Abstract
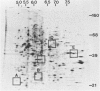
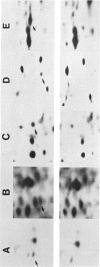
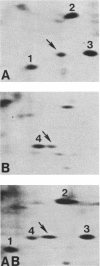
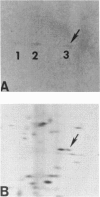
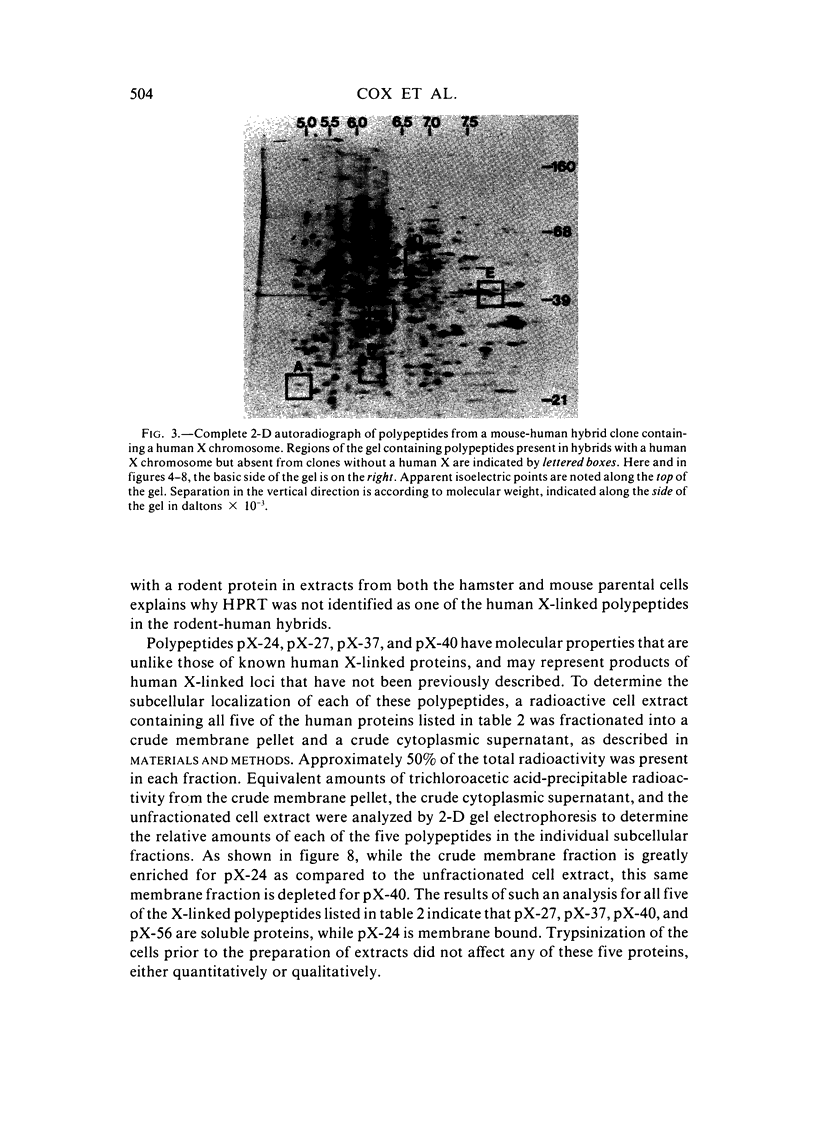
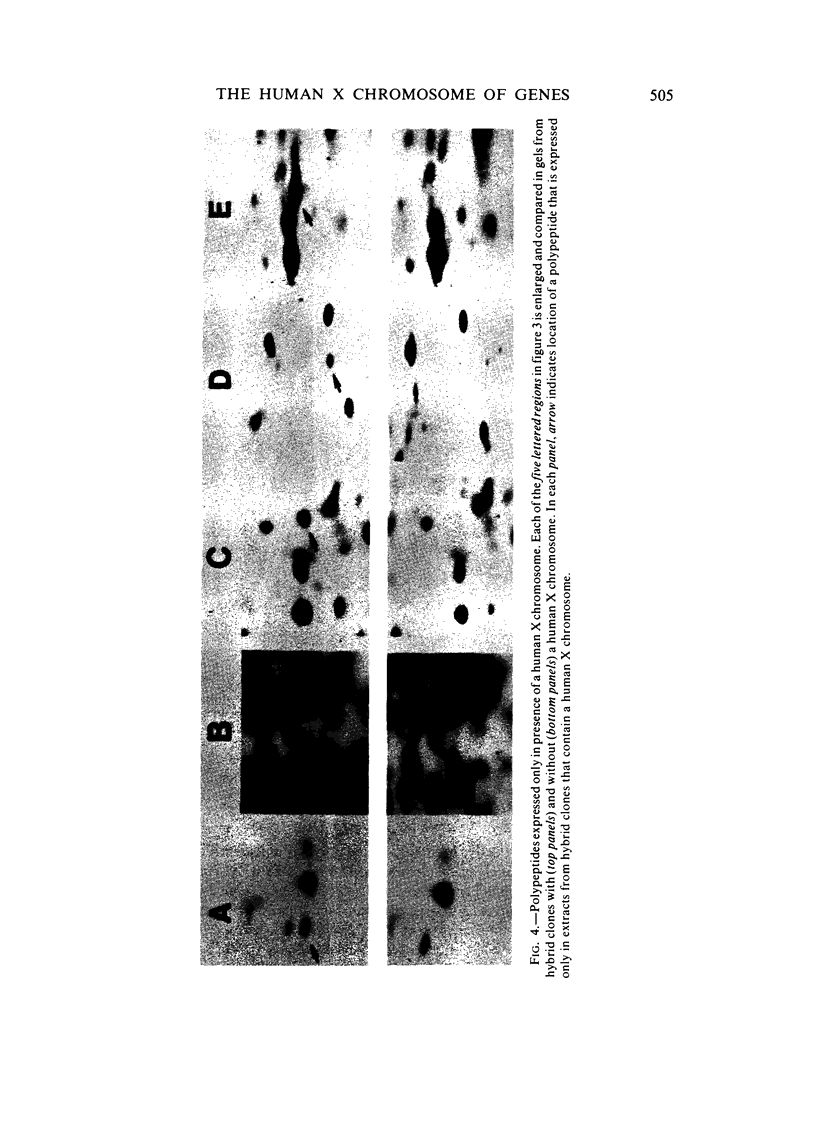
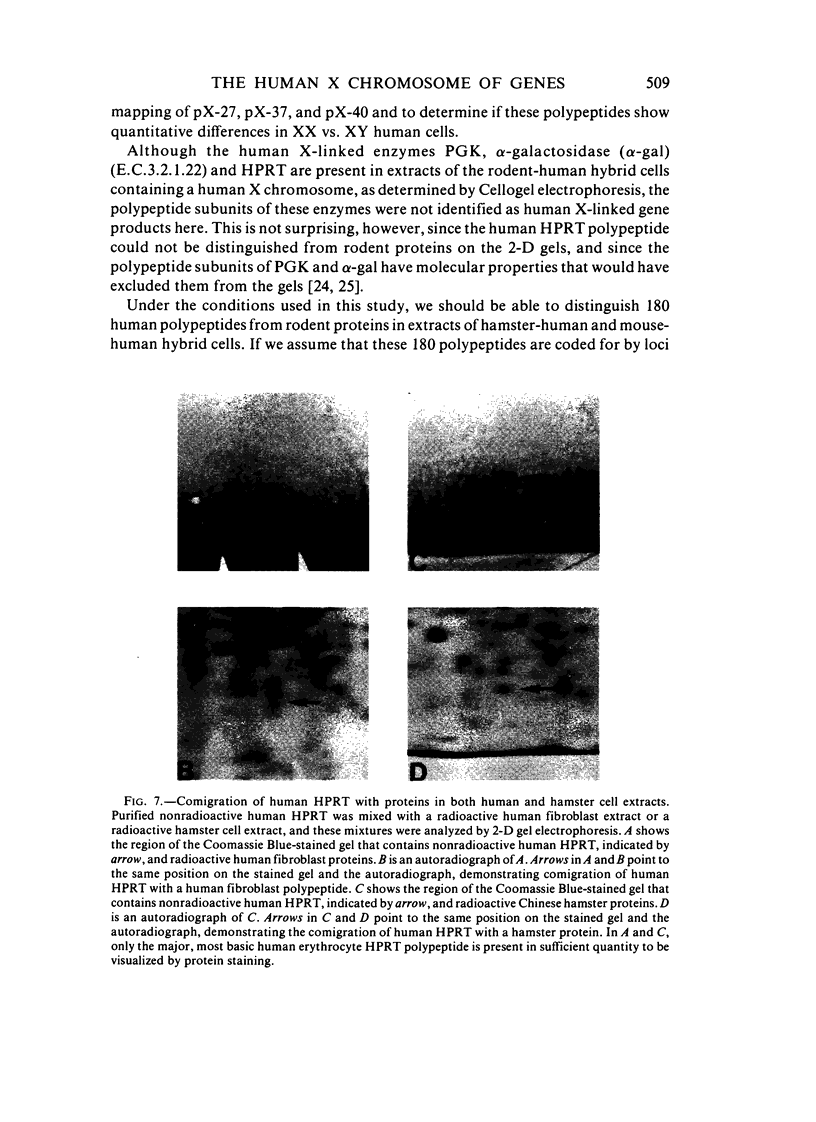
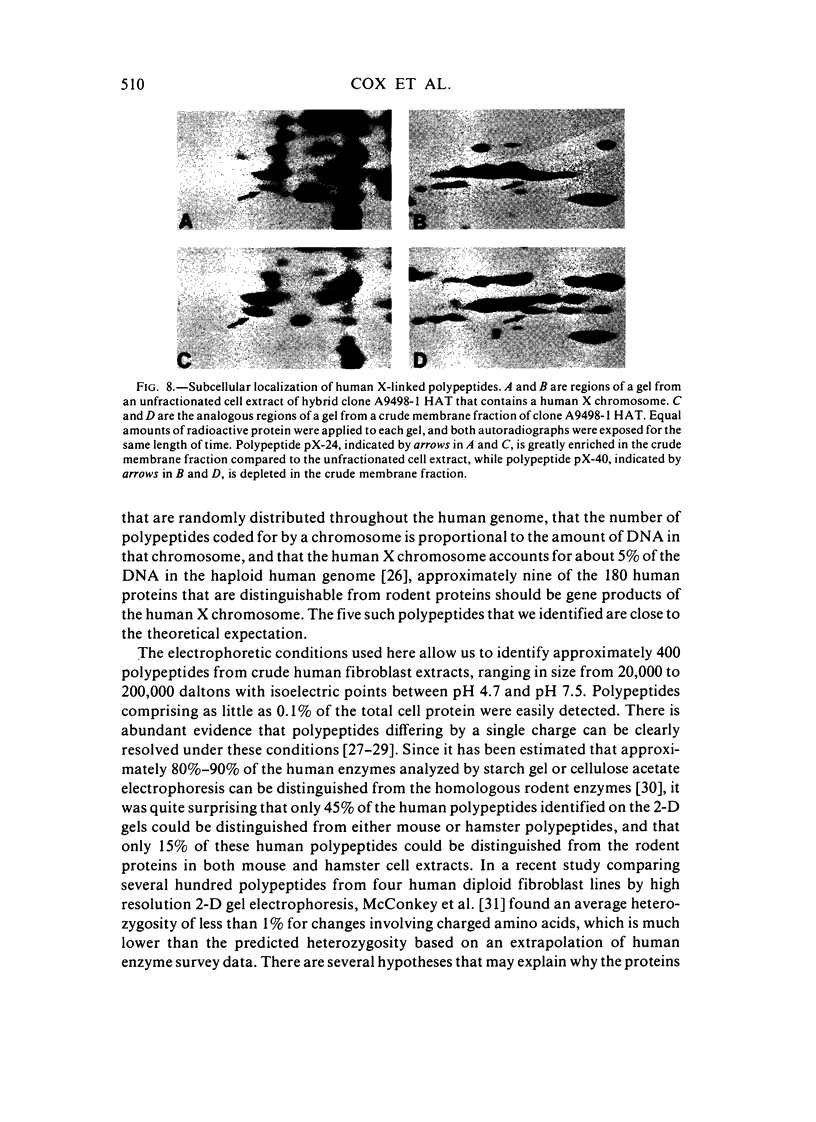
The technique of two-dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis was sued to identify five human X-linked gene products in crude cell extracts of mouse-human and Chinese hamster-human somatic cell hybrids. The human origin of these five polypeptides was demonstrated by their comigration with human fibroblast proteins and their failure to comigrate with polypeptides in extracts from the mouse or hamster parental cells. All five polypeptides were present in extracts of rodent-human hybrids that contained a human X chromosome, but were not found in extracts of cells that lacked a human X chromosome. Chromosome analysis of the hybrid clones revealed that the human X chromosome is both necessary and sufficient for the expression of the five polypeptides, designated pX-24, pX-27, pX-37, pX-40, and pX-56. pX-56 can be identified as the human X-linked enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) (E.C.1.1.1.49), while polypeptides pX-24, pX-27, pX-37 and pX-40 have molecular properties unlike those of known human X-linked gene products. pX-24 appears to be a membrane-bound protein that maps to the distal portion of the long arm of the human X chromosome, while pX-27, pX-37, and pX-40 are soluble proteins that map to the proximal long arm or to the short arm of the human X chromosome. 2-D gel electrophoretic analysis of extracts from somatic cell hybrids provides a general method for identifying polypeptides in crude cell extracts coded for by any specific chromosome and can be used to study primary gene products not previously amenable to genetic analysis.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhadeff B., Velivasakis M., Siniscalco M. Simultaneous identification of chromatid replication and of human chromosomes in metaphases of man-mouse somatic cell hybrids. (With 1 color plate). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(4):236–239. doi: 10.1159/000130814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M., Brownstone Y. S. A study of phosphoglycerate kinase in human erythrocytes. I. Enzyme isolation, purification and assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 12;445(1):74–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L., Anderson N. G. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of human plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5421–5425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosman F. T., van der Ploeg M., van Duijn P., Schaberg A. Photometric determination of the DNA distribution in the 24 human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 15;105(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck D. W., Bodmer W. F. Serological identification of an X-linked human cell surface antigen, SA-X. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):376–377. doi: 10.1159/000130636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., O'Malley K. A., Wheeler T. B. Polyethylene glycol-induced mammalian cell hybridization: effect of polyethylene glycol molecular weight and concentration. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF01538965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald L. J., Hamerton J. L. A summary of the human gene map, 1973-1977. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):5–11. doi: 10.1159/000130914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman B. P., Shimizu N., Ruddle F. H. A cell surface antigen linked to the human X chromosome and present on fibroblasts. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):243–244. doi: 10.1159/000130946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. J., Anderson N. G., Nance S. L., Anderson N. L. Red cell proteins. I. Two-dimensional mapping of human erythrocyte lysate proteins. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1121–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. W. Use of two-dimensional electrophoresis to identify and map new mouse genes. Genetics. 1979 Feb;91(2):295–308. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Busby N., Shaw D., Hansen S., Brown M. G. Intrachromosomal gene mapping in man: assignment of nucleoside phosphorylase to region 14cen leads to 14q21 by interspecific hybridization of cells with a t(X;14) (p22;q21) translocation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Jan;2(1):27–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01539240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Denney R. M., Ruddle F. H. Intrachromosomal gene mapping in man: the gene for tryptophyl-tRNA synthetase maps in region q21 leads to qter of chromosome 14. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Jul;3(4):381–389. doi: 10.1007/BF01542967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghangas G. S., Milman G. Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase: two-dimensional gels from normal and Lesch-Nyhan hemolyzates. Science. 1977 Jun 3;196(4294):1119–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.870972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapes C. A., Suelter C. H., Sweeley C. C. Isolation and characterization of ceramide trihexosidases (form A) from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2471–2479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H. Double-label autoradiography for comparison of complex protein mixtures after gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 1;96(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90551-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H. Identification of human gene products from hybrid cells: a new approach. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Jan;6(1):139–147. doi: 10.1007/BF01538702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H., Taylor B. J., Phan D. Human heterozygosity: a new estimate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6500–6504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel: zymogram patterns in mgh-mouse and man--Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Aug;145(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C. Regional assignment of the steroid sulfatase-X-linked ichthyosis locus: implications for a noninactivated region on the short arm of human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. A review of enzyme polymorphism, linkage and electrophoretic conditions for mouse and somatic cell hybrids in starch gels. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Dec;21(12):1066–1081. doi: 10.1177/21.12.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. Comparative sensitivities of electrophoretic assays for human enzymes. Biochem Genet. 1979 Feb;17(1-2):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00484478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., O'Farrell P. Z. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic fractionation. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:407–420. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver N., Francke U., Pellegrino M. A. Regional assignment of genes for mannose phosphate isomerase, pyruvate kinase-3, and beta 2-microglobulin expression on human chromosome 15 by hybridization of cells from a t(15;22) (q14;q13.3) translocation carrier. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):506–510. doi: 10.1159/000131009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J., Pollard J. W., Friesen J. D., Stanners C. P. Stuttering: high-level mistranslation in animal and bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab R., Siniscalco M. Confirmative evidence for a human X-linked surface antigen and its tentative regional assignment. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):538–540. doi: 10.1159/000131019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J., Mohandas T., Weiss R., Romeo G. Non-inactivation of an x-chromosome locus in man. Science. 1979 Jun 15;204(4398):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.156396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., O'Farrell P. H., Friedrich U., Coffino P. Mutations causing charge alterations in regulatory subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase of cultured S49 lymphoma cells. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Gudas L. J., Martin D. W., Jr Characterization of the subunit composition of HGPRTase from human erythrocytes and cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Genet. 1980 Feb;18(1-2):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00504356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Someren H., Beijersbergen van Henegouwen H., Los W., Wurzer-Figurelli E., Doppert B., Vervloet M., Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel. II. Zymogram patterns in man-Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Humangenetik. 1974;25(3):189–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00281426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]