Abstract
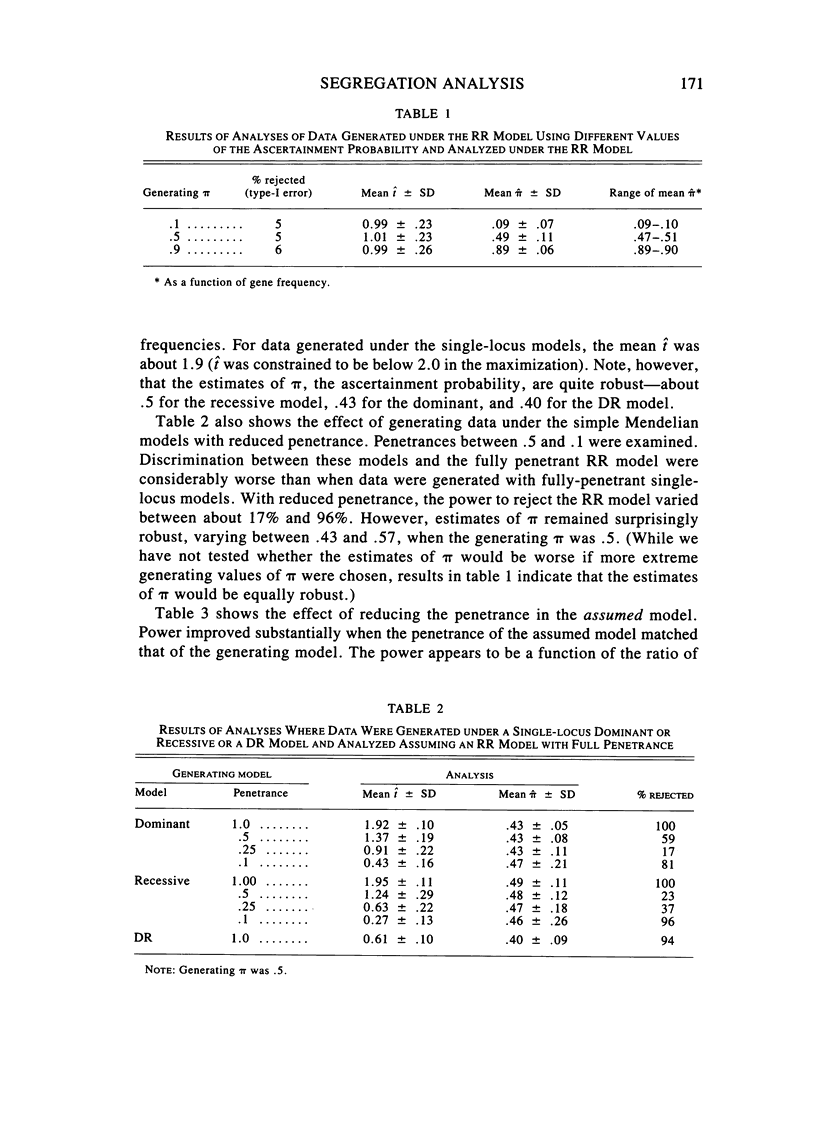
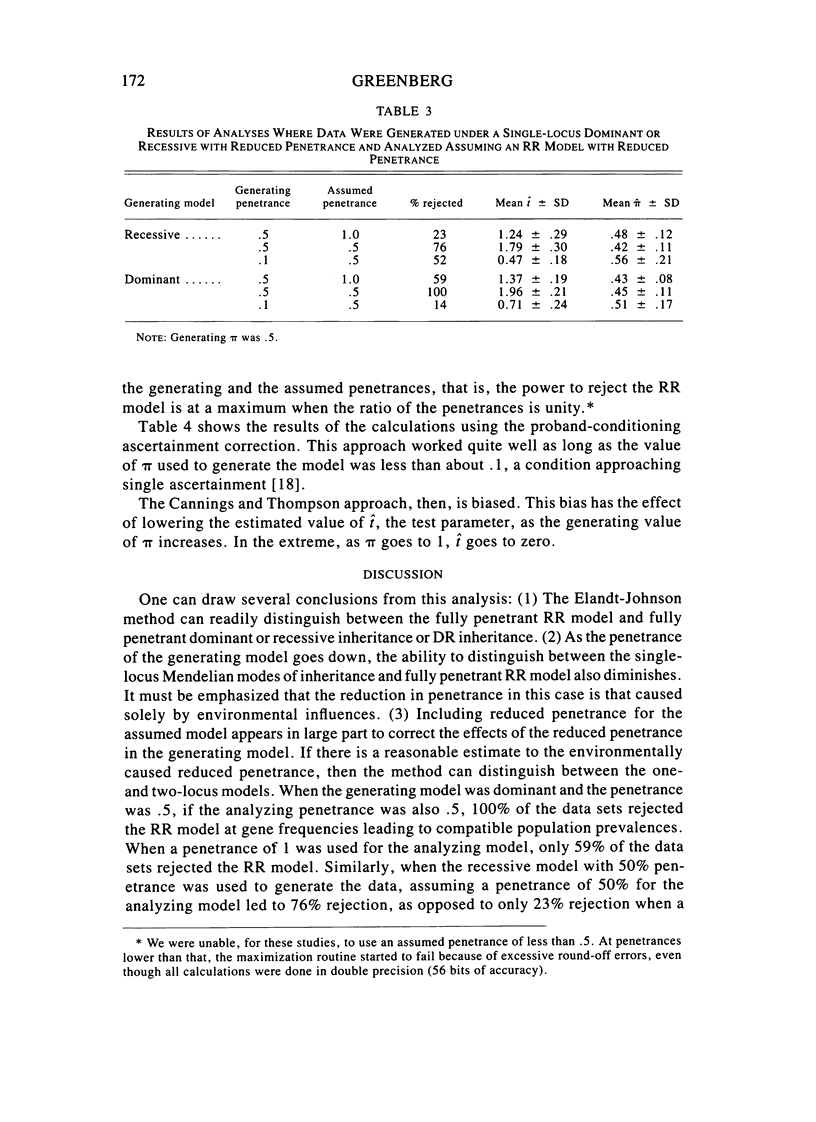
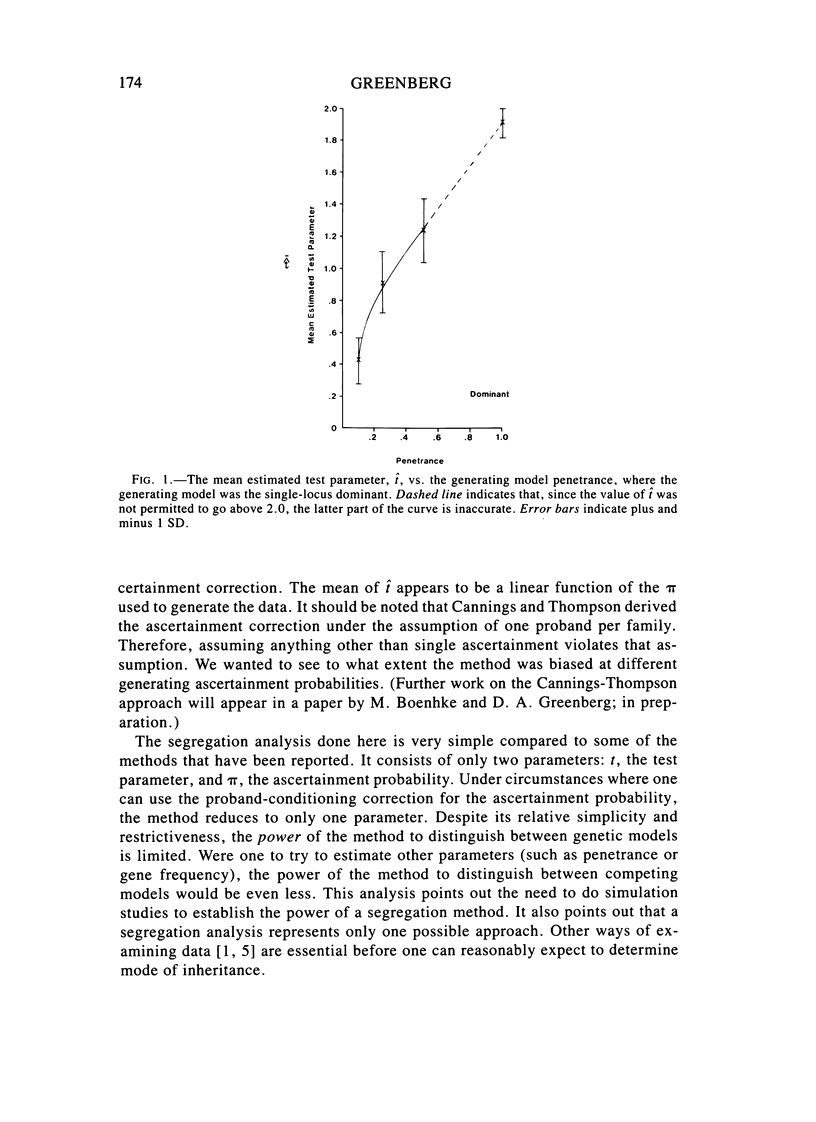
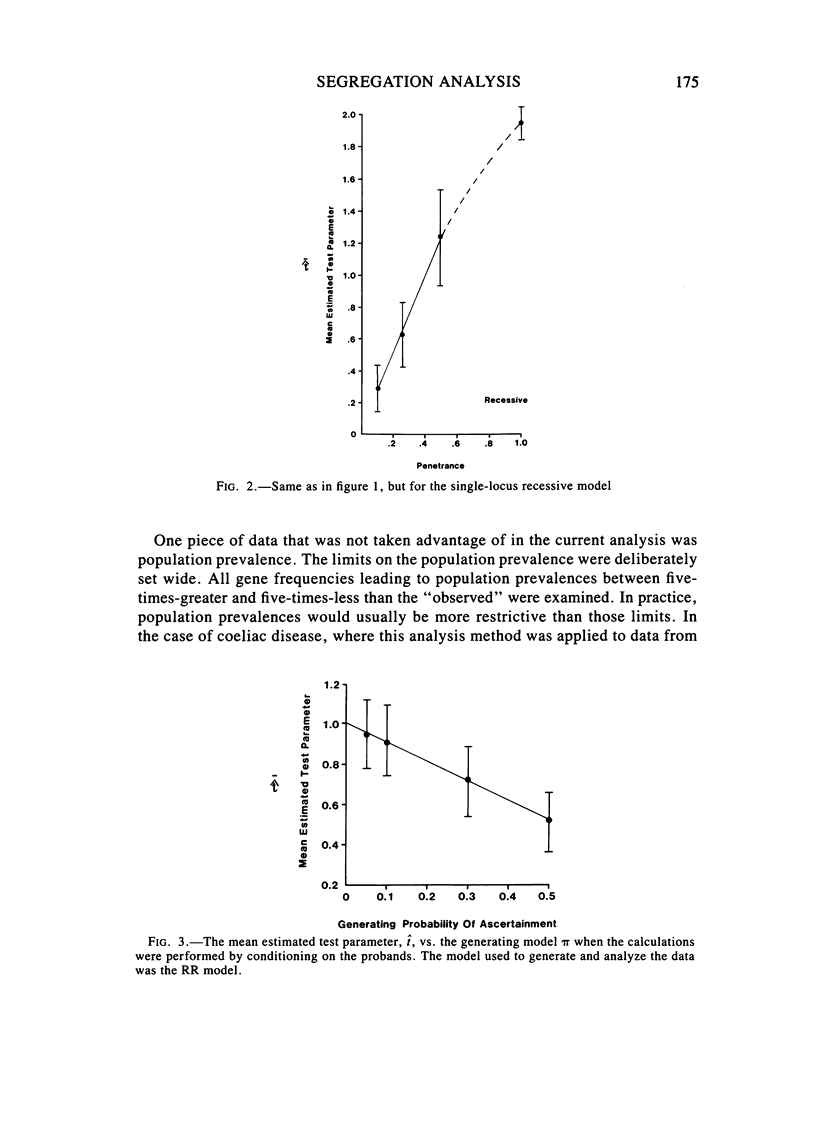
We tested the power of a segregation analysis method (first proposed by Elandt-Johnson) to distinguish between single-locus and two-locus models, with and without environmentally caused reduced penetrance. We also looked at the effect of ascertainment probability on the analysis and at the proband-conditioned ascertainment correction proposed by Cannings and Thompson. We found that: (1) the segregation analysis has sufficient power to distinguish between the fully-penetrant double-recessive (RR) model and the fully-penetrant single-locus dominant and recessive models; (2) the method can also distinguish fairly well between the dominant-recessive (DR) and RR models, even when one does not take into account the population prevalence; (3) the method has much less power to distinguish between the fully-penetrant RR model and the single-locus models with reduced penetrance; (4) when environmental penetrance is taken account of in the analysis, the power of the method to distinguish between the one- and two-locus models improved substantially; (5) the estimates of ascertainment probability, pi, were robust, regardless of the model under which the data were generated; and (6) the Cannings-Thompson approach to ascertainment correction worked well only when the pi used to generate the data was less than .1.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cannings C., Thompson E. A. Ascertainment in the sequential sampling of pedigrees. Clin Genet. 1977 Oct;12(4):208–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elandt-Johnson R. C. Segregation analysis for complex modes of inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Mar;22(2):129–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewens W. J. Aspects of parameter estimation in ascertainment sampling schemes. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Nov;34(6):853–865. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A. A simple method for testing two-locus models of inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jul;33(4):519–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Anderson C. E. The search for heterogeneity in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: evidence for familial and nonfamilial forms. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Mar;14(3):487–499. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Hodge S. E., Rotter J. I. Evidence for recessive and against dominant inheritance at the HLA-"linked" locus in coeliac disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):263–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Lange K. L. A maximum likelihood test of the two locus model for coeliac disease. Am J Med Genet. 1982 May;12(1):75–82. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320120110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Rotter J. I. Two locus models for gluten sensitive enteropathy: population genetic considerations. Am J Med Genet. 1981;8(2):205–214. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320080211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Anderson C. E., Neiswanger K., Field L. L., Spence M. A., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C., Crist M., Terasaki P. I., Rimoin D. L. Close genetic linkage between diabetes mellitus and kidd blood group. Lancet. 1981 Oct 24;2(8252):893–895. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91391-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Two genetic loci control the murine immune response to A-gliadin, a wheat protein that activates coeliac sprue. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):158–160. doi: 10.1038/296158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao Y., Matsumoto H., Miyazaki T., Mizuno N., Arima N., Wakisaka A., Okimoto K., Akazawa Y., Tsuji K., Fujita T. IgG heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and immune response to insulin in insulin-requiring diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):407–409. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. S., Mann D. L., Hague N. E., Heck J. A., van Leeuwen H. A., van Rood J. J., Strober W. Genetic basis of gluten-sentitive enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1978 Aug;75(2):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. A two locus model for juvenile diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 May;43(4):383–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Langenbeck U., Beisiegel U., Weber W. Genetics of the apolipoprotein E system in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):339–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


