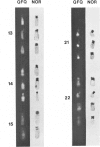
Abstract
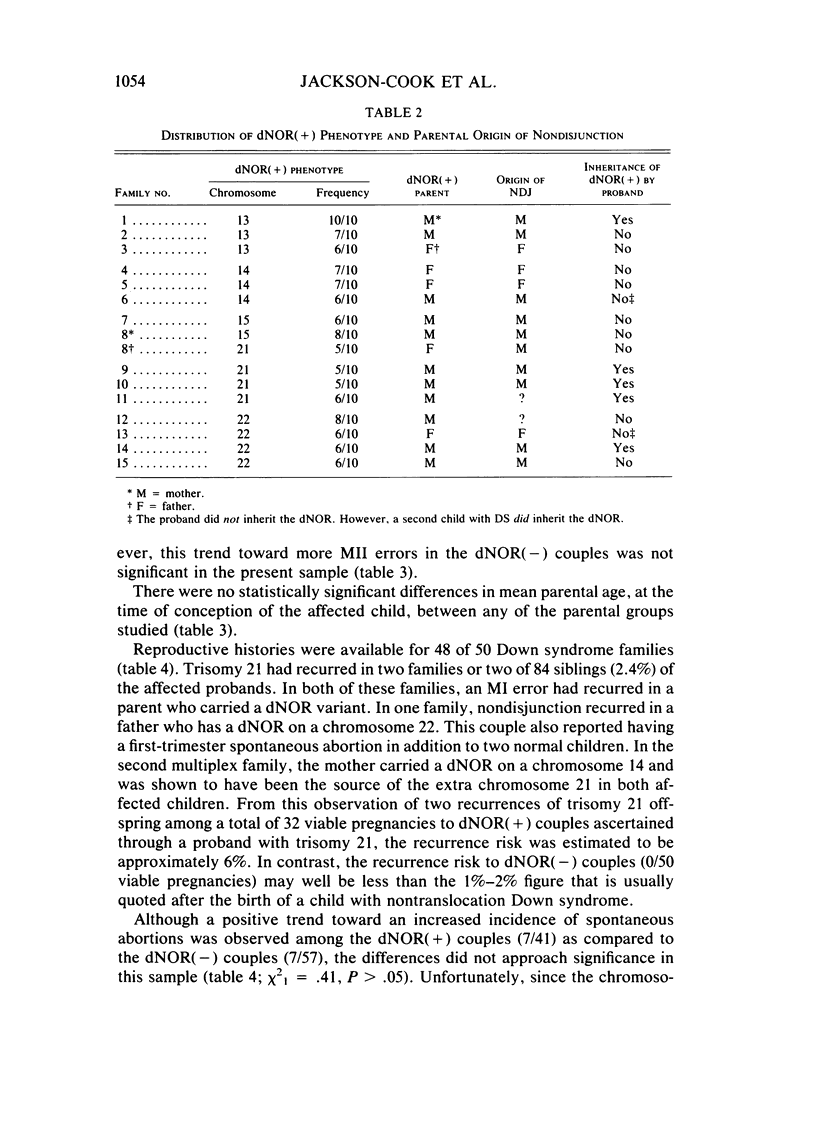
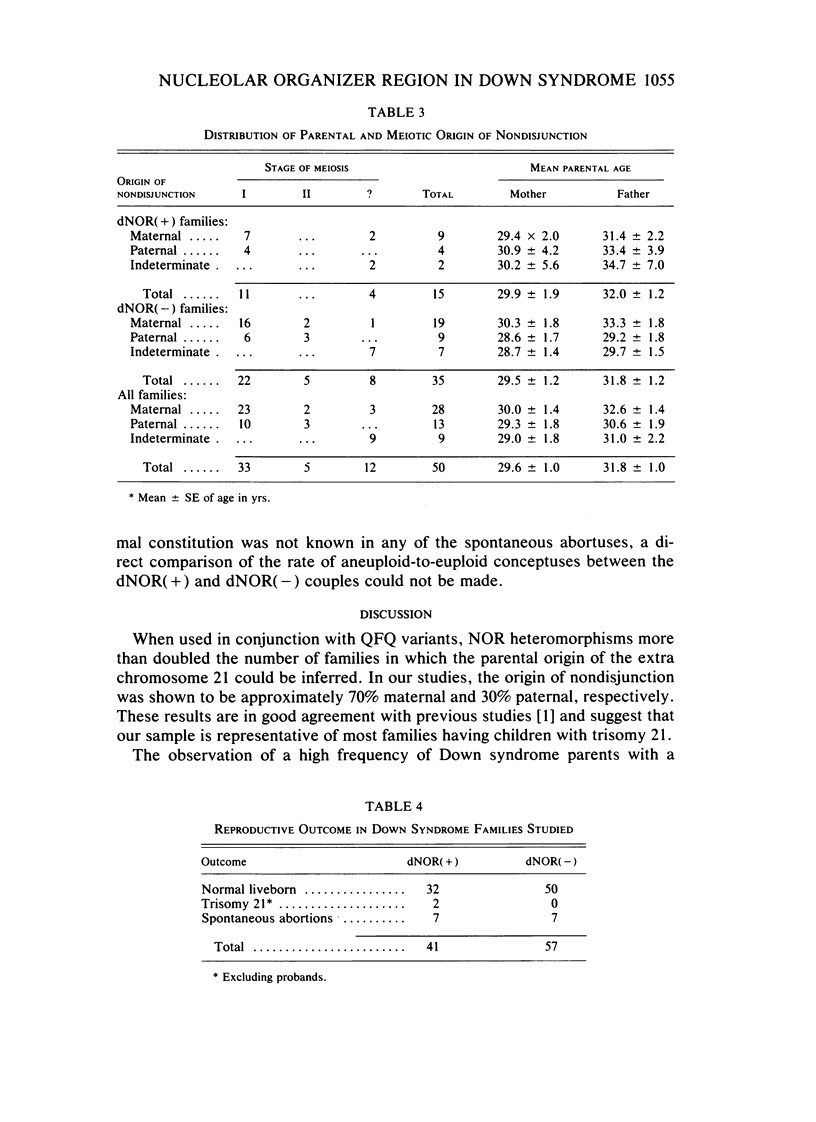
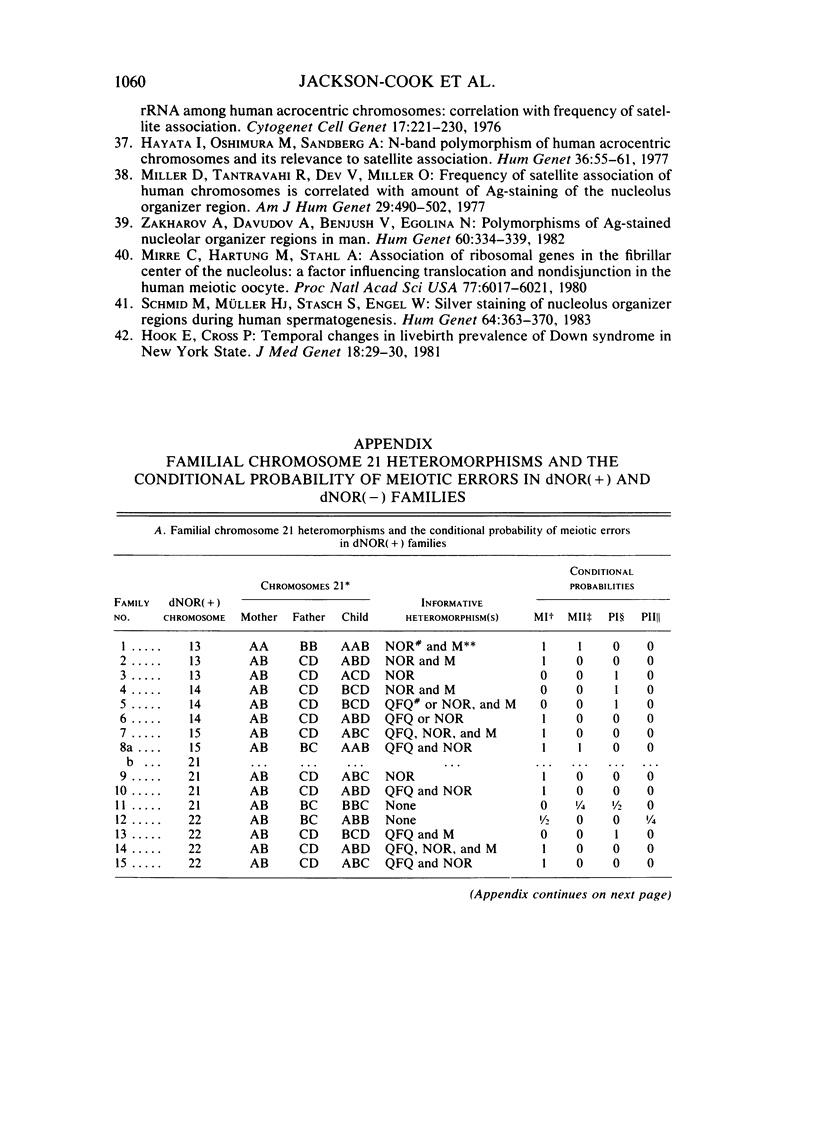
An unusual nucleolar organizer region (NOR) heteromorphism was noted among 13 of 41 parents in whom nondisjunction leading to trisomy 21 was known to have occurred. In contrast, only one of these double NOR (dNOR) variants was found among the 41 normal spouses and none were seen among 50 control individuals. In two dNOR(+) families, a second child with trisomy 21 was conceived. In both families, the extra chromosome in each child was contributed by the parent who carried the dNOR variant and resulted from a recurrent meiosis I error. Our data suggest that the dNOR heteromorphism may play a role in meiotic nondisjunction and could be associated with as much as a 20-fold increased risk for having offspring with trisomy 21.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archidiacono N., de Capoa A., Ferraro M., Pelliccia F., Rocchi A., Rocchi M. Nucleolus organizer and N-band distribution in morphologic and fluorescence variants of human chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1977 Jul 26;37(3):285–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00393610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balícek P., Zizka J. Intercalar satellites of human acrocentric chromosomes as a cytological manifestation of polymorphism in GC-rich material? Hum Genet. 1980;54(3):343–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00291580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R., Dawson B., Griffiths J. Human inherited marker chromosome 22 short-arm enlargement: investigation of rDNA gene multiplicity, Ag-band size, and acrocentric association. Hum Genet. 1981;58(2):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00278697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. E., Goodpasture C. An improved technique for selective silver staining of nucleolar organizer regions in human chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1976 Oct 28;34(2):199–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00278889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall B. F., Ebbin A. J. Trisomy 18 and 21 in two siblings. Clin Genet. 1973 Jun;4(6):517–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEKABAN A. S., BENDER M. A., ECONOMOS G. E. CHROMOSOME STUDIES IN MONGOLOIDS AND THEIR FAMILIES. Cytogenetics. 1963;2:61–75. doi: 10.1159/000129768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhadial R., Pfeiffer R. A. Cytogenetic studies in families with two 47, +21-siblings. J Genet Hum. 1972 Dec;20(4):297–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emberger J. M., Taib J. 21 p + maternel en double exemplaire chez un trisomique 21. J Genet Hum. 1975 Oct;23(Suppl):98–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON-SMITH M. A. THE SITES OF NUCLEOLUS FORMATION IN HUMAN PACHYTENE CHROMOSOMES. Cytogenetics. 1964;3:124–134. doi: 10.1159/000129803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliani F., De Capoa A., Rocchi A. A marker chromosome number 14 with double satellite obseved in two generations: an unbalanced chromosome constitution associated with normal phenotype. Humangenetik. 1972;15(2):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00295748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnemann N., Eiberg H. Antenatal genetic diagnosis in a kindred with a 15p plus chromosome. Clin Genet. 1973 Jun;4(6):464–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson A., Mikkelsen M. The origin of the extra chromosome 21 in Down syndrome. Studies of fluorescent variants and satelite association in 26 informative families. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;20(1-6):194–203. doi: 10.1159/000130851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayata I., Oshimura M., Sandberg A. A. N-band polymorphism of human acrocentric chromosomes and its relevance to satellite association. Hum Genet. 1977 Apr 7;36(1):55–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00390436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Atwood K. C. Satellite-association frequency and rDNA content of a double-satellited chromosome. Hum Genet. 1976 Jan 28;31(1):113–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00270407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B., Cross P. K. Temporal increase in the rate of Down syndrome livebirths to older mothers in New York State. J Med Genet. 1981 Feb;18(1):29–30. doi: 10.1136/jmg.18.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Mayer M. The origin of human trisomy: a study of heteromorphisms and satellite associations. Ann Hum Genet. 1981 Oct;45(Pt 4):357–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1981.tb00349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Morton N. E. Origin of human trisomics and polyploids. Hum Hered. 1977;27(1):59–72. doi: 10.1159/000152852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jotterand-Bellomo M., van Melle G. Is it always the same NOR that is more active in a pair of acrocentrics with distinct AG-stainings? Hum Genet. 1981;59(2):185–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00293075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juberg R. C., Mowrey P. N. Origin of nondisjunction in trisomy 21 syndrome: all studies compiled, parental age analysis, and international comparisons. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Sep;16(1):111–116. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Wertelecki W., Pfeiffer R. A., Arrighi F. E. Cytological analyses of 14p+ variant by means of N-banding and combinations of silver staining and chromosome bandings. Hum Genet. 1979 Jan 19;46(1):75–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00278904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORHEAD P. S., NOWELL P. C., MELLMAN W. J., BATTIPS D. M., HUNGERFORD D. A. Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:613–616. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marković V. D., Worton R. G., Berg J. M. Evidence for the inheritance of silver-stained nucleolus organizer regions. Hum Genet. 1978 Mar 17;41(2):181–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00273100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. O., Miller L., Simpson J. L., Thomas C., Rzeszotarski M. S., Elias S., Sarto G. E., Patel V. A. Localization of the nucleolar organizer by computer-aided analysis of a variant no. 21 in a human isolate. Hum Genet. 1979 Apr 27;48(2):211–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00286906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen M. Parental origin of the extra chromosome in Down's Syndrome. J Ment Defic Res. 1982 Sep;26(Pt 3):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1982.tb00141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen M., Poulsen H., Grinsted J., Lange A. Non-disjunction in trisomy 21: study of chromosomal heteromorphisms in 110 families. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Jul;44(Pt 1):17–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb00942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Breg W. R., Warburton D., Dev V. G., Miller O. J. Regulation of rRNA gene expression in a human familial 14p+ marker chromosome. Hum Genet. 1978 Sep 19;43(3):289–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00278836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Tantravahi R., Dev V. G., Miller O. J. Frequency of satellite association of human chromosomes is correlated with amount of Ag-staining of the nucleolus organizer region. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):490–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirre C., Hartung M., Stahl A. Association of ribosomal genes in the fibrillar center of the nucleolus: a factor influencing translocation and nondisjunction in the human meiotic oocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6017–6021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton C. C., Brown J. A., Holmes W. M., Nance W. E., Wolf B. Stain intensity of human nucleolus organizer region reflects incorporation of uridine into mature ribosomal RNA. Exp Cell Res. 1983 May;145(2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW M. W. Familial mongolism. Cytogenetics. 1962;1:141–179. doi: 10.1159/000129726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands V. E. Short arm enlargement in acrocentric chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):293–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M., Krone W., Vogel W. On the relationship between the frequency of association and the nucleolar constriction of individual acrocentric chromosomes. Humangenetik. 1974;23(4):267–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00272510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M., Müller H., Stasch S., Engel W. Silver staining of nucleolus organizer regions during human spermatogenesis. Hum Genet. 1983;64(4):363–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00292368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofuni T., Tanabe K., Awa A. A. Chromosome heteromorphisms in the Japanese. II. Nucleolus organizer regions of variant chromosomes in D and G groups. Hum Genet. 1980;55(2):265–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00291776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THERKELSEN A. J. ENLARGED SHORT ARM OF A SMALL ACROCENTRIC CHROMOSOME IN GRANDFATHER, MOTHER AND CHILD, THE LATTER WITH DOWN'S SYNDROME. Cytogenetics. 1964;3:441–451. doi: 10.1159/000129832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D., Atwood K. C., Henderson A. S. Variation in the number of genes for rRNA among human acrocentric chromosomes: correlation with frequency of satellite association. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;17(4):221–230. doi: 10.1159/000130715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner W., Herrmann F. H., John B. Cytogenetic studies of a family with trisomy 21 mosaicism in two successive generations as the cause of Down's syndrome. Hum Genet. 1982;60(2):202–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00569714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov A. F., Davudov A. Z., Benjush V. A., Egolina N. A. Polymorphisms of Ag-stained nucleolar organizer regions in man. Hum Genet. 1982;60(4):334–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00569214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zankl H., Zang K. D. Quantitative studies on the arrangement of human metaphase chromosomes. IV. The association frequency of human acrocentric marker chromosomes. Humangenetik. 1974;23(4):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00272509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]