Abstract
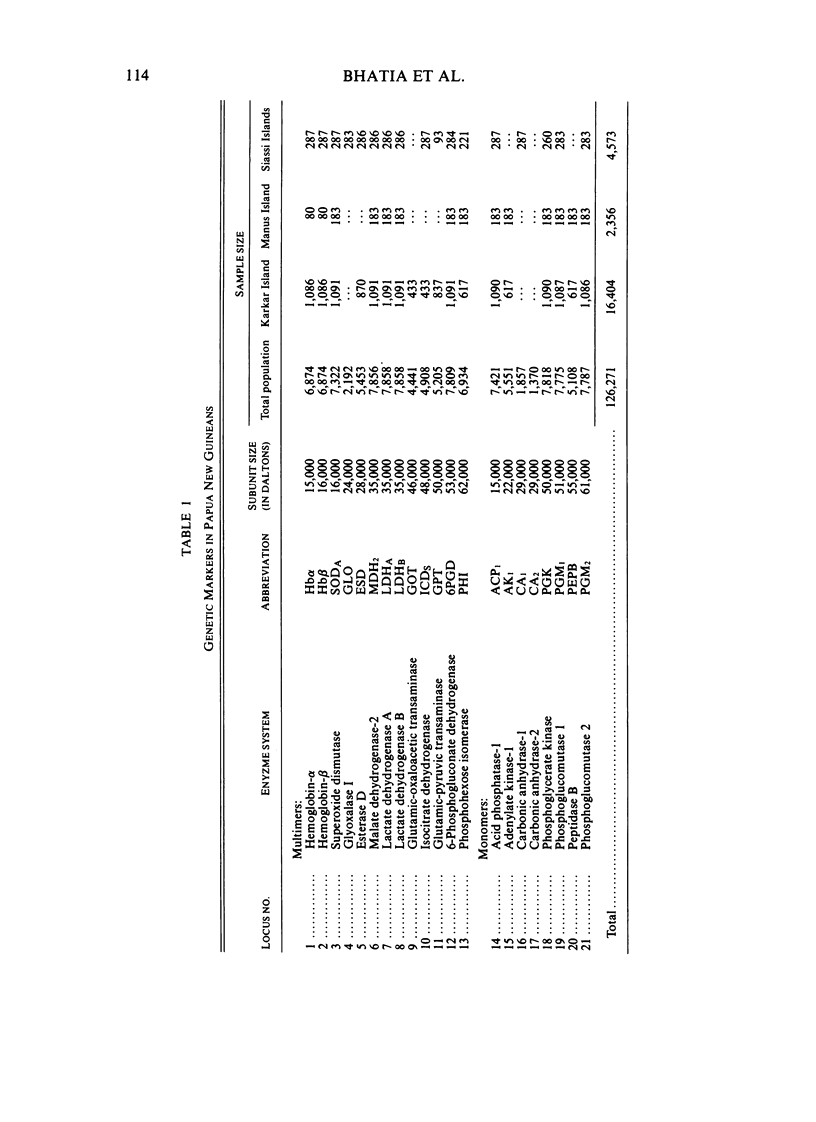
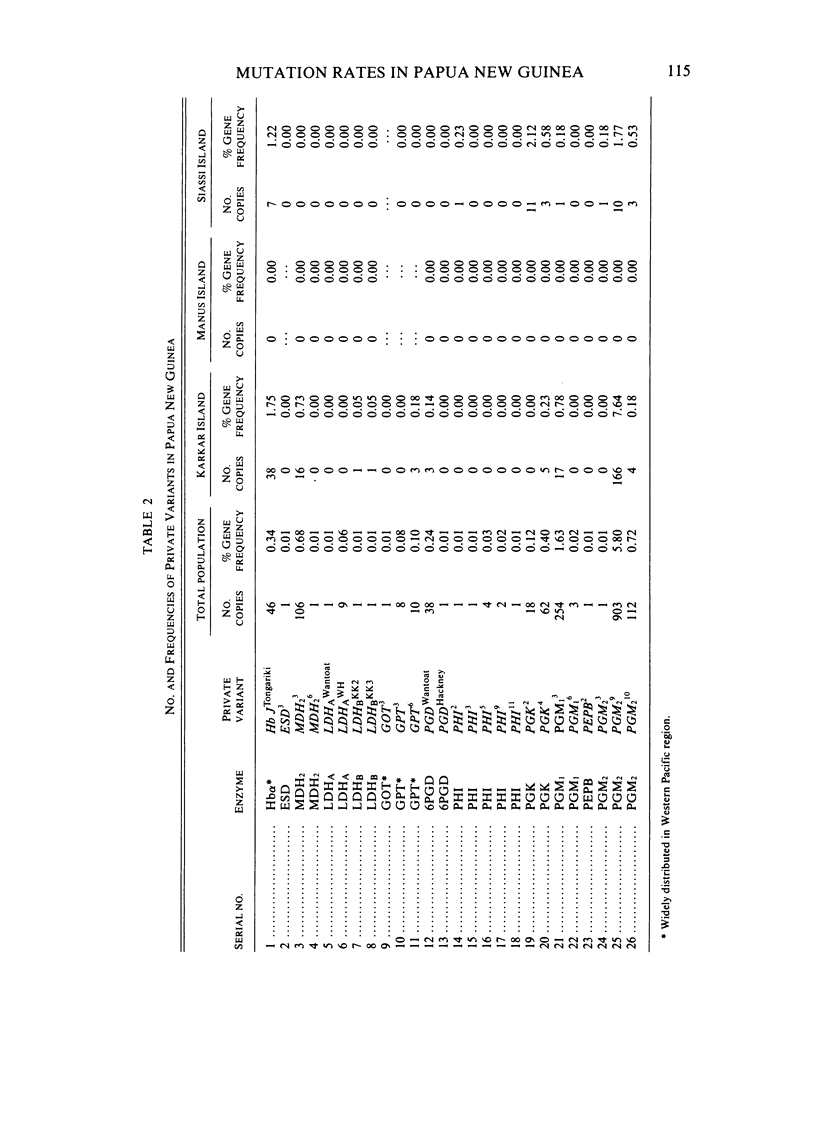
Data on rare and private electrophoretic variants have been used to estimate mutation rates for populations belonging to 55 language groups in Papua New Guinea. Three different methods yield values of 1.42 x 10(-6), 1.40 x 10(-6), and 5.58 x 10(-6)/locus per generation. The estimates for three islands populations off the north coast of New Guinea--Manus, Karkar, and Siassi--are much lower. The variability in mutation rates estimated from rare electrophoretic variants as a function of population size is discussed. The mean mutation rate in Papua New Guinea is less than half the estimates obtained for Australian Aborigines and Amerindians.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhatia K. K., Blake N. M., Kirk R. L. The frequency of private electrophoretic variants in Australian aborigines and indirect estimates of mutation rate. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Nov;31(6):731–740. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia K. K. Factors affecting electromorph mutation rates in man: an analysis of data from Australian Aborigines. Ann Hum Biol. 1980 Jan-Feb;7(1):45–54. doi: 10.1080/03014468000004041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake N. M., Kirk R. L., McDermid E. M., Case J., Bashir H. The distribution of blood, serum protein and enzyme groups in a series of Lebanese in Australia. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1973 Apr;51(2):209–220. doi: 10.1038/icb.1973.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake N. M., Omoto K. Phosphoglucomutase types in the Asian-Pacific area: a critical reveiw including new phenotypes. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;38(3):251–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R., Roychoudhury A. K. Mutation rates from rare variants of proteins in Indian tribes. Hum Genet. 1978 Aug 31;43(2):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00293594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Fossum B. L. Genetics of glutamic-pyruvic transaminase: its inheritance, common and rare variants, population distribution, and differences in catalytic activity. Ann Hum Genet. 1972 Apr;35(4):401–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eanes W. F., Koehn R. K. Relationship between subunit size and number of rare electrophoretic alleles in human enzymes. Biochem Genet. 1978 Oct;16(9-10):971–985. doi: 10.1007/BF00483748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson D. A., Coppock J. S., Mühlemann M. F., Edwards Y. H. The detection and differentiation of the products of the human carbonic anhydrase loci, CAI and CAII using fluorogenic substrates. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Oct;38(2):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson D. A., Mestriner M. A., Cortner J., Harris H. Esterase D: a new human polymorphism. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Oct;37(2):119–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb01820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornabrook R. W. The demography of the population of Karkar Island. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Aug 1;268(893):229–239. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1974.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ota T. The average number of generations until extinction of an individual mutant gene in a finite population. Genetics. 1969 Nov;63(3):701–709. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kömpf J., Bissbort S., Gussmann S., Ritter H. Polymorphism of red cell glyoxalase I (EI: 4.4.1.5); a new genetic marker in man. Investigation of 169 mother-child combinations. Humangenetik. 1975;27(2):141–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00273329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V. "Private" genetic variants and the frequency of mutation among South American Indians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3311–3315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V., Rothman E. D. Indirect estimates of mutation rates in tribal Amerindians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5585–5588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Chakraborty R. Electrophoretically silent alleles in a finite population. J Mol Evol. 1976 Dec 30;8(4):381–385. doi: 10.1007/BF01739262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Chakraborty R., Fuerst P. A. Infinite allele model with varying mutation rate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4164–4168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Estimation of mutation rate from rare protein variants. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 May;29(3):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Extinction time of deleterious mutant genes in large populations. Theor Popul Biol. 1971 Dec;2(4):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(71)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman E. D., Adams J. Estimation of expected number of rare alleles of a locus and calculation of mutation rate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5094–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S. Marriage patterns and fertility in three Papua New Guinean populations. Hum Biol. 1975 Dec;47(4):399–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchen P., Séger J., Bois E., Grenand F., Fribourg-Blanc A., Feingold N. A genetic study of two French Guiana Amerindian populations. II. Rare electrophoretic variants. Hum Genet. 1978 Dec 29;45(3):317–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00278729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


