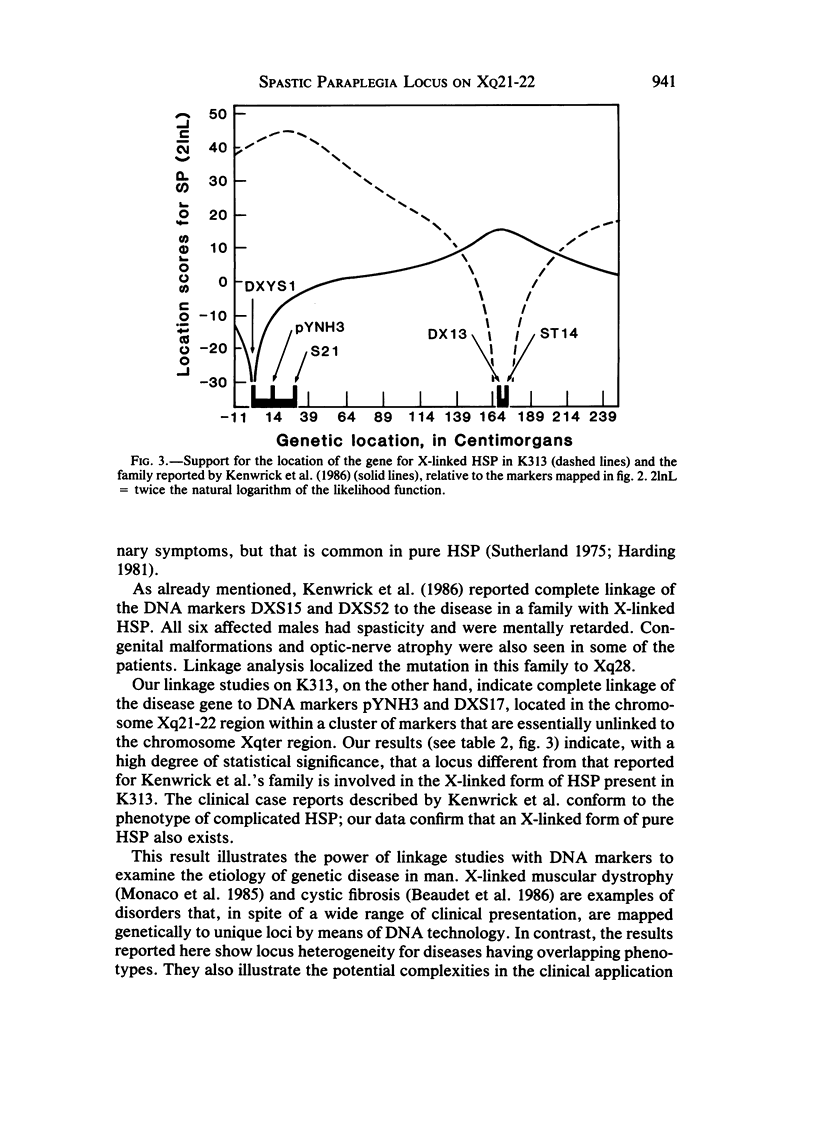
We describe a large family (K313) having 12 males affected with X chromosome-linked recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP). The disease phenotype in K313 is characterized by hyperreflexia and a spastic gait, but intelligence is normal. Carrier females have normal gait and unremarkable neurologic profiles. Eight widely spaced X-linked DNA markers were used to genotype 43 family members. In contrast to a published study of another family, in whom complete linkage of X-linked recessive HSP to distal chromosome Xq markers DXS15 and DXS52 was reported, we observed complete linkage with two DNA markers, pYNH3 and DXS17, located on the middle of the long arm of the X chromosome. These data have been combined with linkage data from a large reference panel of normal families to localize the new X-chromosome marker, pYNH3, and to provide evidence of significant locus heterogeneity between phenotypically distinct forms of X-linked recessive HSP.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUMEL J., EVANS E. B., EGGERS G. W. Hereditary cerebral palsy; a preliminary report. J Pediatr. 1957 Apr;50(4):454–458. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baar H. S., Gabriel A. M. Sex-linked spastic paraplegia. Am J Ment Defic. 1966 Jul;71(1):13–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudet A., Bowcock A., Buchwald M., Cavalli-Sforza L., Farrall M., King M. C., Klinger K., Lalouel J. M., Lathrop G., Naylor S. Linkage of cystic fibrosis to two tightly linked DNA markers: joint report from a collaborative study. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Dec;39(6):681–693. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W., Leach R., Mohandas T., Pearson P., White R. Isolation and regional localization of DNA segments revealing polymorphic loci from human chromosome 13. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):10–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E. Hereditary "pure" spastic paraplegia: a clinical and genetic study of 22 families. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Oct;44(10):871–883. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.10.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. L., Shaywitz B. A. Strumpell's pure familial spastic paraplegia: case study and review of the literature. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Oct;40(10):1003–1008. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.10.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON A. W., McKUSICK V. A. A sex-linked recessive form of spastic paraplegia. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Mar;14:83–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu G., Searby C., King A., Dubowitz M., Davies K. E. Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00401241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Aldridge J., Fischbeck K. H., Bartlett R., Pericak-Vance M. A., Roses A. D., Kunkel L. M. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):842–845. doi: 10.1038/316842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmon T. F., Walker B. A., Scott C. I., Abbott M. H. Two kindreds with a sex-linked recessive form of spastic paraplegia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Feb;7(1):219–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Penha-Serrano C., Otto P. A. X-linked recessive type of pure spastic paraplegia in a large pedigree: absence of detectable linkage with Xg. J Med Genet. 1976 Jun;13(3):217–222. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.3.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


