Abstract
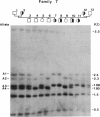
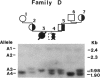
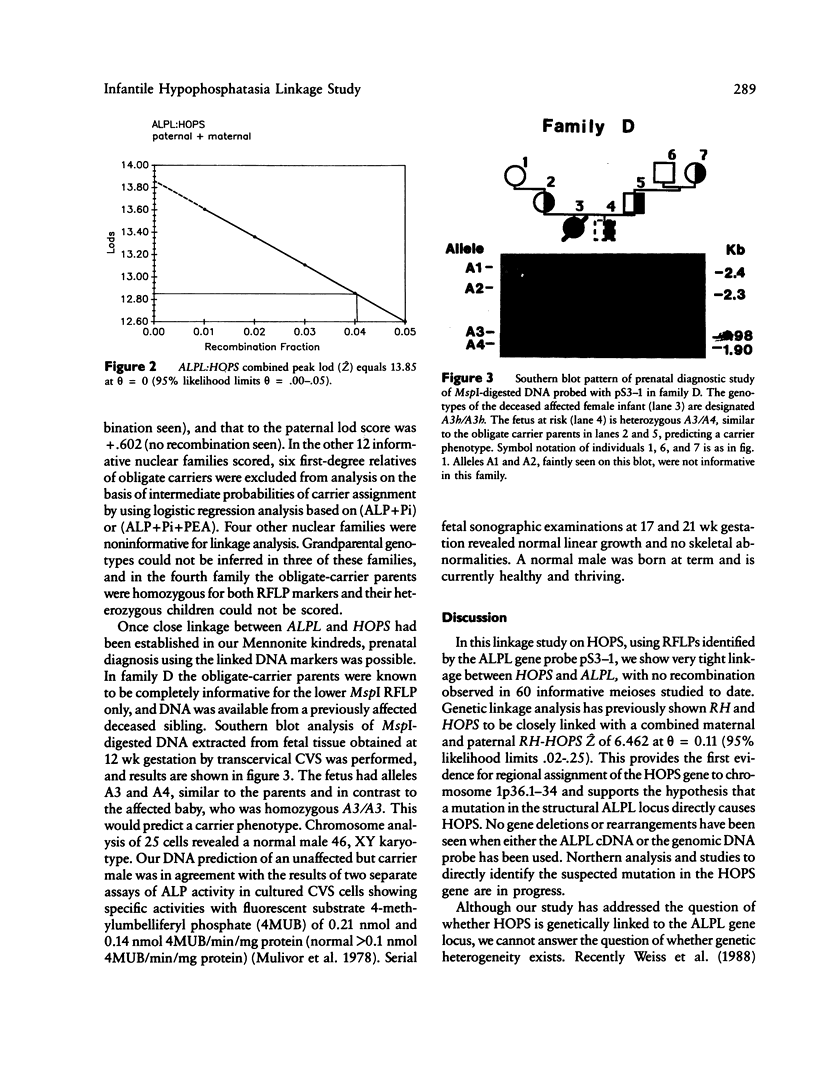
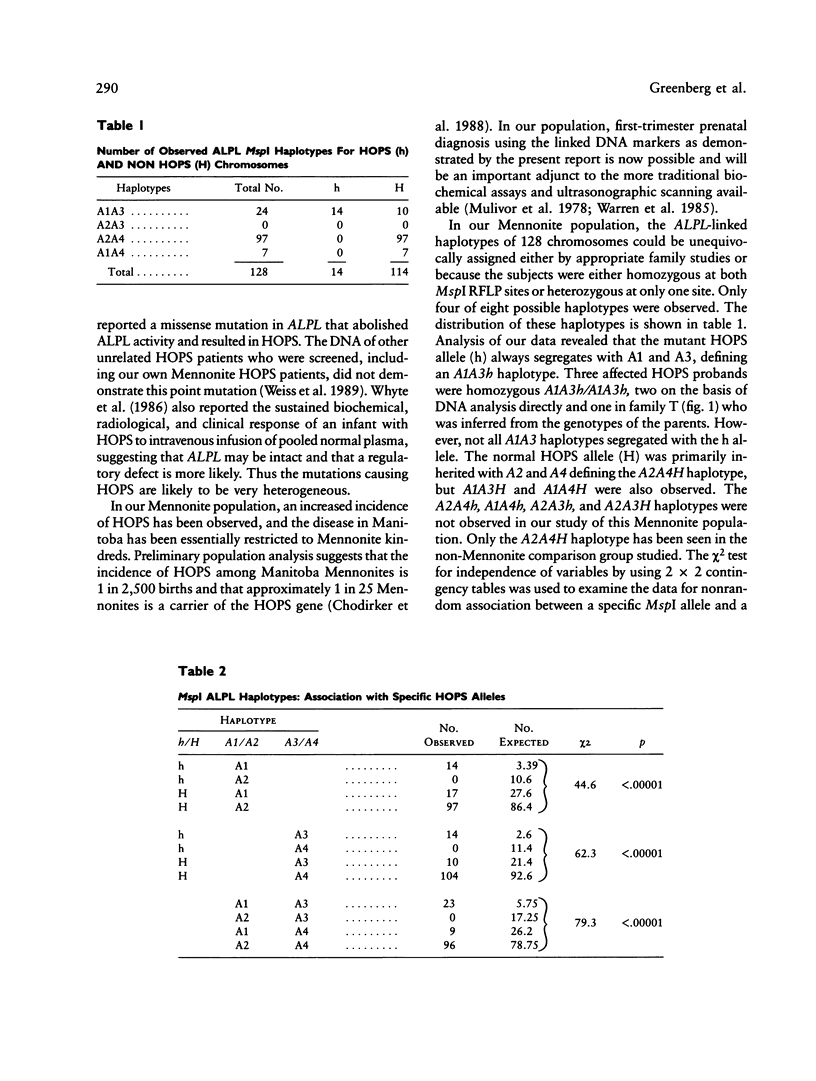
Linkage analysis was performed on data from Manitoba Mennonite families identified by a proband with infantile hypophosphatasia (HOPS), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by defective skeletal mineralization. Southern blot analysis of Msp-I-digested DNA from HOPS nuclear families probed with a 2.55-kb liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase (ALPL) cDNA revealed two previously undescribed RFLPs at 2.4/2.3 kb and 2.0/1.9 kb. Maximum combined lod score equals 13.25 at theta = 0. This establishes very close linkage between ALPL and HOPS and allows for the regional assignment of the HOPS gene to chromosome 1p36.1-34. Prenatal RFLP studies in an informative Mennonite family correctly predicted an unaffected fetus following chorionic villus sampling at 12 wk gestation. In addition in our Mennonite population, a nonrandom association exists between the polymorphic ALPL alleles and HOPS. These results suggest that strong linkage disequilibrium exists between HOPS and the ALPL markers. This will allow for improved carrier assignment in this high-risk population. Preliminary analysis suggests approximately 1/25 Manitoba Mennonites are HOPS carriers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chodirker B. N., Evans J. A., Lewis M., Coghlan G., Belcher E., Philipps S., Seargeant L. E., Sus C., Greenberg C. R. Infantile hypophosphatasia--linkage with the RH locus. Genomics. 1987 Nov;1(3):280–282. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. A marker algebra. Clin Genet. 1972;3(5):371–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1972.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivill X., Scambler P. J., Wainwright B. J., Hawley K., Frederick P., Schwartz M., Baiget M., Kere J., Williamson R., Farrall M. Patterns of polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium for cystic fibrosis. Genomics. 1987 Nov;1(3):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER D. Hypophosphatasia. Am J Med. 1957 May;22(5):730–746. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg C. R., Hamerton J. L., Nigli M., Wrogemann K. DNA studies in a family with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and a deletion at Xp21. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;41(2):128–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson R. I., Kroeker M., Houston C. S. Hypophosphatasia. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1972 Mar;23(1):16–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Mennuti M., Zackai E. H., Harris H. Prenatal diagnosis of hypophosphatasia; genetic, biochemical, and clinical studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1978 May;30(3):271–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray K., Weiss M. J., Dracopoli N. C., Harris H. Probe 8B/E5' detects a second RFLP at the human liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase (ALPL) locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2361–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Weiss M. J., Griffin C. A., Murray J. C., Buetow K. H., Emanuel B. S., Henthorn P. S., Harris H. Regional assignment of the gene for human liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase to chromosome 1p36.1-p34. Genomics. 1988 Feb;2(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. C., McKenzie C. F., Rodeck C. H., Moscoso G., Brock D. J., Barron L. First trimester diagnosis of hypophosphatasia with a monoclonal antibody to the liver/bone/kidney isoenzyme of alkaline phosphatase. Lancet. 1985 Oct 19;2(8460):856–858. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Cole D. E., Ray K., Whyte M. P., Lafferty M. A., Mulivor R. A., Harris H. A missense mutation in the human liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase gene causing a lethal form of hypophosphatasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7666–7669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Henthorn P. S., Lafferty M. A., Slaughter C., Raducha M., Harris H. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a human liver/bone/kidney-type alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Ray K., Fallon M. D., Whyte M. P., Fedde K. N., Lafferty M. A., Mulivor R. A., Harris H. Analysis of liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase mRNA, DNA, and enzymatic activity in cultured skin fibroblasts from 14 unrelated patients with severe hypophosphatasia. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):686–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Spielman R. S., Harris H. A high-frequency RFLP at the human liver/bone/kidney-type alkaline phosphatase locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):860–860. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Magill H. L., Fallon M. D., Herrod H. G. Infantile hypophosphatasia: normalization of circulating bone alkaline phosphatase activity followed by skeletal remineralization. Evidence for an intact structural gene for tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase. J Pediatr. 1986 Jan;108(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80773-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]