Abstract
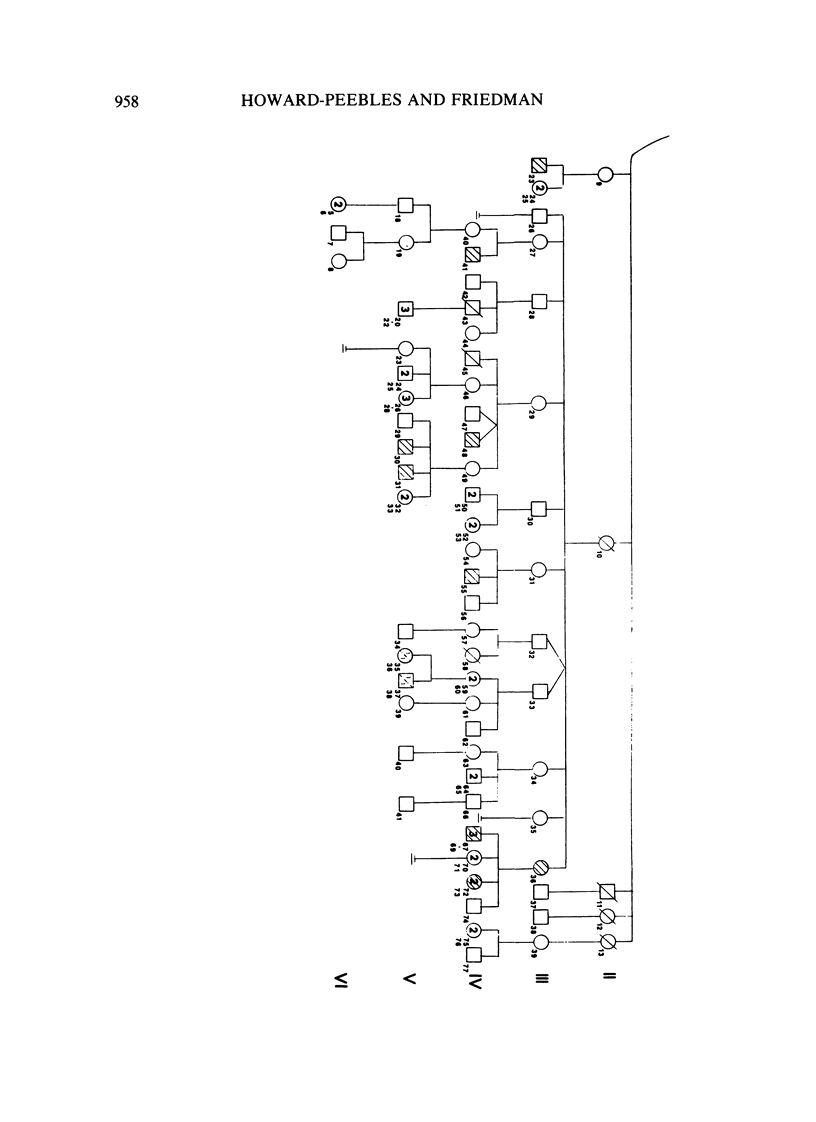
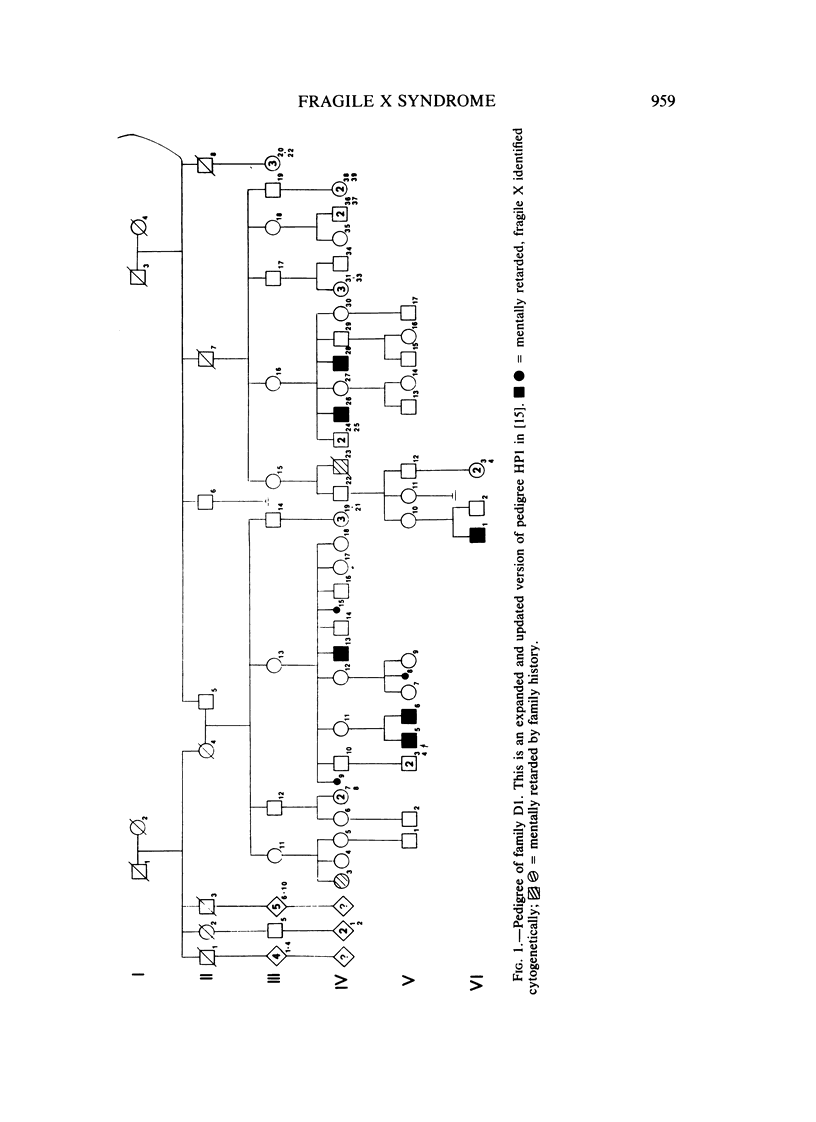
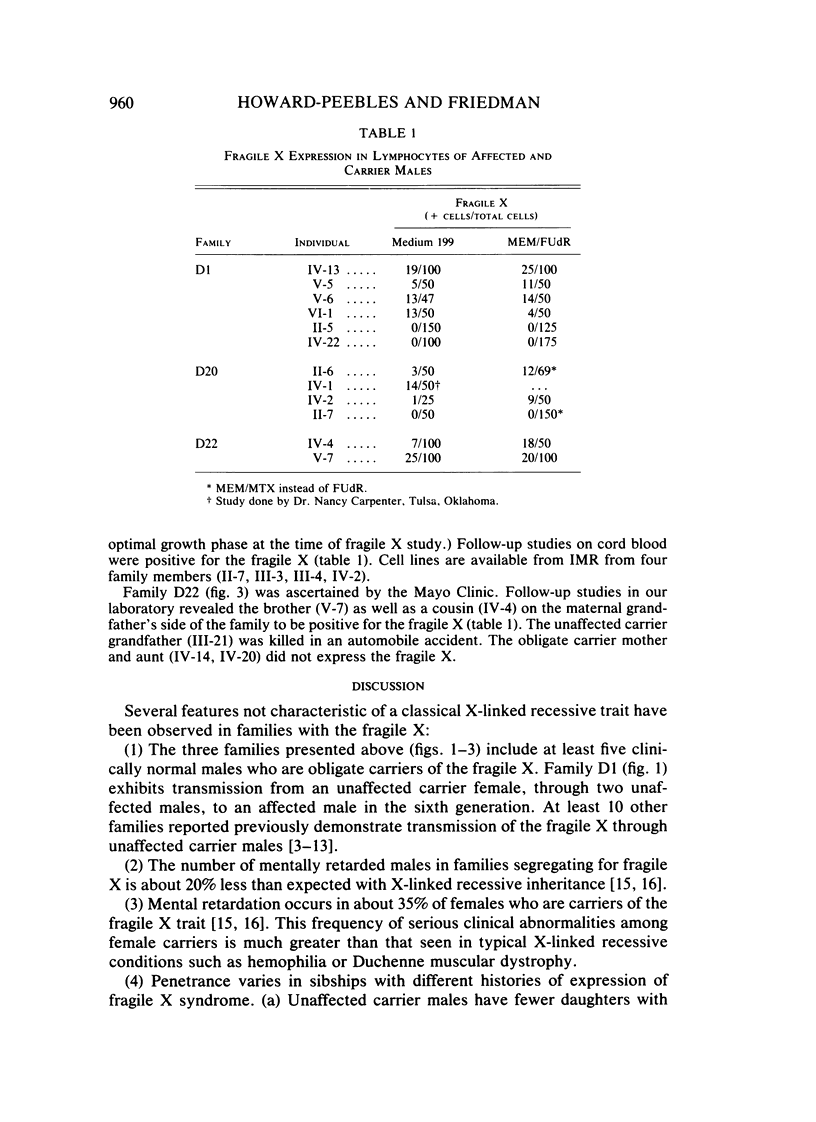
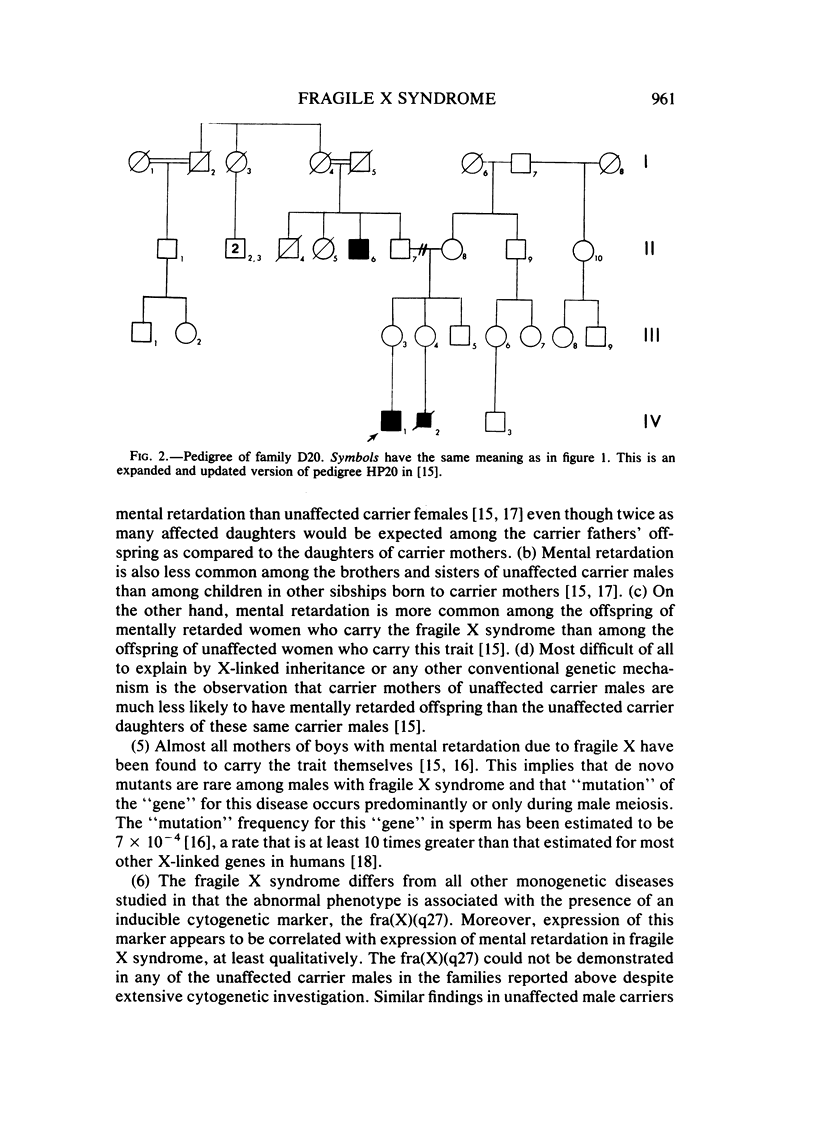
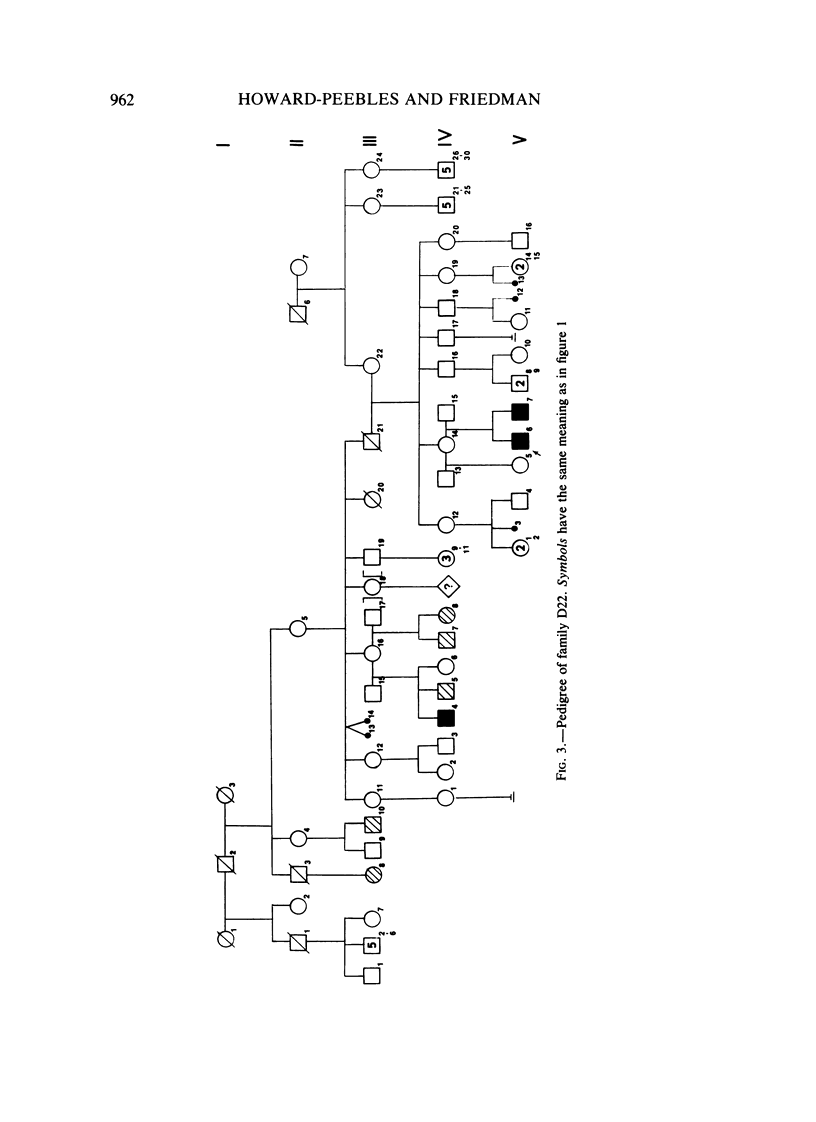
Males who transmit the fragile X chromosome but are themselves clinically normal have occasionally been observed. We have studied three families segregating the fragile X. In one family, there are three unaffected carrier males, and in each of the other two families, there is one unaffected carrier male. Three of these carrier males were studied cytogenetically, and none exhibited the fra(X)(q27) marker. The occurrence of carrier males and of other unusual genetic features in fragile X families suggest that this condition is not inherited as a standard recessive trait linked to the X chromosome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camerino G., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Jaye M., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of fragile X-mental retardation syndrome to haemophilia B and transmission through a normal male. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):701–704. doi: 10.1038/306701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froster-Iskenius U., Schulze A., Schwinger E. Transmission of the marker X syndrome trait by unaffected males: conclusions from studies of large families. Hum Genet. 1984;67(4):419–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00291403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P. The fragile X syndrome. A study of 83 families. Clin Genet. 1984 Dec;26(6):497–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., van den Berghe H. Transmission of fragile (X)(q27) from normal male(s). Hum Genet. 1982;61(3):262–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00296456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. J., Smart R. D., Cornell J. M., Merckel L. M., Beighton P. The fragile X chromosome in a large Indian kindred. Clin Genet. 1983 Apr;23(4):311–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb01883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. J., Wang H. S., White B. N. The fragile-X syndrome, IV. Progress towards the identification of linked restriction fragment length variants (RFLVs). Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):259–273. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Glover T. W., Mayer M., Fox P., Gerrard J. W., Dunn H. G., Herbst D. S. X-linked mental retardation: a study of 7 families. Am J Med Genet. 1980;7(4):471–489. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320070408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Mayer M., Matsuura J., Rhoads F., Yee S. C. A cytogenetic study of a population of mentally retarded males with special reference to the marker (X) syndrome. Hum Genet. 1983;63(2):139–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00291533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähkönen M., Leisti J., Wilska M., Varonen S. Marker X-associated mental retardation. A study of 150 retarded males. Clin Genet. 1983 Jun;23(6):397–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb01973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. B., Tommerup N., Poulsen H., Mikkelsen M. X-linked mental retardation with fragile X. A pedigree showing transmission by apparently unaffected males and partial expression in female carriers. Hum Genet. 1981;59(1):23–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00278849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz J. M., Sutherland G. R. Conference report: International Workshop on the fragile X and X-linked mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):5–94. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J., Froster-Iskenius U., Moje W., Schwinger E. Heterozygous female carriers of the marker-X-chromosome: IQ estimation and replication status of fra(X)(q). Hum Genet. 1984;66(4):344–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00287638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky L., Kaufman M., Killinger D. W., Burko B., Shatz D., Volpé R. Human minimal androgen insensitivity with normal dihydrotestosterone-binding capacity in cultured genital skin fibroblasts: evidence for an androgen-selective qualitative abnormality of the receptor. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Sep;36(5):965–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads F. A., Oglesby A. C., Mayer M., Jacobs P. A. Marker X syndrome in an oriental family with probable transmission by a normal male. Am J Med Genet. 1982 Jun;12(2):205–217. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320120211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards B. W., Sylvester P. E., Brooker C. Fragile X-linked mental retardation: the Martin-Bell syndrome. J Ment Defic Res. 1981 Dec;25(Pt 4):253–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1981.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Jacobs P. A., Morton N. E., Froster-Iskenius U., Howard-Peebles P. N., Nielsen K. B., Partington M. W., Sutherland G. R., Turner G., Watson M. Further segregation analysis of the fragile X syndrome with special reference to transmitting males. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):289–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00291644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Morton N. E., Jacobs P. A., Turner G. The marker (X) syndrome: a cytogenetic and genetic analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):21–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes I. Factors affecting expression in lymphocyte culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy B. C., De Smedt M. C., Raes R. A., Dumon J. E., Leroy J. G. Fragile X trait in a large kindred: transmission also through normal males. J Med Genet. 1983 Aug;20(4):286–289. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.4.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Rathenberg R. Spontaneous mutation in man. Adv Hum Genet. 1975;5:223–318. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9068-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


