Abstract
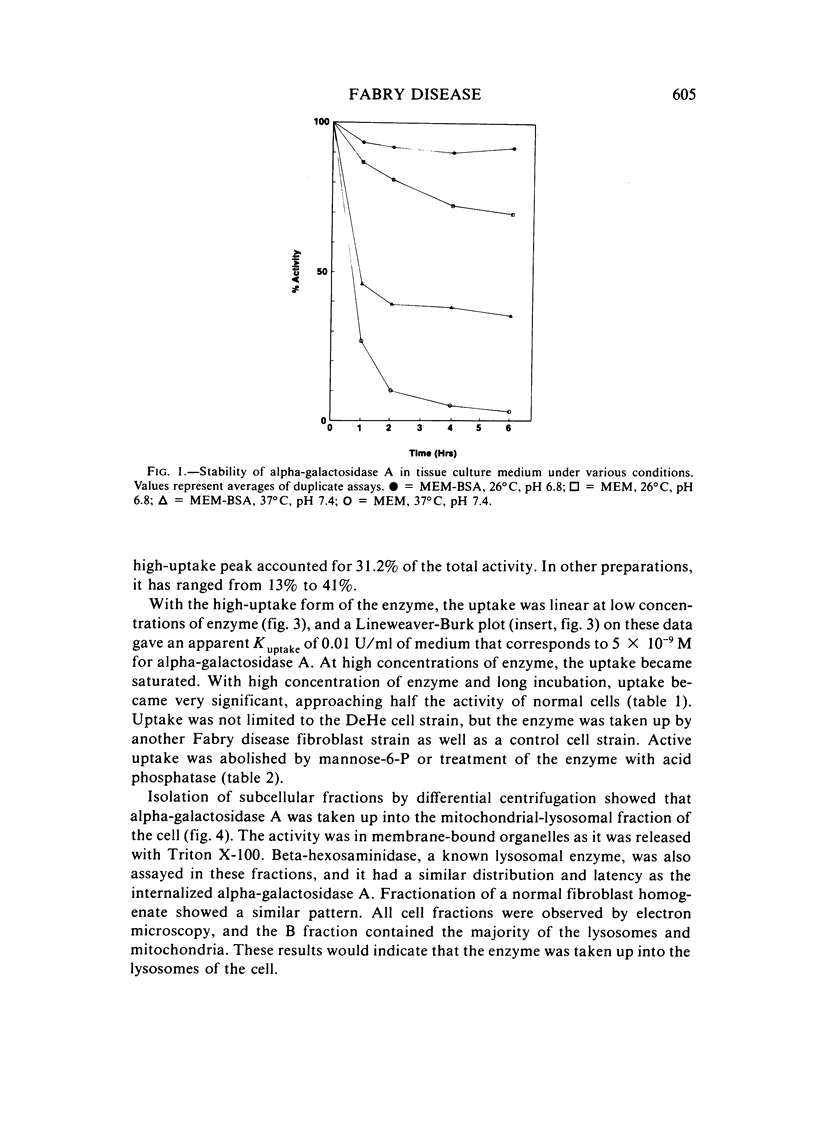
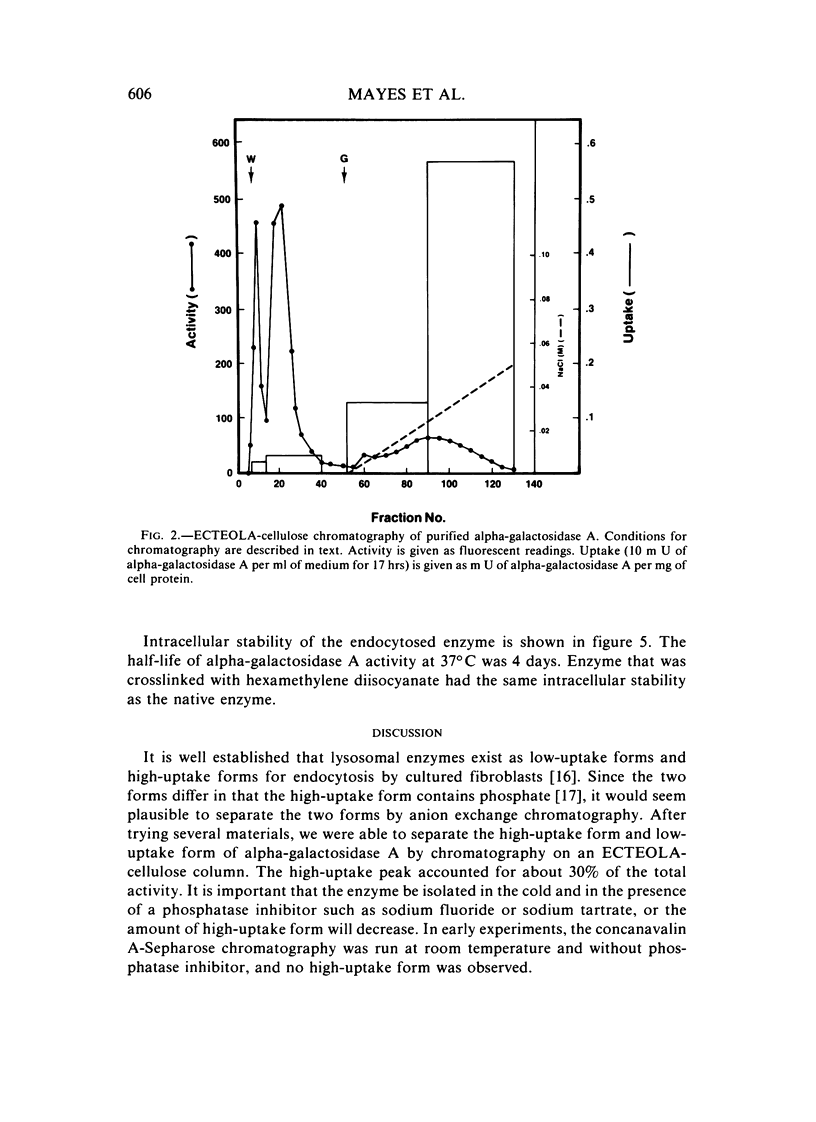
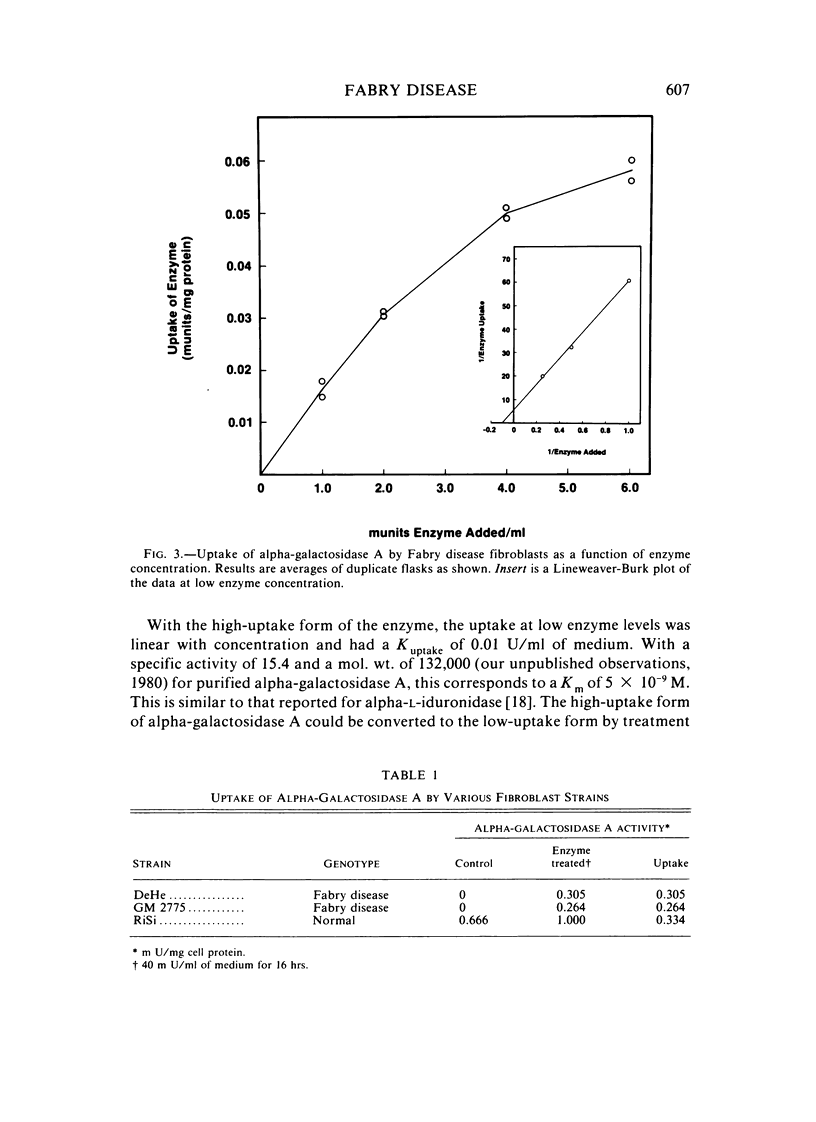
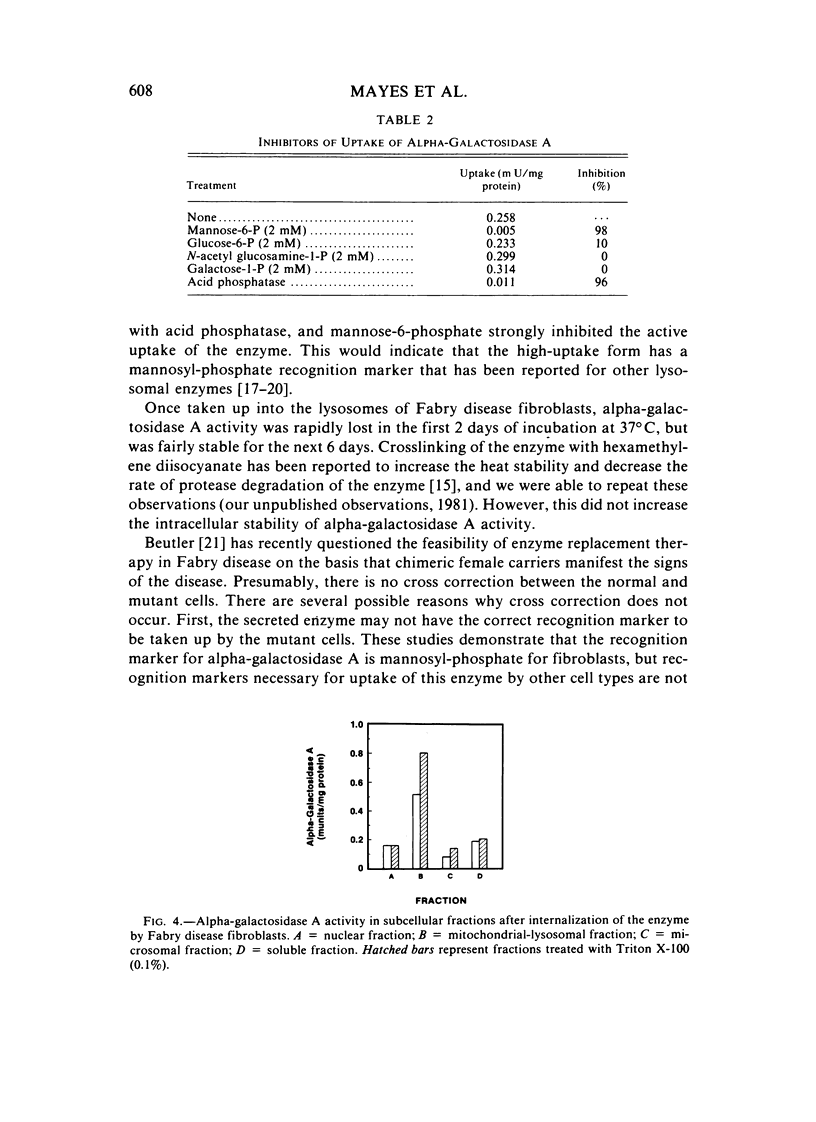
The endocytosis of alpha-galactosidase A was studied in cultured fibroblasts from patients with Fabry disease. Alpha-galactosidase A was purified from human placenta by chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose, DEAE-cellulose, and N-epsilon-aminocaproyl-alpha-D-galactosylamine-Sepharose. Separation of the high-uptake form of the enzyme from the low-uptake form was accomplished by chromatography on ECTEOLA-cellulose. With the high-uptake form of the enzyme, the uptake was linear at low concentrations of enzyme and had a Kuptake of 0.01 U/ml of medium that corresponds to a Km of 5.0 x 10(-9) M. At high concentrations of enzyme, it became saturated. The high-uptake form could be converted to the low-uptake form by treatment with acid phosphatase. Mannose-6-P strongly inhibited the active uptake of the enzyme. Once taken up into the lysosomes of Fabry disease fibroblasts, alpha-galactosidase A activity was rapidly lost in the first 2 days of incubation at 37 degrees C, but was fairly stable for the next 6 days. The half-life of internalized alpha-galactosidase A activity was calculated to be 4 days. Crosslinking of the enzyme with hexamethylene diisocyanate did not increase the intracellular stability of alpha-galactosidase A activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler E., Kuhl W. Biochemical and electrophoretic studies of -galactosidase in normal man, in patients with Fabry's disease, and in Equidae. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 May;24(3):237–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W. Purification and properties of human alpha-galactosidases. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7195–7200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E. Nature's transplant in Fabry's disease. Lancet. 1979 Jul 28;2(8135):199–199. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91464-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady R. O., Tallman J. F., Johnson W. G., Gal A. E., Leahy W. R., Quirk J. M., Dekaban A. S. Replacement therapy for inherited enzyme deficiency. Use of purified ceramidetrihexosidase in Fabry's disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jul 5;289(1):9–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197307052890103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson G., Matalon R., Li Y. T. Correction of the enzymic defect in cultured fibroblasts from patients with Fabry's disease: treatment with purified alpha-galactosidase from ficin. Pediatr Res. 1973 Aug;7(8):684–690. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197308000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. D., Willetts S. R., Blanch J. E. Phosphatases: applications of new methods for their separation. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnick R. J., Dean K. J., Grabowski G., Bishop D. F., Sweeley C. C. Enzyme therapy in Fabry disease: differential in vivo plasma clearance and metabolic effectiveness of plasma and splenic alpha-galactosidase A isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5326–5330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnick R. J., Thorpe S. R., Fiddler M. B. Toward enzyme therapy for lysosomal storage diseases. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):57–99. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpaz N., Flowers H. M. Isolation of alpha-galactosidase by affinity chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:347–350. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Achord D. T., Sly W. S. Phosphohexosyl components of a lysosomal enzyme are recognized by pinocytosis receptors on human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2026–2030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Fischer D., Achord D., Sly W. Phosphohexosyl recognition is a general characteristic of pinocytosis of lysosomal glycosidases by human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1088–1093. doi: 10.1172/JCI108860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes J. S., Beutler E. alpha-galactosidase A from human placenta. Stability and subunit size. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 13;484(2):408–416. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes J. S., Scheerer J. B., Sifers R. N., Donaldson M. L. Differential assay for lysosomal alpha-galactosidases in human tissues and its application to Fabry's disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 May 5;112(2):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Sando G. N., Garvin A. J., Rome L. H. The transport of lysosomal enzymes. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):95–101. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEELEY C. C., KLIONSKY B. FABRY'S DISEASE: CLASSIFICATION AS A SPHINGOLIPIDOSIS AND PARTIAL CHARACTERIZATION OF A NOVEL GLYCOLIPID. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3148–3150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando G. N., Neufeld E. F. Recognition and receptor-mediated uptake of a lysosomal enzyme, alpha-l-iduronidase, by cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. D., Jr, Wold F., Bernlohr R. W., Dullum C., Desnick R. J., Krivit W., Condie R. M. Enzyme therapy. II. Purified human alpha-galactosidase A. Stabilization to heat and protease degradation by complexing with antibody and by chemical modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 18;350(2):432–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90518-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K., Mersmann G., Weber E., Von Figura K. Evidence for lysosomal enzyme recognition by human fibroblasts via a phosphorylated carbohydrate moiety. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1700643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S., Nadler H. L. Fabry's disease: absence of an -galactosidase isozyme. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 May;24(3):250–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


