Abstract
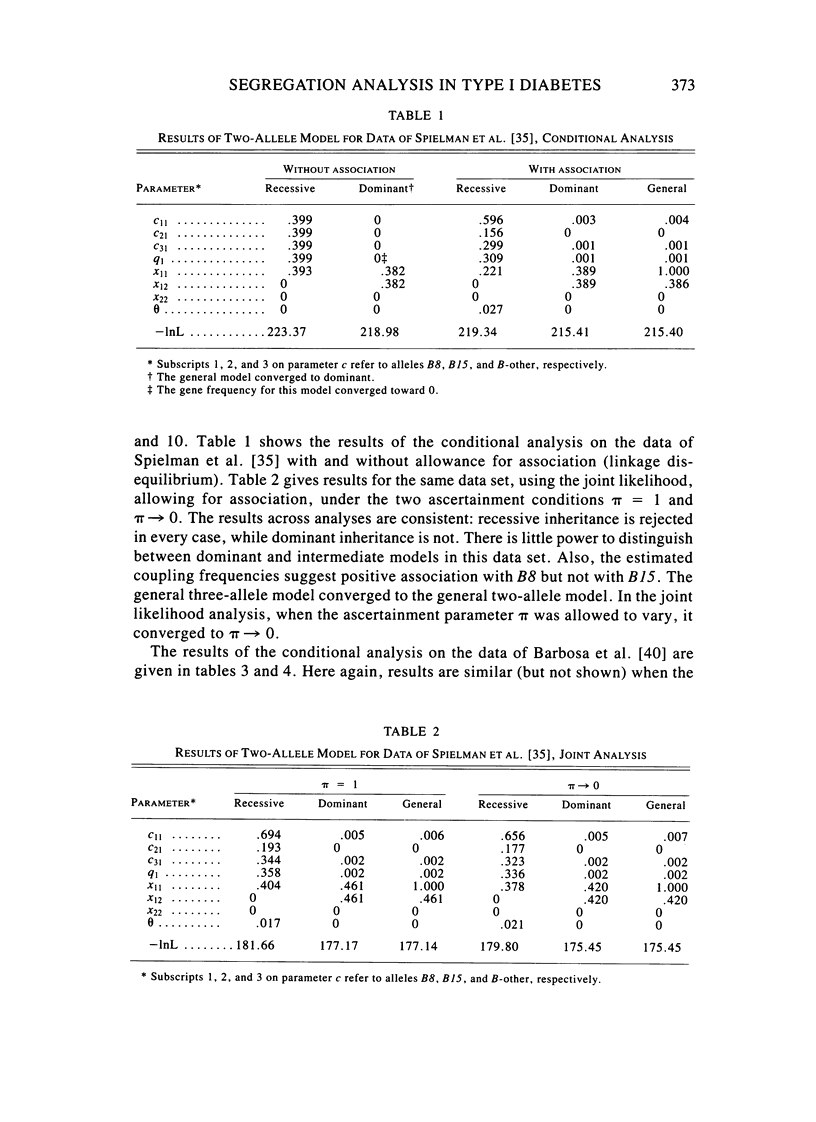
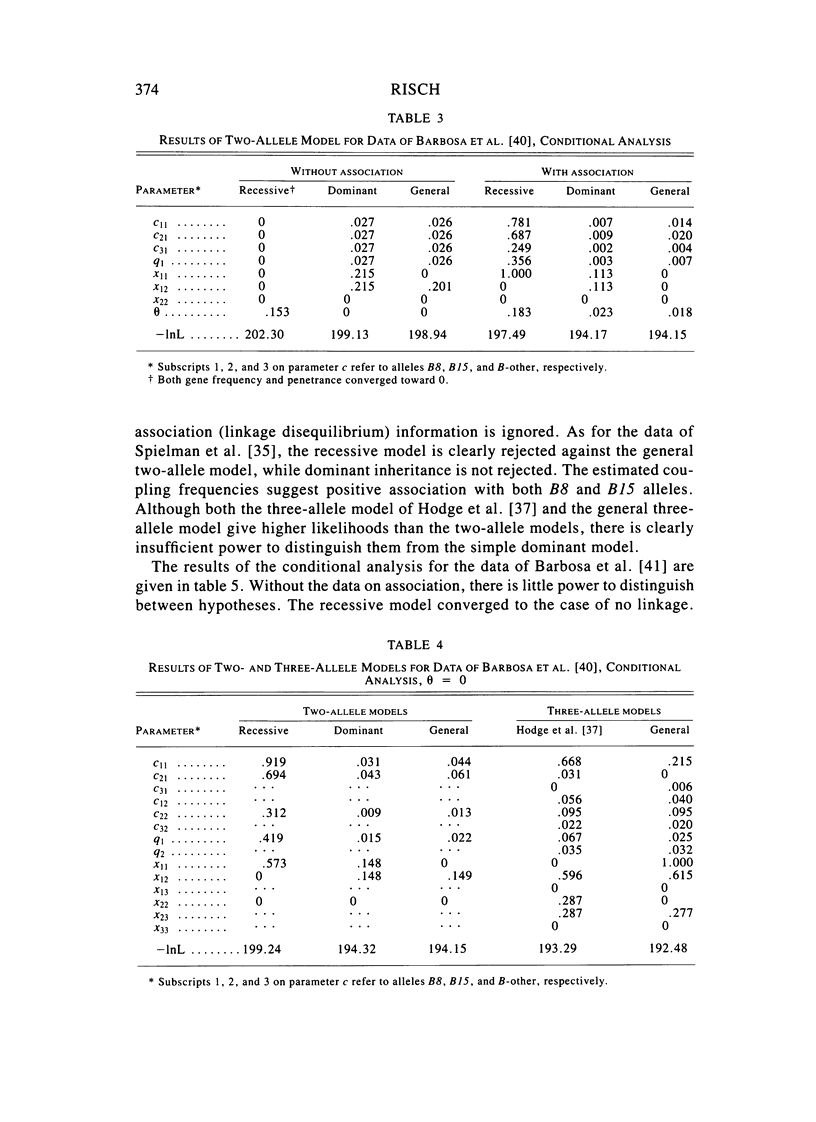
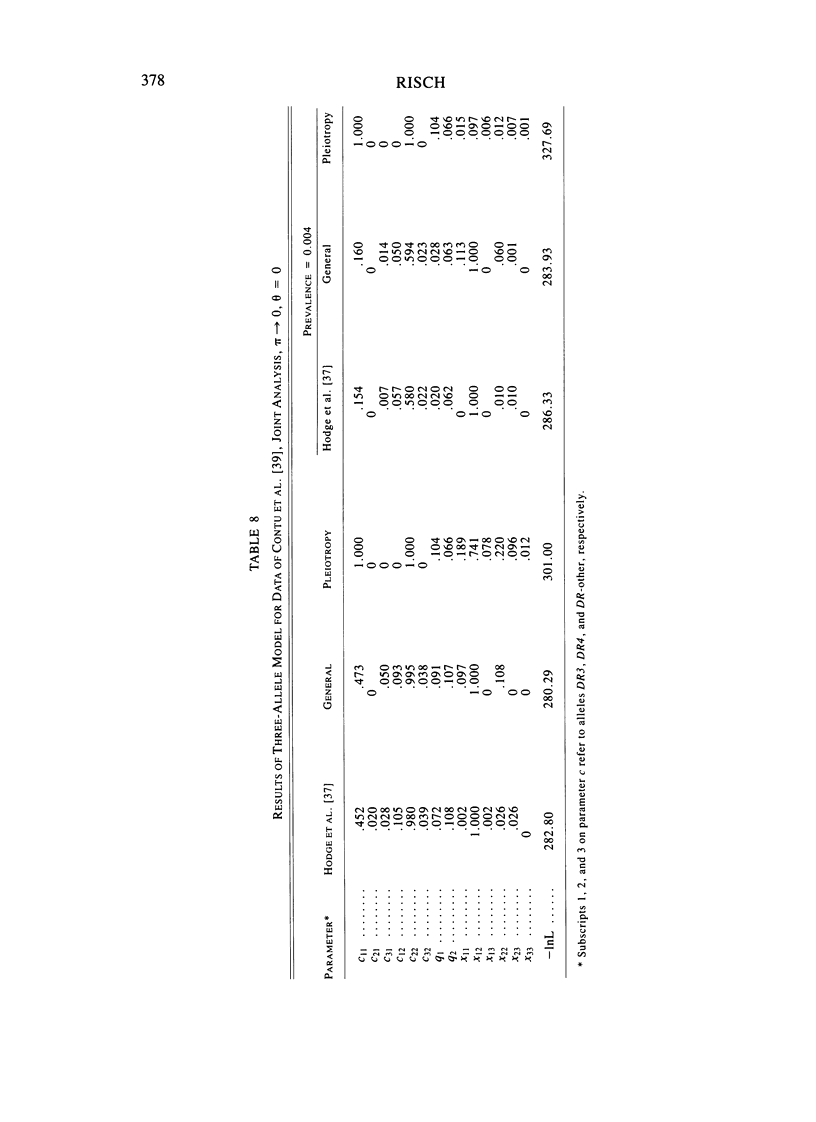
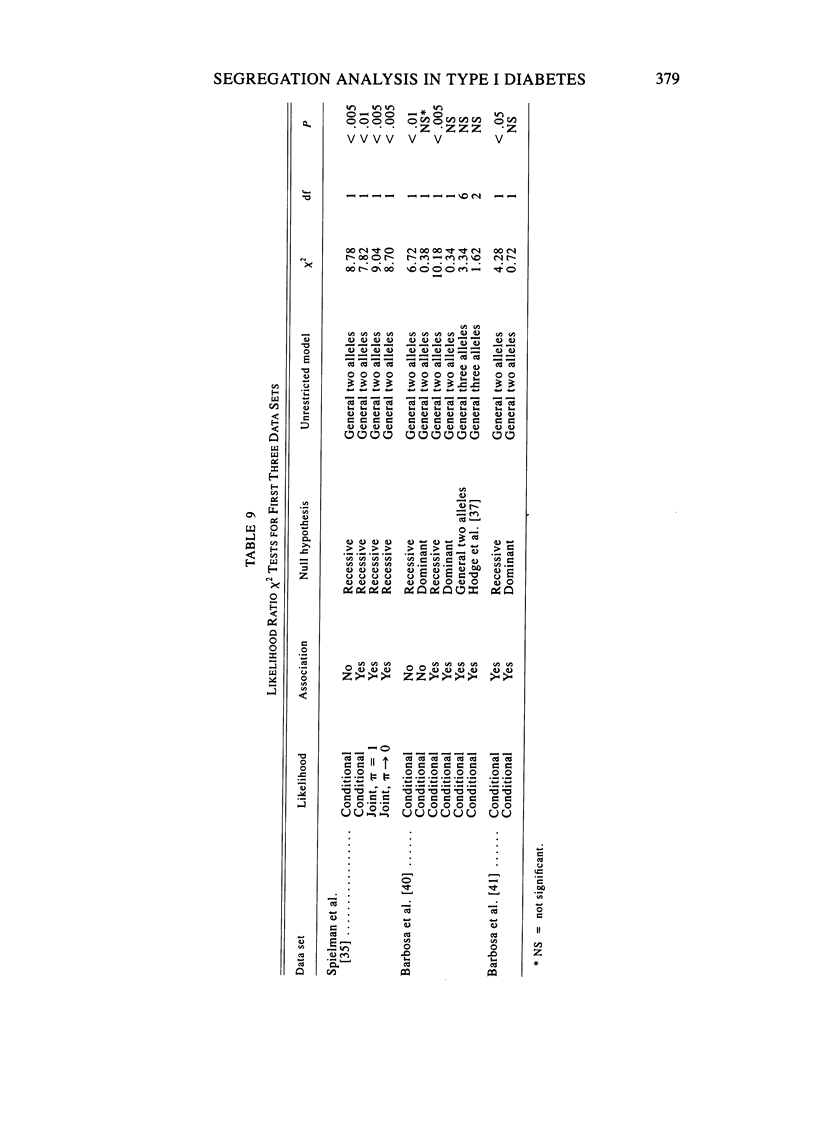
A method is described for segregation analysis that incorporates linkage markers. The model allows for segregation (penetrance), linkage (recombination fraction), and association (linkage disequilibrium) parameters. A single-locus-multiple-allele model underlying the trait phenotype is assumed. When families have been ascertained in a systematic fashion, a joint (markers, phenotypes) likelihood with ascertainment is advocated. When ascertainment correction is not feasible, a conditional (markers given phenotypes) approach is recommended, which is also valid in the presence of reduced fertility and assortative mating. This approach, oriented toward determining mode of inheritance, differs from conventional linkage analysis, which is oriented toward detection of linkage. Therefore, it is more appropriately considered an extension of the affected sib-pair method to arbitrary pedigrees, including association information and allowing for multiple alleles. Incorporation of coupling parameters allows for discrimination between pleiotropy and linkage disequilibrium. The method is demonstrated through a reanalysis of four recently published family studies on type 1 diabetes and HLA. Recessive inheritance is rejected in all four data sets. For three of them, dominant inheritance is not rejected, while in the fourth, all two-allele models are rejected in favor of three alleles. Although association with the DR3 and DR4 alleles is quite strong, pleiotropy with regard to these alleles is unlikely. The results also suggest an additional familial factor(s) (e.g., locus).
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRAI I., MI M. P., MORTON N. E., YASUDA N. ESTIMATION OF PREVALENCE UNDER INCOMPLETE SELECTION. Am J Hum Genet. 1965 May;17:221–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., Chern M. M., Anderson V. E., Noreen H., Johnson S., Reinsmoen N., McCarty R., King R., Greenberg L. Linkage analysis between the major histocompatibility system and insulin-dependent diabetes in families with patients in two consecutive generations. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):592–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI109704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., Chern M. M., Noreen H., Anderson V. E. Analysis of linkage between the major histocompatibility system and juvenile, insulin-dependent diabetes in multiplex families. Reanalysis of data. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):492–495. doi: 10.1172/JCI109151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., King R., Noreen H., Yunis E. J. The histocompatibility system in juvenile, insulin-dependent diabetic multiplex kindreds. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):989–998. doi: 10.1172/JCI108879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger A., Gold R. Z. On estimating recessive frequencies from truncated samples. Biometrics. 1967 Jun;23(2):356–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannings C., Thompson E. A. Ascertainment in the sequential sampling of pedigrees. Clin Genet. 1977 Oct;12(4):208–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget-Darpoux F., Bonaiti-Pellie C., Hors J., Deschamps I., Feingold N. Application of the lod score method to detection of linkage between HLA and juvenile insulin-dependent diabetes. Clin Genet. 1980 Jul;18(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb01365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contu L., Deschamps I., Lestradet H., Hors J., Schmid M., Busson M., Benajam A., Marcelli-Barge A., Dausset J. HLA haplotype study of 53 juvenile insulin-dependent diabetic (I.D.D.) families. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Aug;20(2):123–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb00335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G. Type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1978 May;14(5):281–291. doi: 10.1007/BF01223018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day N. E., Simons M. J. Disease susceptibility genes--their identification by multiple case family studies. Tissue Antigens. 1976 Aug;8(2):109–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsworth T. S., Rich S. S., Morton N. E., Barbosa J. Heterogeneity of insulin-dependent diabetes-new evidence. Clin Genet. 1982 Apr;21(4):233–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb00756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C. Ascertainment and age of onset in pedigree analysis. Hum Hered. 1973;23(2):105–112. doi: 10.1159/000152561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Sobel E. Sampling considerations in the gathering and analysis of pedigree data. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Jan;31(1):62–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Stewart J. A general model for the genetic analysis of pedigree data. Hum Hered. 1971;21(6):523–542. doi: 10.1159/000152448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewens W. J. Aspects of parameter estimation in ascertainment sampling schemes. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Nov;34(6):853–865. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Morton N. E., Iselius L., Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Hauge M. Genetic studies of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: segregation and linkage analyses. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Mar;19(3):213–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb01442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. R., Low H. C., Woodrow J. C. Inference on inheritance of disease using repetitions of HLA haplotypes in affected siblings. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Jan;47(Pt 1):73–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb00972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Anderson C. E. The search for heterogeneity in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: evidence for familial and nonfamilial forms. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Mar;14(3):487–499. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Rotter J. I., Lange K. L. A three-allele model for heterogeneity of juvenile onset insulin-dependent diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 May;43(4):399–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Spence M. A. Some epistatic two-locus models of disease. II. The confounding of linkage and association. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 May;33(3):396–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravitz K., Skolnick M., Cannings C., Carmelli D., Baty B., Amos B., Johnson A., Mendell N., Edwards C., Cartwright G. Genetic linkage between hereditary hemochromatosis and HLA. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Sep;31(5):601–619. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E. Complex segregation analysis with pointers. Hum Hered. 1981;31(5):312–321. doi: 10.1159/000153231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Elston R. C. Extensions to pedigree analysis I. Likehood calculations for simple and complex pedigrees. Hum Hered. 1975;25(2):95–105. doi: 10.1159/000152714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Genetic tests under incomplete ascertainment. Am J Hum Genet. 1959 Mar;11(1):1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. The detection and estimation of linkage between the genes for elliptocytosis and the Rh blood type. Am J Hum Genet. 1956 Jun;8(2):80–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Green A., Dunsworth T., Svejgaard A., Barbosa J., Rich S. S., Iselius L., Platz P., Ryder L. P. Heterozygous expression of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) determinants in the HLA system. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Mar;35(2):201–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Lalouel J. M. Resolution of linkage for irregular phenotype systems. Hum Hered. 1981;31(1):3–7. doi: 10.1159/000153168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., MacLean C. J. Analysis of family resemblance. 3. Complex segregation of quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;26(4):489–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. A general model for disease-marker association. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Jul;47(Pt 3):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb00992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. The effects of reduced fertility, method of ascertainment, and a second unlinked locus on affected sib-pair marker allele sharing. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):243–259. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein P., Ginsberg-Fellner F., Falk C. Genetics of Type I diabetes mellitus: a single, recessive predisposition gene mapping between HLA-B and GLO. With an appendix on the estimation of selection bias. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Nov;33(6):865–882. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman R. S., Baker L., Zmijewski C. M. Gene dosage and suceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Oct;44(Pt 2):135–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb00954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman R. S., Baker L., Zmijewski C. M. Inheritance of susceptibility to juvenile onset diabetes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;32:567–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez B. K., Rice J., Reich T. The generalized sib pair IBD distribution: its use in the detection of linkage. Ann Hum Genet. 1978 Jul;42(1):87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1978.tb00933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez B. K., Van Eerdewegh P. Type I (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus. Is there strong evidence for a non-HLA linked gene? Diabetologia. 1981 May;20(5):524–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00252759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez B., O'Rourke D., Van Eerdewegh P. Power of the affected-sib-pair method to defect disease susceptibility loci of small effect: an application to multiple sclerosis. Am J Med Genet. 1982 Jul;12(3):309–326. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320120309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. A two locus model for juvenile diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 May;43(4):383–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


