Abstract
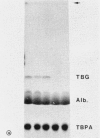
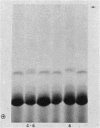
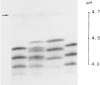
A genetically determined, polymorphic electrophoretic variant of thyroxin-binding alpha-globulin (TBG) is found in sera from populations of African and Oceania origin, although not in Caucasians nor Orientals. The TBG polymorphism is inherited in X-linked fashion, based on data from American blacks, and thus provides an X-chromosome marker with a relatively high gene frequency in this ethnic group (frequency of the slow allele, TBGs, is 11%). This slow variant should prove valuable in expanding the map of the X chromosome and in linkage studies. An additional family exhibiting X-linked TBG deficiency is also described.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Daiger S. P., Rummel D. P. Detection of genetic variation with radioactive ligands. I. Electrophoretic screening of plasma proteins with a selected panel of compounds. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Nov;29(6):581–592. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Gregerman R. I. Separation of thyroxine-binding proteins in human serum at pH 7.4. II. Effect of pH and temperature on the bindng capacities of thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) and thyroxine-binding prealbumin (TBPA). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):699–708. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell R. E., Nunez A., Bertin T., Labarthe D. R., Schull W. J. The blacks of Panama: their genetic diversity as assessed by 15 inherited biochemical systems. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1978 Mar;48(3):269–275. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330480302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Giblett E. R., Musa B. Increased serum thyroxine-binding globulin capacity: inheritance and linkage relationships. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jan;30(1):66–70. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-1-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Dussault J. H., Foley T. P., Jr, Klein A. H., LaFranchi S., Larsen P. R., Mitchell M. L., Murphey W. H., Walfish P. G. Screening for congenital hypothyroidism: results of screening one million North American infants. J Pediatr. 1979 May;94(5):700–705. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman T., Pearson J. D. The use of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis to investigate thyroxine-binding human serum proteins. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Nov;26(2):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocman G. Human thyroxine-binding globulin. Isolation and chemical properties. II. Properties. Int J Biochem. 1978;9(5):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(78)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köbberling J., Emrich D. The genetic polymorphism of the thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). Humangenetik. 1972;14(2):85–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00273290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiba S., Landau B., Ber A., Adam A., Sterling K. Thyroxine-binding-globulin (T.B.G.) deficiency and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) deficiency in the same family. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):569–573. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Pensky J., Green A. M. Studies on human thyroxine-binding globulin. VI. The nature of slow thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3173–3181. doi: 10.1172/JCI107144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusynowitz M. L., Clark R. F., Strader W. J., 3rd, Estrin H. M., Seal U. S. Thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency in three families, and total deficiency in a normal woman. Am J Med. 1971 Apr;50(4):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90335-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premachandra B. N., Perlstein I. B., Blumenthal H. T. Studies on obesity. II. Slow-moving thyroxine binding globulin in the sera of normal and obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jun;30(6):752–762. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-6-752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Fang V. S., Marshall J. S. Studies on human thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). IX. Some physical, chemical, and biological properties of radioiodinated TBG and partially desialylated TBG. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):177–187. doi: 10.1172/JCI108066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Robin N. I., Alper C. A. Study of four new kindreds with inherited thyroxine-binding globulin abnormalities. Possible mutations of a single gene locus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):848–867. doi: 10.1172/JCI106880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbruggen Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods: a literature survey. Clin Chem. 1975 Jan;21(1):5–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]