Abstract
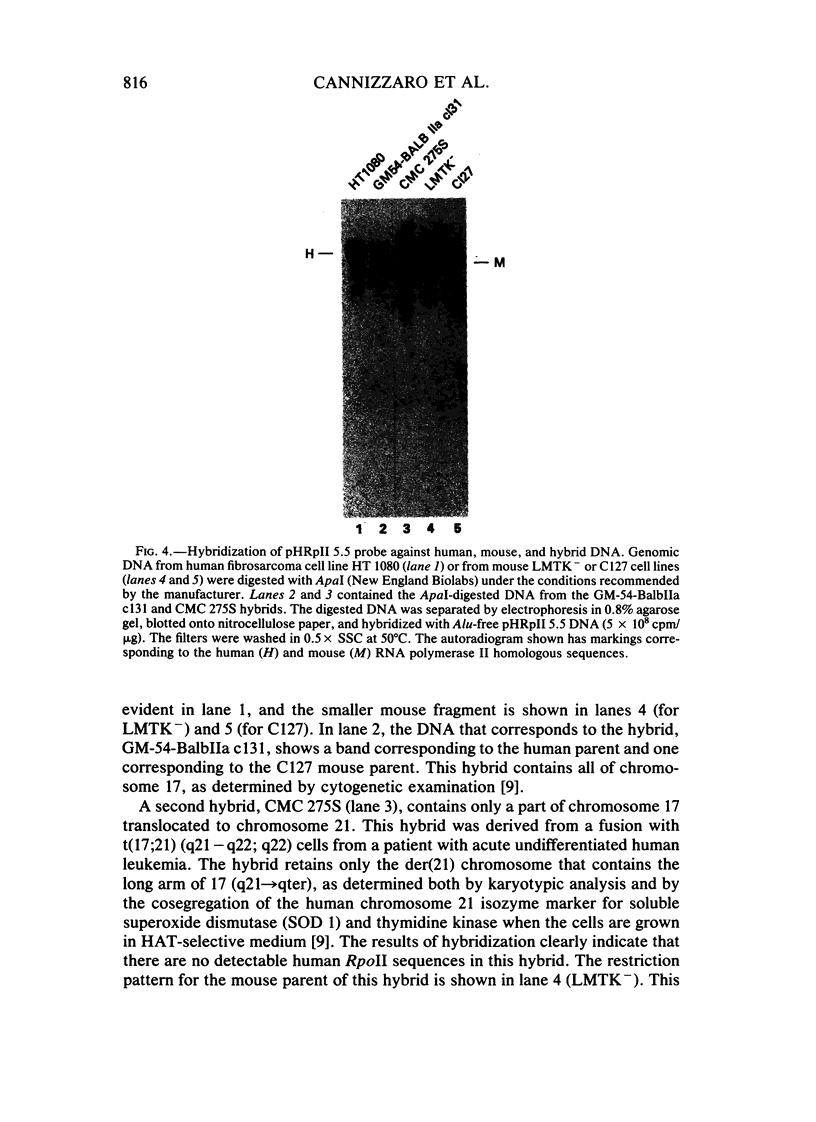
We have used chromosomal in situ hybridization and Southern blot analysis of DNA from somatic cell hybrids to determine the chromosomal localization of the subgenomic DNA fragment that encodes part of the large subunit of human RNA polymerase II. The results of our analysis demonstrate localization of the human RNA polymerase II large subunit gene to the short arm of chromosome 17.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cannizzaro L. A., Aronson M. M., Emanuel B. S. In situ hybridization and translocation breakpoint mapping. II. Two unusual t(21;22) translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(3):173–178. doi: 10.1159/000132130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Emanuel B. S. An improved method for G-banding chromosomes after in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):308–309. doi: 10.1159/000132079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Khalili K., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. The gene encoding the large subunit of human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15204–15210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Selden J. R., Laws G., Dorney D. J., Finan J., Tripputi P., Emanuel B. S., Rovera G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. A human c-erbA oncogene homologue is closely proximal to the chromosome 17 breakpoint in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Weeks J. R., Voelker R. A., Ohnishi S., Dickson B. Genetic and biochemical characterization of mutants at an RNA polymerase II locus in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Lebo R. V., Kan Y. W., Tjian R., Cox D. R., Martin G. R. Comparative chromosome mapping of a conserved homoeo box region in mouse and human. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):173–175. doi: 10.1038/314173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinwand L. A., Fournier R. E., Nadal-Ginard B., Shows T. B. Multigene family for sarcomeric myosin heavy chain in mouse and human DNA: localization on a single chromosome. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):766–769. doi: 10.1126/science.6879174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortin M. A., Lefevre G., Jr An RNA polymerase II mutation in Drosophila melanogaster that mimics ultrabithorax. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):237–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00286108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M., Hart C. P., Ferguson-Smith A., McGinnis W., Levine M., Ruddle F. H. Two homoeo box loci mapped in evolutionarily related mouse and human chromosomes. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):175–178. doi: 10.1038/314175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Human oncogene locations and chromosome aberrations. Nature. 1983 Jan 27;301(5898):290–291. doi: 10.1038/301290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Jokerst R. S., Bingham P. M., Voelker R. A., Greenleaf A. L. Molecular cloning of sequences from a Drosophila RNA polymerase II locus by P element transposon tagging. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton R. F., Dobyns W. B., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. New chromosomal syndrome: Miller-Dieker syndrome and monosomy 17p13. Hum Genet. 1984;67(2):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00273000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Faulstich H. Amatoxins, phallotoxins, phallolysin, and antamanide: the biologically active components of poisonous Amanita mushrooms. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978 Dec;5(3):185–260. doi: 10.3109/10409237809149870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]