Abstract
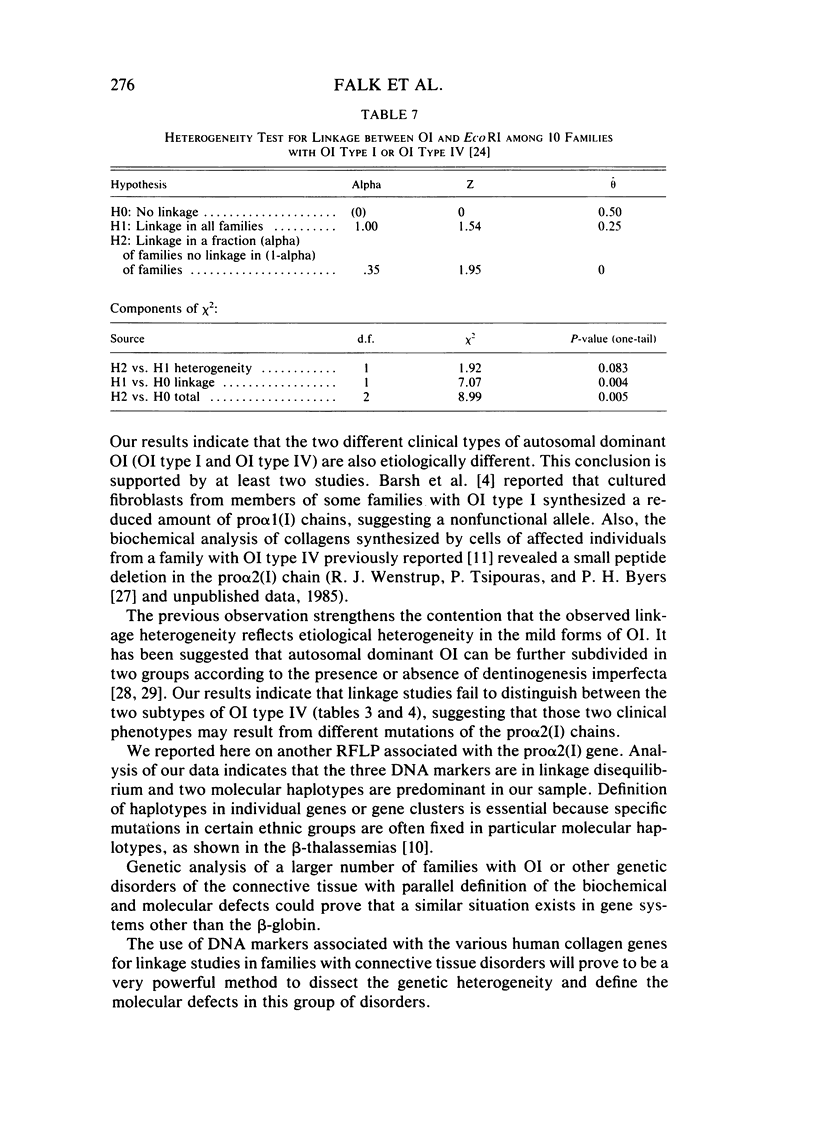
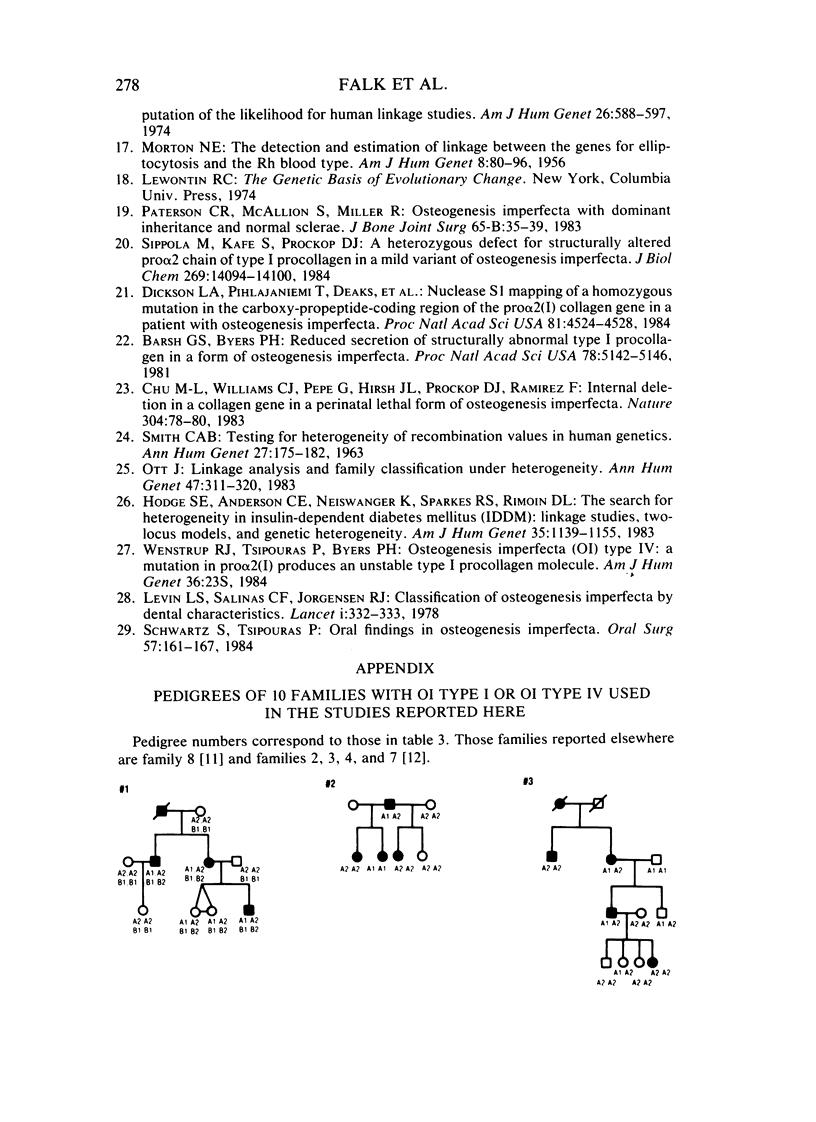
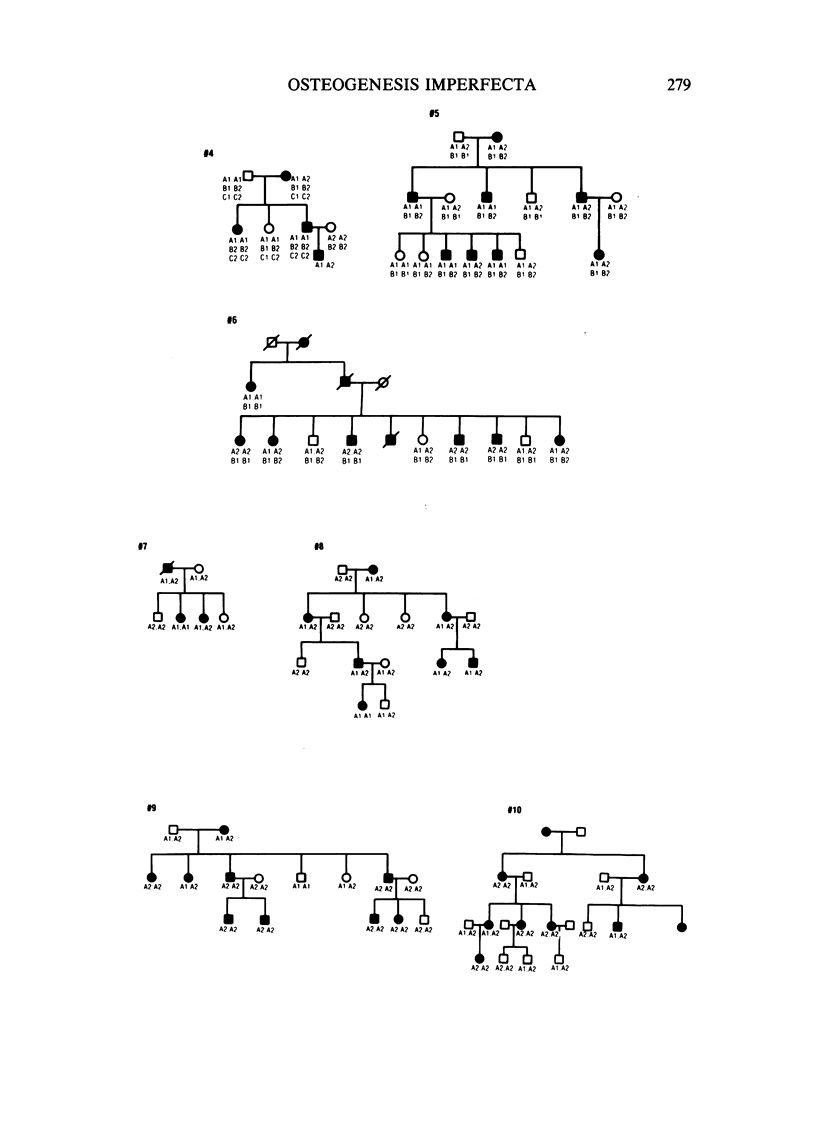
Autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a heterogeneous group of disorders. Molecular haplotypes associated with the pro alpha 2(I) gene of human type I procollagen were used for genetic linkage studies in a group of 10 families with OI. The clinical phenotypes of the families studied were those of OI type I and OI type IV. Evidence for linkage was highly suggestive in the four families with OI type IV (Z = 3.91 for theta = 0). In contrast, little or no indication for linkage was found in the six families with OI type I (Z = .055 for theta = .415). Heterogeneity between the two groups of families was highly significant (chi 2 = 11.14, P = .0008), suggesting that at least two separate gene defects may be the cause of the autosomal dominant forms of OI.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsh G. S., Byers P. H. Reduced secretion of structurally abnormal type I procollagen in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., David K. E., Byers P. H. Type I osteogenesis imperfecta: a nonfunctional allele for pro alpha 1 (I) chains of type I procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3838–3842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Shapiro J. R., Rowe D. W., David K. E., Holbrook K. A. Abnormal alpha 2-chain in type I collagen from a patient with a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):689–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI110815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Dryja T. P., Phillips R. A., Benedict W. F., Godbout R., Gallie B. L., Murphree A. L., Strong L. C., White R. L. Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):779–784. doi: 10.1038/305779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Williams C. J., Pepe G., Hirsch J. L., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Internal deletion in a collagen gene in a perinatal lethal form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):78–80. doi: 10.1038/304078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson L. A., Pihlajaniemi T., Deak S., Pope F. M., Nicholls A., Prockop D. J., Myers J. C. Nuclease S1 mapping of a homozygous mutation in the carboxyl-propeptide-coding region of the pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene in a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4524–4528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Anderson C. E., Neiswanger K., Sparkes R. S., Rimoin D. L. The search for heterogeneity in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM): linkage studies, two-locus models, and genetic heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Nov;35(6):1139–1155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. S., Salinas C. F., Jorgenson R. J. Classification of osteogenesis imperfecta by dental characteristics. Lancet. 1978 Feb 11;1(8059):332–333. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. The detection and estimation of linkage between the genes for elliptocytosis and the Rh blood type. Am J Hum Genet. 1956 Jun;8(2):80–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dickson L. A., de Wet W. J., Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Di Liberto M., Pepe G., Sangiorgi F. O., Ramirez F. Analysis of the 3' end of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Utilization of multiple polyadenylation sites in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10128–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Linkage analysis and family classification under heterogeneity. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Oct;47(Pt 4):311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb01001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson C. R., McAllion S., Miller R. Osteogenesis imperfecta with dominant inheritance and normal sclerae. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983 Jan;65(1):35–39. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.65B1.6822598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. A., 3rd, Hjelle B. L., Seeburg P. H., Zachmann M. Molecular basis for familial isolated growth hormone deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6372–6375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Antonarakis S., Bauer K. A., Rosenberg R. D., Fearon E. R., Orkin S. H. Molecular heterogeneity of inherited antithrombin III deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 30;308(26):1549–1552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306303082601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. A. TESTING FOR HETEROGENEITY OF RECOMBINATION FRACTION VALUES IN HUMAN GENETICS. Ann Hum Genet. 1963 Nov;27:175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1963.tb00210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Tsipouras P. Oral findings in osteogenesis imperfecta. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984 Feb;57(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(84)90206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. O., Senn A., Danks D. M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1979 Apr;16(2):101–116. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick M. H., Willard H. F., Menlove L. A. Report of the Committee on Human Gene Mapping by Recombinant DNA Techniques. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):210–273. doi: 10.1159/000132011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Børresen A. L., Dickson L. A., Berg K., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Molecular heterogeneity in the mild autosomal dominant forms of osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1172–1179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Myers J. C., Ramirez F., Prockop D. J. Restriction fragment length polymorphism associated with the pro alpha 2(I) gene of human type I procollagen. Application to a family with an autosomal dominant form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1262–1267. doi: 10.1172/JCI111082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]